Working Memory Model Simply Psychology

Working Memory Model Simply Psychology The working memory model, proposed by baddeley and hitch in 1974, describes short term memory as a system with multiple components. it comprises the central executive, which controls attention and coordinates the phonological loop (handling auditory information) and the visuospatial sketchpad (processing visual and spatial information). The multi store model is an explanation of memory proposed by atkinson and shiffrin which assumes there are three unitary (separate) memory stores, and that information is transferred between these stores in a linear sequence. the three main stores are the sensory memory, short term memory (stm) and long term memory (ltm).

Working Memory Model In Psychology Baddeley Hitch Ao1. the multistore model of memory was proposed by atkinson and shiffrin and is a structural model. they proposed that memory consisted of three stores: sensory register, short term memory (stm), and long term memory (ltm). information passes from store to store in a linear way. both stm and ltm are unitary stores. It also supports the claim that working memory has two components: one for visual information and one for verbal information. if working memory was processed in one unitary store, different types of distracting tasks (verbal or visual) would have the same effects. alloway et al. claim their results “…can be explained by the multicomponent. This section provides a brief overview of the key features of the ‘original’ working memory model (baddeley, 1986; baddeley & hitch, 1974) and the ‘revised’ work ing memory model (baddeley, 2000, 2007). in most respects, the revised working memory model simply adds to the original, but there are some changes to indi. The working memory model suggests that verbal rehearsal is optional, explaining why we don't have to rehearse information verbally in order to remember it. it is difficult to prove the existence of the central executive, as it is not related to any specific kind of information, such as auditory or visual coding. a theory on how our memory.

Memory Psychology A Level This section provides a brief overview of the key features of the ‘original’ working memory model (baddeley, 1986; baddeley & hitch, 1974) and the ‘revised’ work ing memory model (baddeley, 2000, 2007). in most respects, the revised working memory model simply adds to the original, but there are some changes to indi. The working memory model suggests that verbal rehearsal is optional, explaining why we don't have to rehearse information verbally in order to remember it. it is difficult to prove the existence of the central executive, as it is not related to any specific kind of information, such as auditory or visual coding. a theory on how our memory. Summary. working memory is an aspect of human memory that permits the maintenance and manipulation of temporary information in the service of goal directed behavior. its apparently inelastic capacity limits impose constraints on a huge range of activities from language learning to planning, problem solving, and decision making. The central executive is the most important but least understood component of working memory. in the original model, it was simply treated as a pool of general processing capacity, to which all.
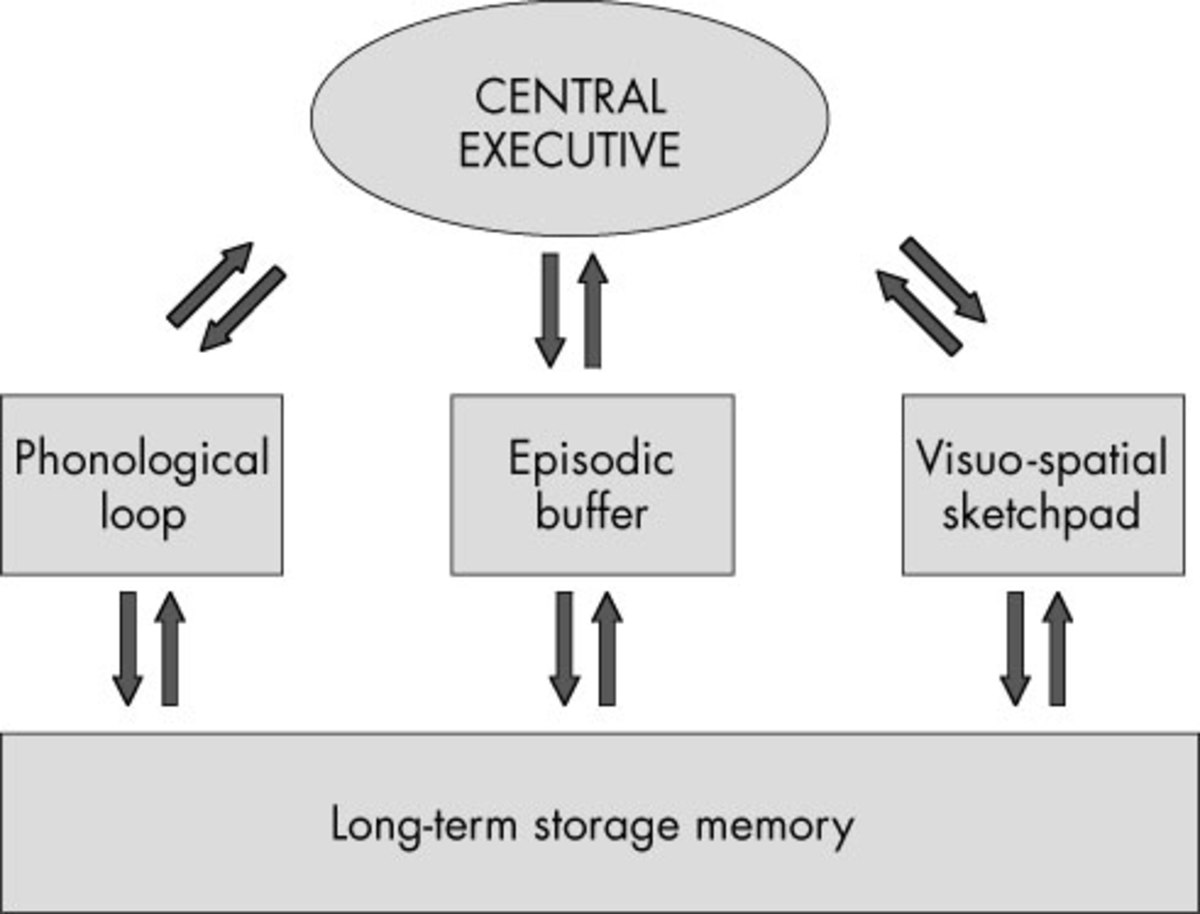
As Psychology The Working Memory Model Owlcation Summary. working memory is an aspect of human memory that permits the maintenance and manipulation of temporary information in the service of goal directed behavior. its apparently inelastic capacity limits impose constraints on a huge range of activities from language learning to planning, problem solving, and decision making. The central executive is the most important but least understood component of working memory. in the original model, it was simply treated as a pool of general processing capacity, to which all.

Working Memory

Working Memory Model As Psychology

Comments are closed.