What Is The Difference Between Primary Consumers And Secondary
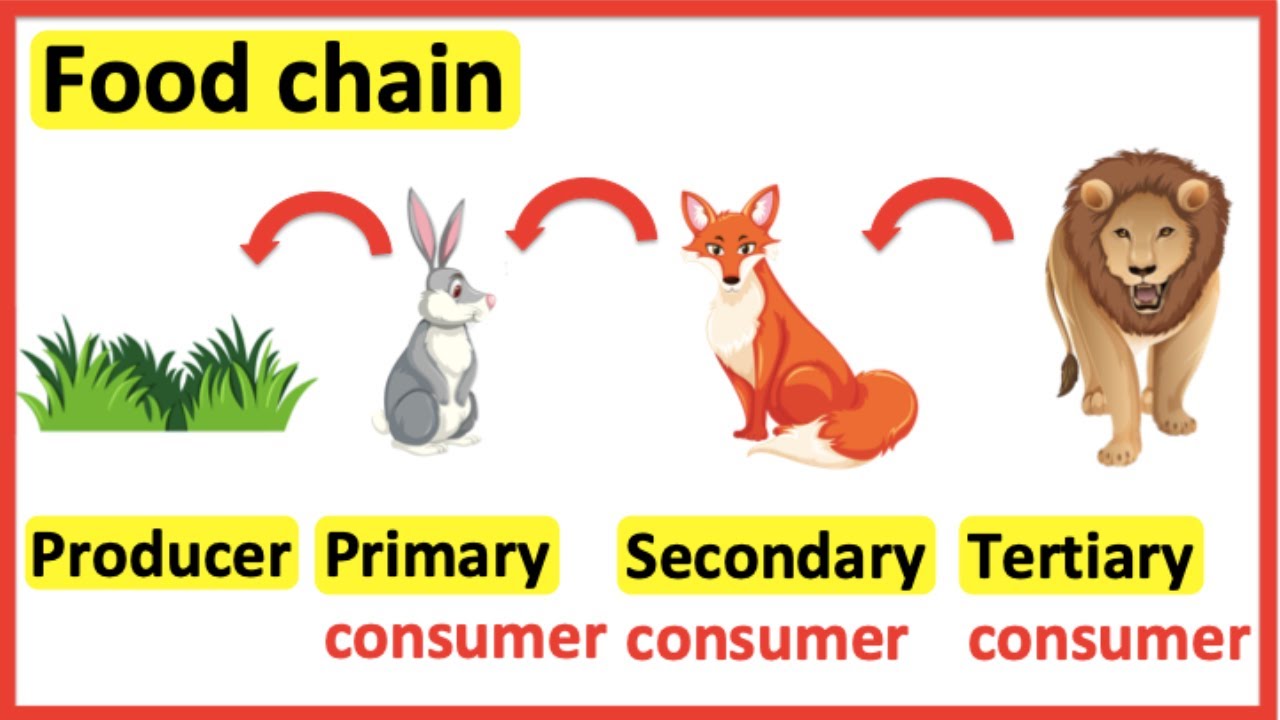
Food Chains Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary 5 min read. the main difference between primary secondary and tertiary consumers is that primary consumers are the herbivores that feed on plants, and secondary consumers can be either carnivores, which prey on other animals, or omnivores, which feed on both animals and plants, whereas tertiary consumers are the apex predators that feed on both. Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web.
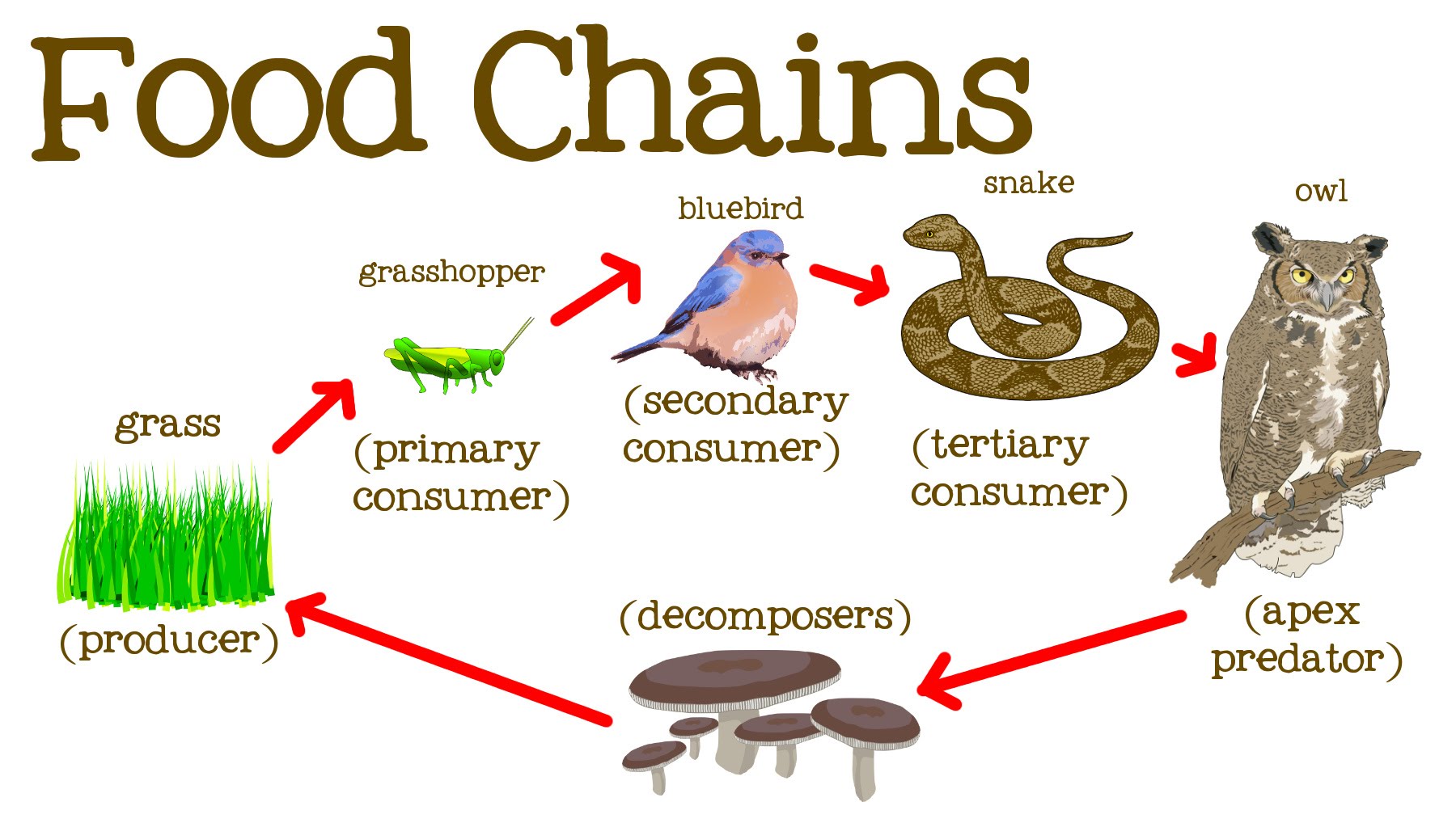
What Is The Difference Between A Producer Secondary Consumer Primary A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. For example, a grasshopper living in the everglades is a primary consumer. some other examples of primary consumers are white tailed deer that forage on prairie grasses, and zooplankton that eat microscopic algae in the water. next are the secondary consumers, which eat primary consumers. secondary consumers are mostly carnivores, from the. Primary consumers are organisms that eat producers or autotrophs, which are typically plants. secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers. in other words, primary consumers are herbivores, while secondary consumers can be either carnivores or omnivores. The opossum shrimp eats both primary producers and primary consumers; it is, therefore, both a primary consumer and a secondary consumer. the loss of energy in tropic levels it is rare to find food chains that have more than four or five links because the loss of energy limits the length of food chains.

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Primary consumers are organisms that eat producers or autotrophs, which are typically plants. secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers. in other words, primary consumers are herbivores, while secondary consumers can be either carnivores or omnivores. The opossum shrimp eats both primary producers and primary consumers; it is, therefore, both a primary consumer and a secondary consumer. the loss of energy in tropic levels it is rare to find food chains that have more than four or five links because the loss of energy limits the length of food chains. The grass is the producer, and the animals are consumers: the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer the next one is the secondary consumer. Higher level consumers. secondary or second level consumers eat primary consumers. tertiary or third level consumers eat lower level consumers and are sometimes called final consumers. some secondary and tertiary consumers eat plants as well as lower level consumers, making them omnivores. humans are good example of omnivorous upper level.

Trophic Levels Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer The grass is the producer, and the animals are consumers: the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer the next one is the secondary consumer. Higher level consumers. secondary or second level consumers eat primary consumers. tertiary or third level consumers eat lower level consumers and are sometimes called final consumers. some secondary and tertiary consumers eat plants as well as lower level consumers, making them omnivores. humans are good example of omnivorous upper level.

What Is The Difference Between Primary Secondary And Tertiary Consumers

Comments are closed.