What Is Monopoly In Economics Types And Characteristics
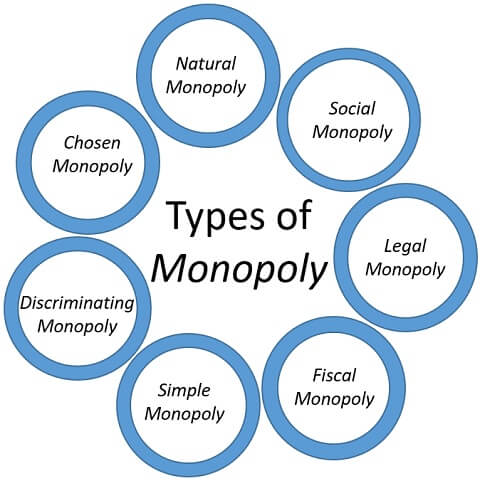
What Is Monopoly Defintion Types And Characteristics The Investors Book These different types of monopolies are listed below: private monopoly – a private monopoly is one that is owned by an individual or a group of individuals. these monopolies mainly aim for profits. public monopoly – a public monopoly is one that is owned by the government. these monopolies are set up for the welfare of the masses. A monopoly is a market structure that consists of a single seller or producer and no close substitutes. a monopoly limits available alternatives for its product and creates barriers for.

13 Types Of Monopoly 2024 Legal monopolies. a legal monopoly is a monopoly that exists because of laws and regulations restrict competition. monopolists whose products are protected by intellectual property rights, such as trademarks, patents, and copyrights are good examples of legal monopolies. legal monopolies can also arise if the costs of complying with. A pure monopoly is defined as a single seller of a product, i.e. 100% of market share. in the uk a firm is said to have monopoly power if it has more than 25% of the market share. for example, tesco @30% market share or google 90% of search engine traffic. A monopoly is a specific type of economic market structure. a monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular good. as a result, monopolies are characterized by a lack of competition within the market producing a good or service. monopoly: the graph shows a monopoly and the price (p) and change in price. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. in law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. [3] although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly.
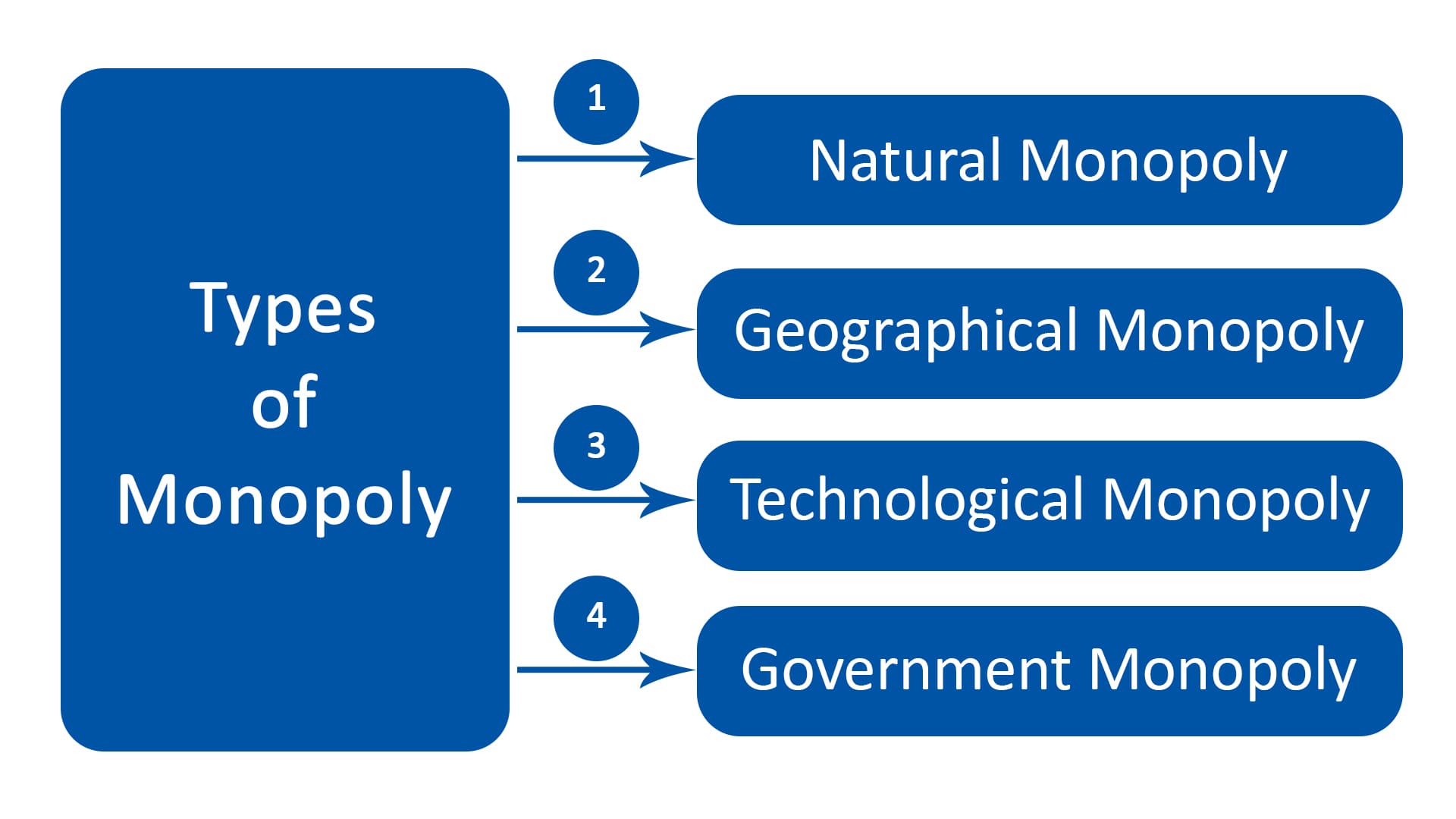
Monopoly Definition Types Characteristics Parsadi A monopoly is a specific type of economic market structure. a monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular good. as a result, monopolies are characterized by a lack of competition within the market producing a good or service. monopoly: the graph shows a monopoly and the price (p) and change in price. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. in law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. [3] although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. In economics, monopoly and competition signify certain complex relations among firms in an industry. a monopoly implies an exclusive possession of a market by a supplier of a product or a service for which there is no substitute. in this situation the supplier is able to determine the price of the product without fear of competition from other. A monopolistic market is a market structure with the characteristics of a pure monopoly. a monopoly exists when one supplier provides a particular good or service to many consumers ultimately.

Comments are closed.