What Is Diabetic Retinopathy 👁️
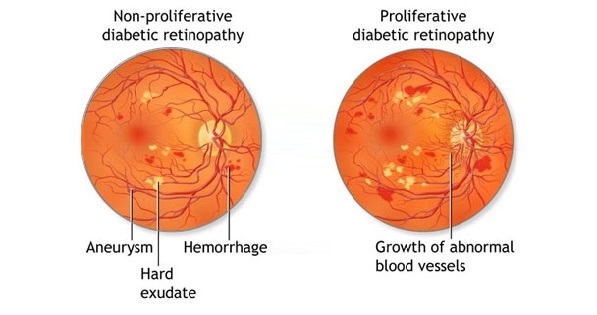
Back To Basics Diabetic Retinopathy Sydney Ophthalmic Specialists Diabetic retinopathy (die uh bet ik ret ih nop uh thee) is a diabetes complication that affects eyes. it's caused by damage to the blood vessels of the light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (retina). at first, diabetic retinopathy might cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems. but it can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy treatment. people with diabetes can have an eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. this is when high blood sugar levels cause damage to blood vessels in the retina. these blood vessels can swell and leak. or they can close, stopping blood from passing through. sometimes abnormal, new blood vessels grow on the retina.

Diabetic Retinopathy Symptoms Causes Complications Treatment Diabetic retinopathy can cause abnormal blood vessels to grow out of the retina and block fluid from draining out of the eye. this causes a type of glaucoma (a group of eye diseases that can cause vision loss and blindness). retinal detachment. diabetic retinopathy can cause scars to form in the back of your eye. For some people, symptoms come and go. symptoms of diabetes related retinopathy include: blurred or distorted vision. new color blindness or seeing colors as faded. poor night vision (night blindness). small dark spots (eye floaters) or streaks in your vision. trouble reading or seeing faraway objects. Diabetic retinopathy is best diagnosed with a comprehensive dilated eye exam. for this exam, drops placed in your eyes widen (dilate) your pupils to allow your doctor a better view inside your eyes. the drops can cause your close vision to blur until they wear off, several hours later. during the exam, your eye doctor will look for. Disease. diabetic retinopathy represents microvascular end organ damage as a result of diabetes. it ranges from non proliferative diabetic retinopathy (npdr) and its stages to proliferative diabetic retinopathy (pdr). as the disease progresses, associated diabetic macular edema (dme) may also become apparent.
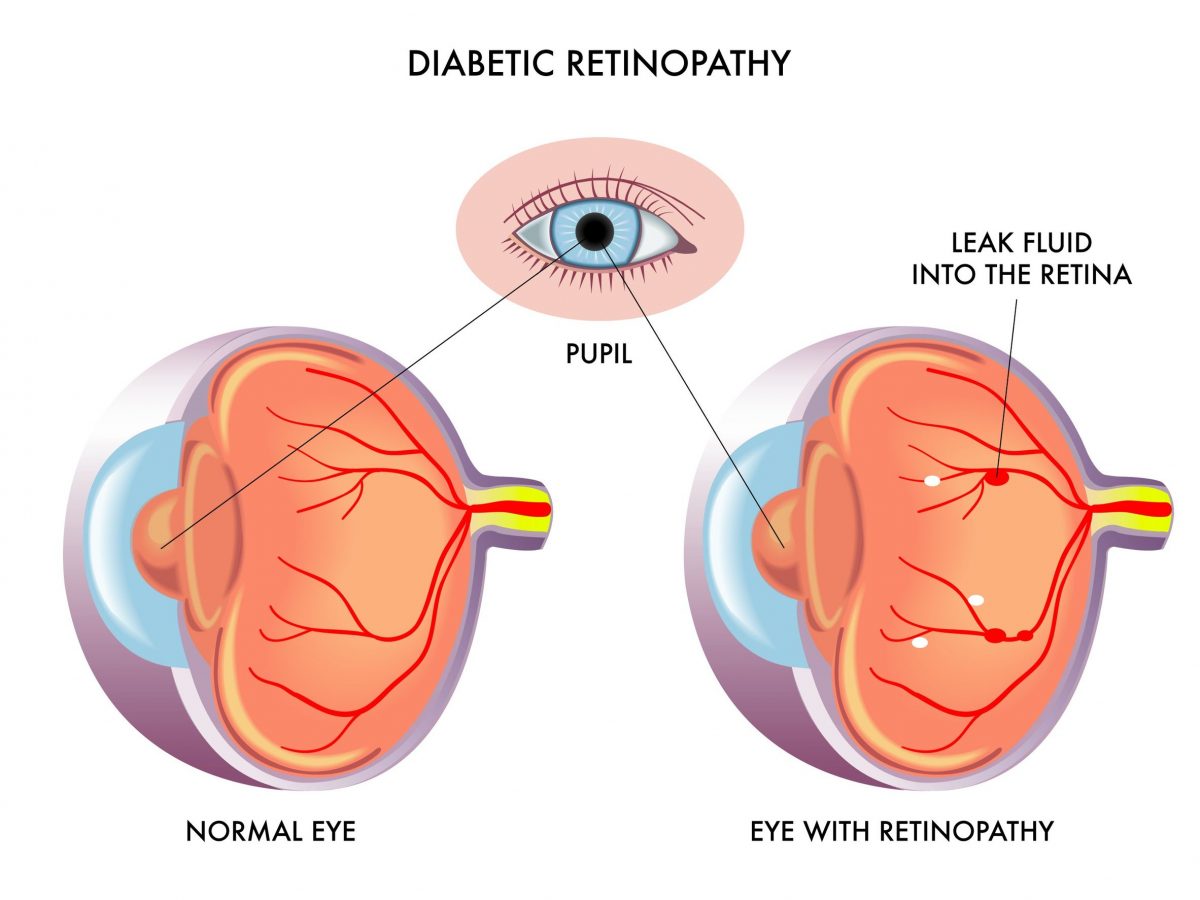
Diabetic Retinopathy Lasiksurgeons Diabetic retinopathy is best diagnosed with a comprehensive dilated eye exam. for this exam, drops placed in your eyes widen (dilate) your pupils to allow your doctor a better view inside your eyes. the drops can cause your close vision to blur until they wear off, several hours later. during the exam, your eye doctor will look for. Disease. diabetic retinopathy represents microvascular end organ damage as a result of diabetes. it ranges from non proliferative diabetic retinopathy (npdr) and its stages to proliferative diabetic retinopathy (pdr). as the disease progresses, associated diabetic macular edema (dme) may also become apparent. Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition that can cause vision loss and blindness in people with diabetes. the condition affects the blood vessels in the retina, which is the light sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye.1. having high blood sugar (blood glucose) damages your retina over time. if you have diabetes, it’s important to. Diabetic retinopathy (dr) is a microvascular disorder occurring due to the long term effects of diabetes mellitus. diabetic retinopathy may lead to vision threatening damage to the retina, eventually leading to blindness. it is the most common cause of severe vision loss in adults of working age groups in the western world.[1] early detection and timely intervention are the keys to avoiding.
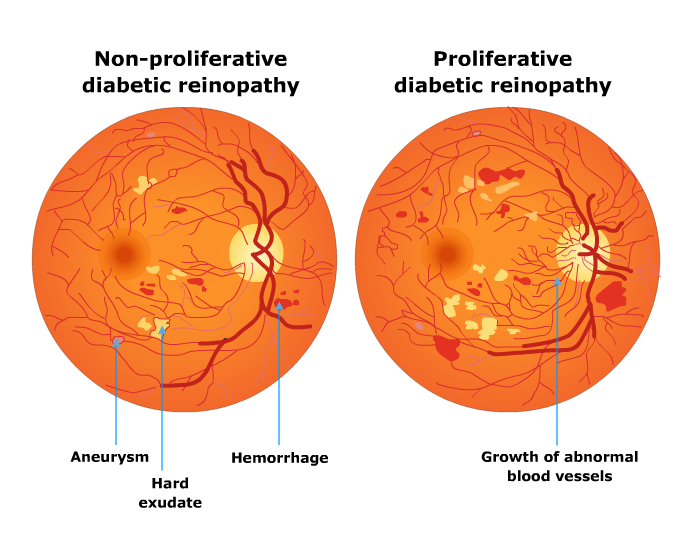
Diabetic Retinopathy Ishwar Eye Centre Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition that can cause vision loss and blindness in people with diabetes. the condition affects the blood vessels in the retina, which is the light sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye.1. having high blood sugar (blood glucose) damages your retina over time. if you have diabetes, it’s important to. Diabetic retinopathy (dr) is a microvascular disorder occurring due to the long term effects of diabetes mellitus. diabetic retinopathy may lead to vision threatening damage to the retina, eventually leading to blindness. it is the most common cause of severe vision loss in adults of working age groups in the western world.[1] early detection and timely intervention are the keys to avoiding.

Comments are closed.