What Is A Neuron Diagrams Types Function And More
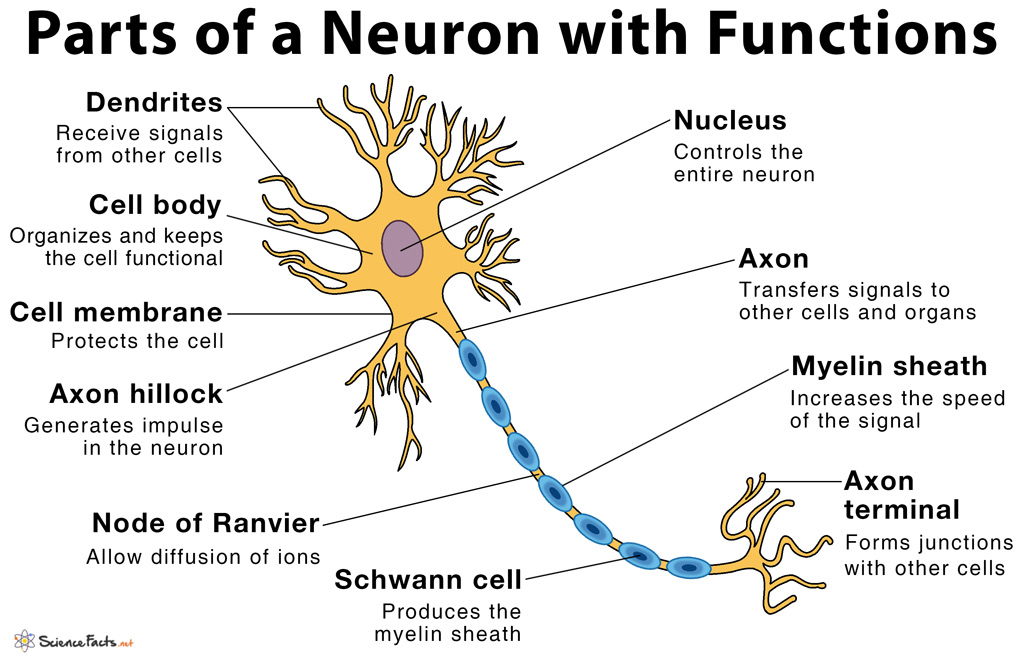
Parts Of A Neuron And Their Functions With Labelled Diagram An easy guide to neuron anatomy with diagrams. neurons, also known as nerve cells, send and receive signals from your brain. while neurons have a lot in common with other types of cells, they’re. The neuron contains the soma (cell body), which extends the axon (a nerve fiber conducting electrical impulses away from the soma), and dendrites (tree like structures that receive signals from other neurons). the myelin sheath is an insulating layer that forms around the axon and allows nerve impulses to transmit more rapidly along the axon.
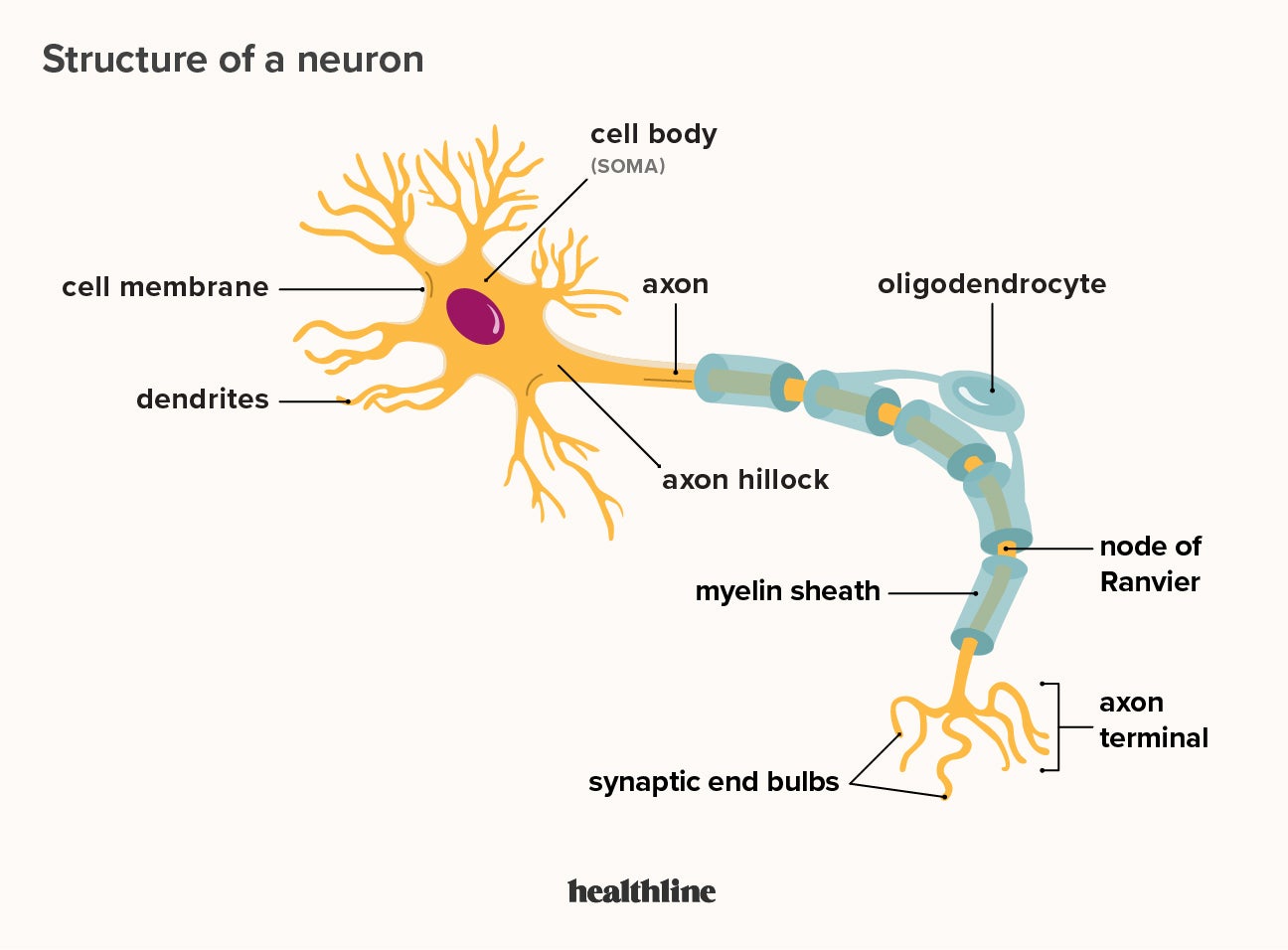
What Is A Neuron Diagrams Types Function And More Different types of neurons include sensory, motor, and interneurons, as well as structurally based neurons, which include unipolar, multipolar, bipolar, and pseudo unipolar neurons. these cells coordinate bodily functions and movement so quickly, we don't even notice it happening. 9 sources. Overview of neuron structure and function. the membrane potential. electrotonic and action potentials. saltatory conduction in neurons. neuronal synapses (chemical) the synapse. neurotransmitters and receptors. q & a: neuron depolarization, hyperpolarization, and action potentials. overview of the functions of the cerebral cortex. The nervous system consists of two main cell types, neurons and supporting glial cells. the neuron (or nerve cell) is the functional unit of both the central nervous system (cns) and the peripheral nervous system (pns). the basic functions of neurons can be summarized into four main tasks: receiving signals, integrating these signals generating. Anaxonic neurons: lacks an axon, or it cannot be distinguished from its many dendrites. function. motor neurons, sensory neurons, interneurons (short axon or long axon) connectivity. afferent, efferent (or projection), local circuit neurons (or intrinsic neurons), excitatory, inhibitory, modulatory. neurochemistry.

Neurotransmitter Pmg Biology The nervous system consists of two main cell types, neurons and supporting glial cells. the neuron (or nerve cell) is the functional unit of both the central nervous system (cns) and the peripheral nervous system (pns). the basic functions of neurons can be summarized into four main tasks: receiving signals, integrating these signals generating. Anaxonic neurons: lacks an axon, or it cannot be distinguished from its many dendrites. function. motor neurons, sensory neurons, interneurons (short axon or long axon) connectivity. afferent, efferent (or projection), local circuit neurons (or intrinsic neurons), excitatory, inhibitory, modulatory. neurochemistry. The neuron is one of two basic types of cells in the nervous system, the other type being the glial cell. figure 11.3.1: interneurons of adult visual cortex. neurons, also called nerve cells, are electrically excitable cells that are the main functional units of the nervous system. Neurons are electrically excitable cells that transmit signals throughout the body. neurons employ both electrical and chemical components in the transmission of information. neurons are connected to other neurons at synapses and connected to effector organs or cells at neuroeffector junctions. a typical multipolar neuron is comprised of soma or cell body, an axon, and dendrites. the axon is.

Comments are closed.