What Eats Secondary Consumers

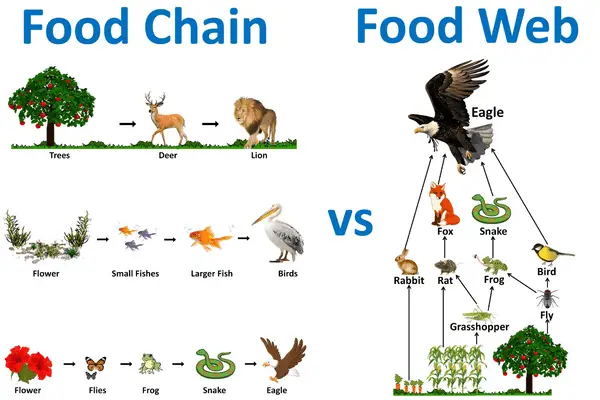
What Eats Secondary Consumers Learn what secondary consumers are, how they function in the food chain, and what types of animals they are. find out how they differ from primary and tertiary consumers, and see examples of aquatic and terrestrial secondary consumers. Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are carnivores or omnivores that transfer energy to higher trophic levels in the food chain.
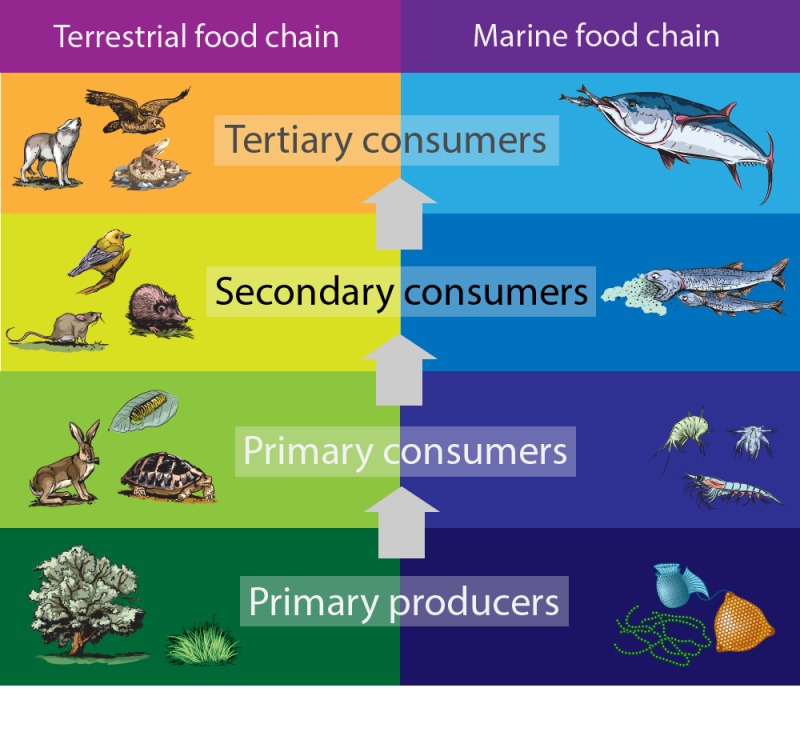
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. Secondary consumers occupy the third trophic level in a typical food chain. they are organisms that feed on primary consumers for nutrients and energy. while primary consumers are always herbivores; organisms that only feed on autotrophic plants, secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores eat only animals, but omnivores eat. These small herbivores eat dozens of kilograms (pounds) of giant kelp every day. secondary consumers eat herbivores. they are at the third trophic level. in a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. in the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. tertiary consumers eat the secondary. Secondary consumers are those that predate upon primary consumers, and tertiary consumers predate upon secondary consumers. secondary consumers are either carnivores (which eat meat) or omnivores.
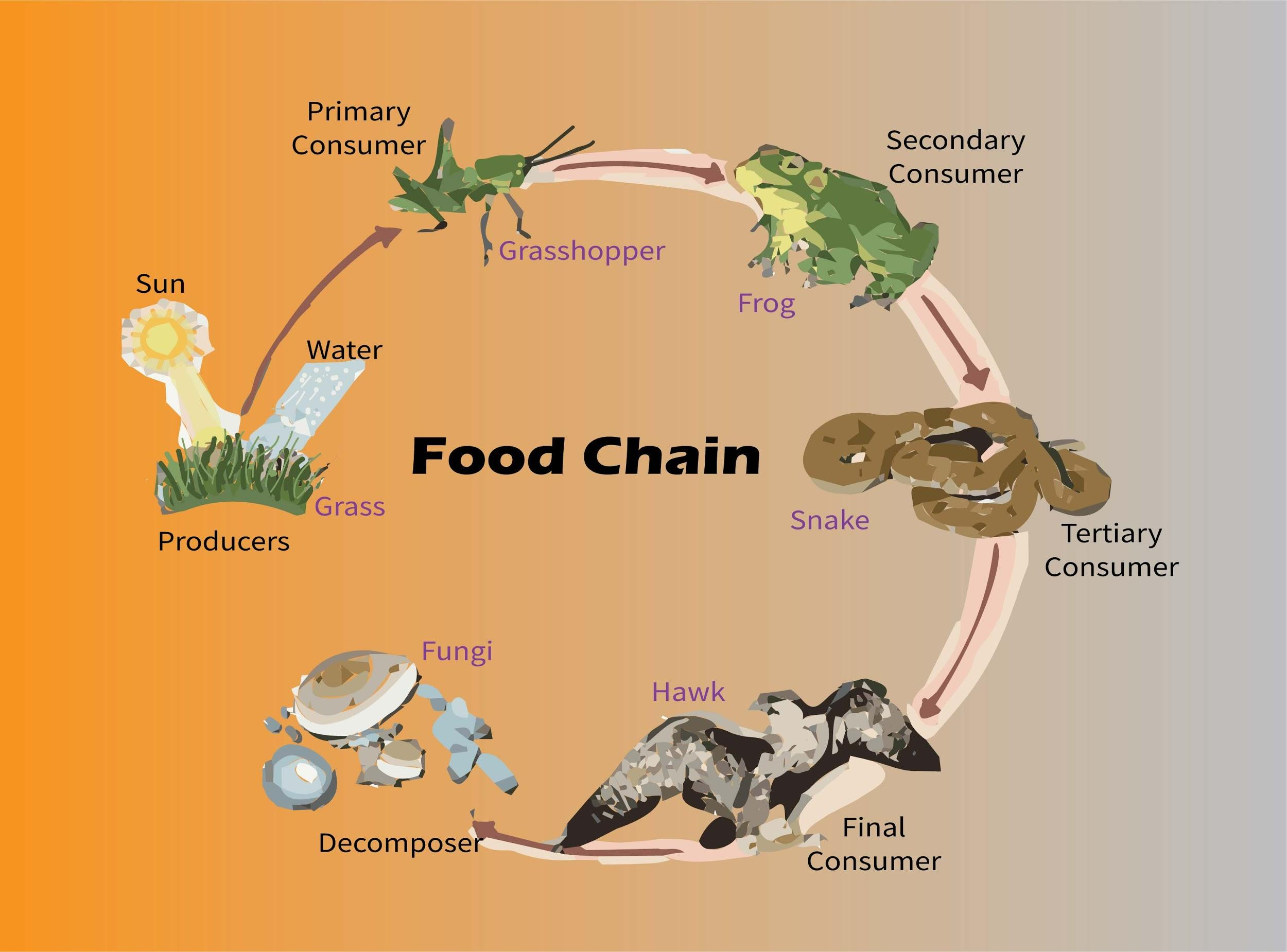
What Is The Correct Food Chain In Grassland A Grass Snake Insect Deer These small herbivores eat dozens of kilograms (pounds) of giant kelp every day. secondary consumers eat herbivores. they are at the third trophic level. in a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. in the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. tertiary consumers eat the secondary. Secondary consumers are those that predate upon primary consumers, and tertiary consumers predate upon secondary consumers. secondary consumers are either carnivores (which eat meat) or omnivores. Secondary consumers: a lion preying on a gazelle, a spider catching flies, or a bear that eats fish are examples of secondary consumers. ecological impact: primary consumers: they directly affect the population and health of primary producers and are crucial for sustaining many primary producers through processes like seed dispersal. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores, from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals. ecosystems can also have tertiary consumers.
Birds And Humans Are They Secondary Consumers Examples Ecowut Secondary consumers: a lion preying on a gazelle, a spider catching flies, or a bear that eats fish are examples of secondary consumers. ecological impact: primary consumers: they directly affect the population and health of primary producers and are crucial for sustaining many primary producers through processes like seed dispersal. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores, from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals. ecosystems can also have tertiary consumers.

Ppt 1 St Law Everything Is Connected To Everything Else Powerpoint
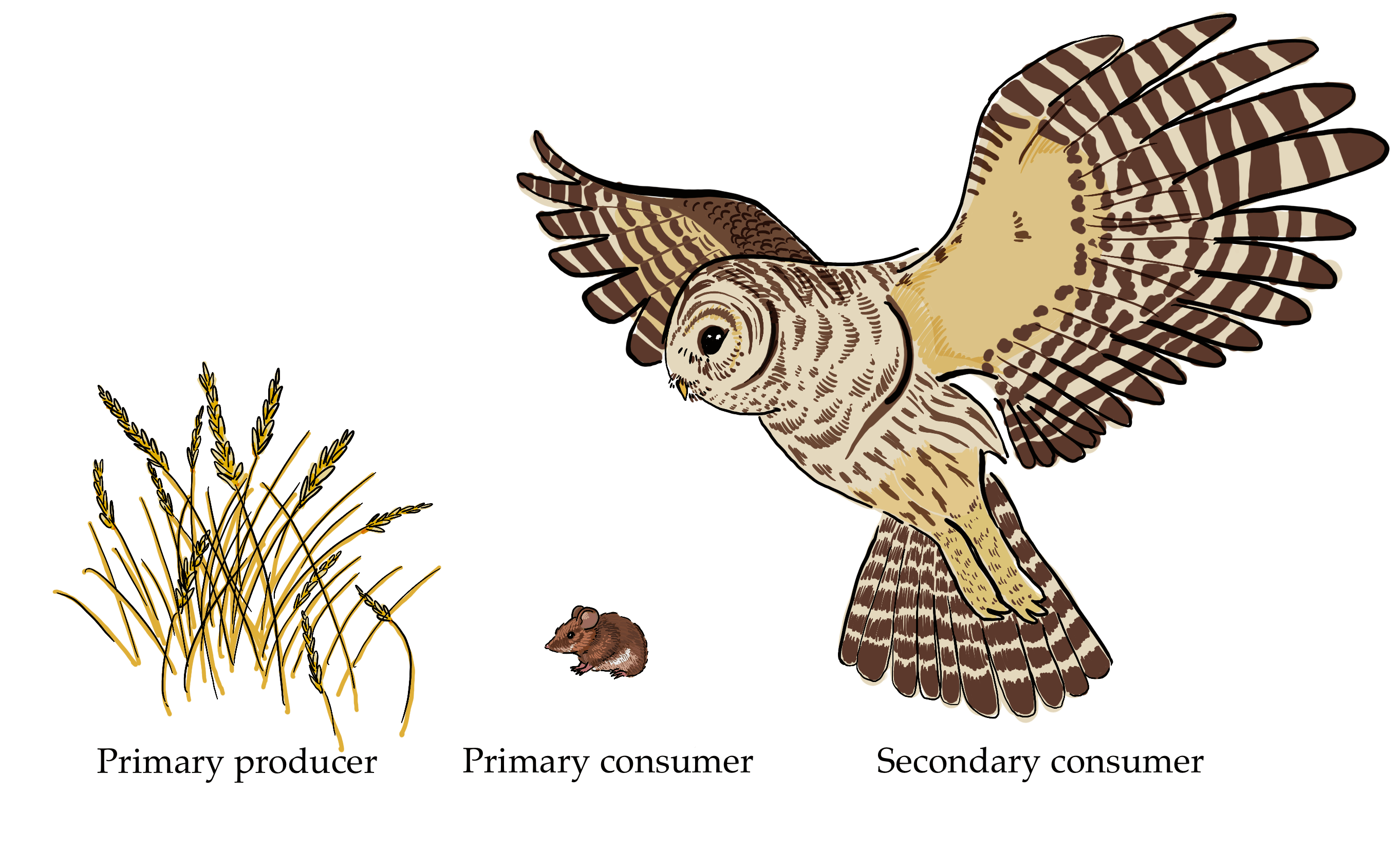
Secondary Consumer Definition Role Expii

Comments are closed.