What Causes Volcanic Hotspots
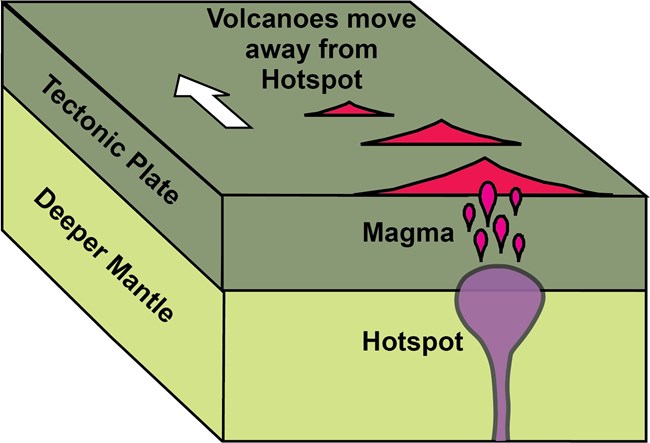
Hotspots Geology U S National Park Service Intensely hot region deep within the earth that rises to just underneath the surface. some hot spots produce volcanoes. to live in a specific place. body of land surrounded by water. molten rock, or magma, that erupts from volcanoes or fissures in the earth's surface. outer, solid portion of the earth. In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. [ 1 ] examples include the hawaii, iceland, and yellowstone hotspots. a hotspot's position on the earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a.

What Causes A Volcanic Eruption Illustration Stock Vector Image Art In geology, a hotspot is an area of the earth’s mantle from which hot plumes rise upward, forming volcanoes on the overlying crust. samoa is composed of a linear chain of volcanic islands situated atop the pacific tectonic plate. samoa is an example of one of at least 28 plume fed volcanic hotspots are suggested to exist on the earth’s surface. Volcanic hot spots are plumes of molten rock which rise from the mantle and cause the crust to melt, creating magma resulting in volcanic activity. the map below shows the location of volcanic hot spots. a map to show volcanic hotspots. the diagram below illustrates the formation of a hot spot and its associated landforms. A hot spot is an intensely hot area in the mantle below earth's crust. the heat that fuels the hot spot comes from very deep in the planet. this heat causes the mantle in that region to melt. the molten magma rises up and breaks through the crust to form a volcano. while the hot spot stays in one place, rooted to its deep source of heat, the. A hot spot is an area on earth over a mantle plume or an area under the rocky outer layer of earth, called the crust, where magma is hotter than surrounding magma. the magma plume causes melting and thinning of the rocky crust and widespread volcanic activity.
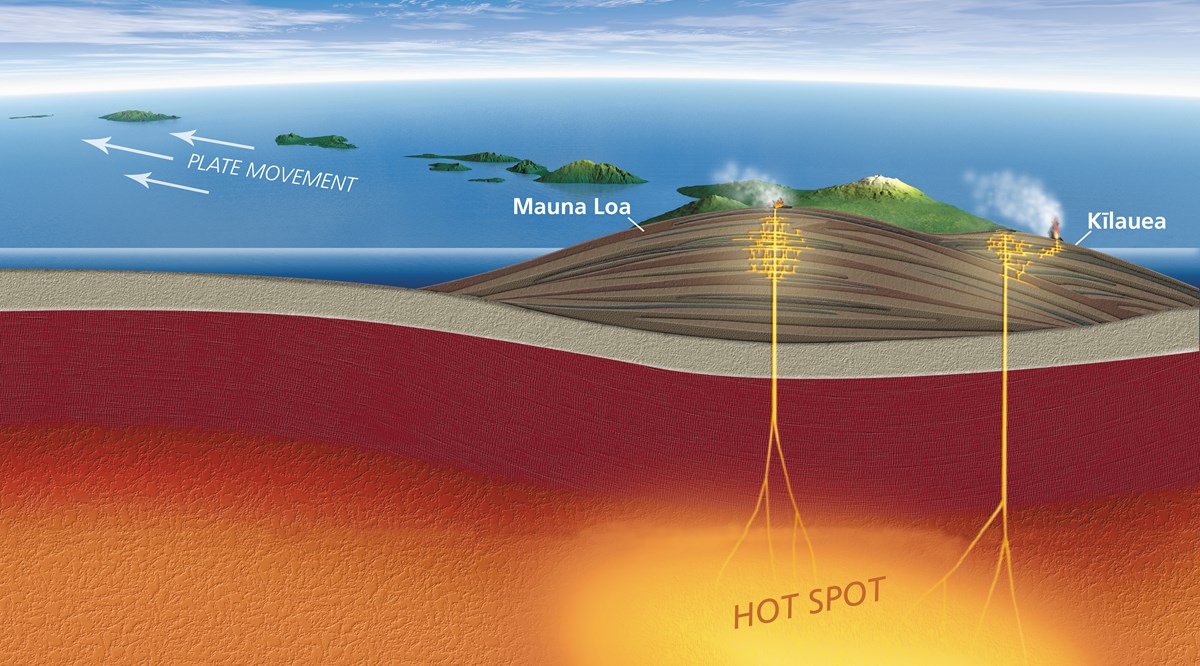
Volcanoes Hawai併i Volcanoes National Park U S National Park Service A hot spot is an intensely hot area in the mantle below earth's crust. the heat that fuels the hot spot comes from very deep in the planet. this heat causes the mantle in that region to melt. the molten magma rises up and breaks through the crust to form a volcano. while the hot spot stays in one place, rooted to its deep source of heat, the. A hot spot is an area on earth over a mantle plume or an area under the rocky outer layer of earth, called the crust, where magma is hotter than surrounding magma. the magma plume causes melting and thinning of the rocky crust and widespread volcanic activity. Intraplate (hot spot) volcanism. a third tectonic setting where volcanism occurs is called intraplate or hot spot volcanism, which describes volcanic activity that occurs within tectonic plates and is generally not related to plate boundaries and plate movements. most volcanic activity occurs at plate boundaries, but there are also a large. 5.16: hot spots. in geology, the places known as hotspots or hot spots are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. they may be on, near to, or far from tectonic plate boundaries. currently, there are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins.

Volcanic Hotspot The Geo Room Intraplate (hot spot) volcanism. a third tectonic setting where volcanism occurs is called intraplate or hot spot volcanism, which describes volcanic activity that occurs within tectonic plates and is generally not related to plate boundaries and plate movements. most volcanic activity occurs at plate boundaries, but there are also a large. 5.16: hot spots. in geology, the places known as hotspots or hot spots are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. they may be on, near to, or far from tectonic plate boundaries. currently, there are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins.

Comments are closed.