What Are The Differences Between Producers Consumers And Decomposers

Producers Consumers And Decomposers Science Quizizz Producers are also called autotrophs. auto means self, while troph means food. they are organisms that create their food from inorganic molecules such as water, co2, nitrogen, and phosphate. most. Decomposers break down dead organic matter, while producers produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. decomposers recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem, while producers provide food and energy to other organisms. decomposers release carbon dioxide during decomposition, while producers release oxygen during photosynthesis.

Food Chain Producers Consumers Decomposers Food Chain In Pond Consumers are also called heterotrophs. heterotrophs are classified by what they eat: herbivores consume producers such as plants or algae. they are a necessary link between producers and other consumers. examples include deer, rabbits, and mice. carnivores consume animals. examples include lions, polar bears, hawks, frogs, salmon, and spiders. Aquatic animal that strains nutrients from water. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web. A food chain represents the relationship between predator and prey. it is a way of classifying animals, plants, and fungi that eat other organisms in order to survive. the four levels in this food chain are primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and finally decomposers or phytoremediators.
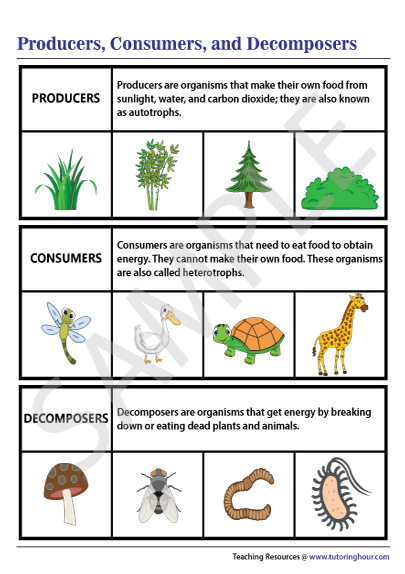
Producers Consumers And Decomposers Chart Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web. A food chain represents the relationship between predator and prey. it is a way of classifying animals, plants, and fungi that eat other organisms in order to survive. the four levels in this food chain are primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and finally decomposers or phytoremediators. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 19.1.1). figure 19.1.1: example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems. This tutorial will introduce the main types of biotic (living) factors in ecosystems as producers, consumers, and decomposers. students will learn how producers (e.g., plants) and consumers (e.g., animals) interact in the environment and the role they play in sustaining healthy ecosystems. watch the video to learn more.

Comments are closed.