What Are The Changes Of State Of Matter With Examples⚛️
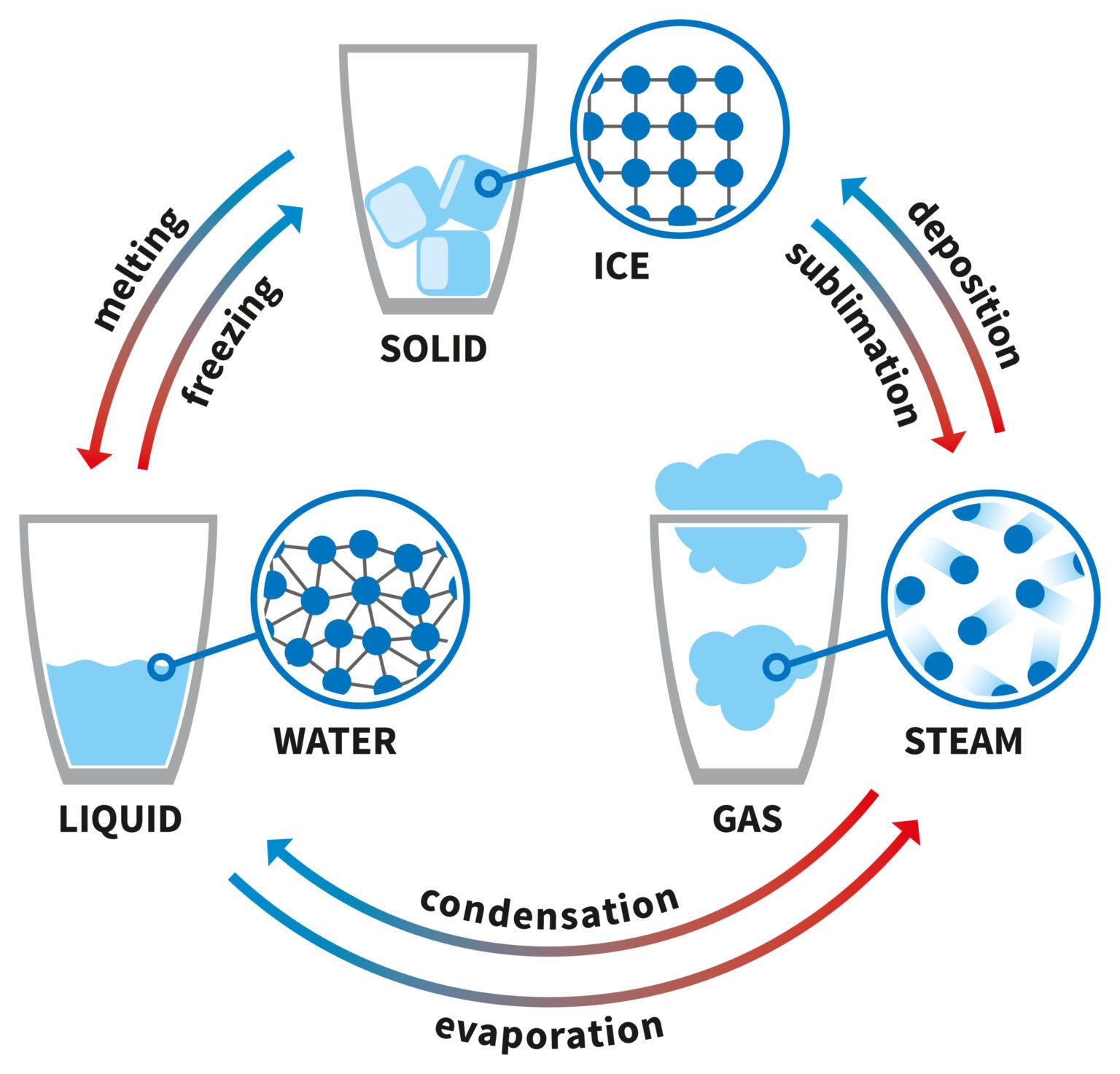
Explainer What Are The Different States Of Matter A change of state is a physical change in a matter. they are reversible changes and do not involve any changes in the chemical makeup of the matter. common changes of the state include melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, condensation, and vaporization. these changes are shown in the figure given below. States of matter describe the qualities displayed by matter. basically, the state of matter of a substance depends on how much energy its particles have. we can change the energy of matter by altering its temperature or pressure, causing matter to transition from one state to another. but, when matter changes state, its chemical identity.
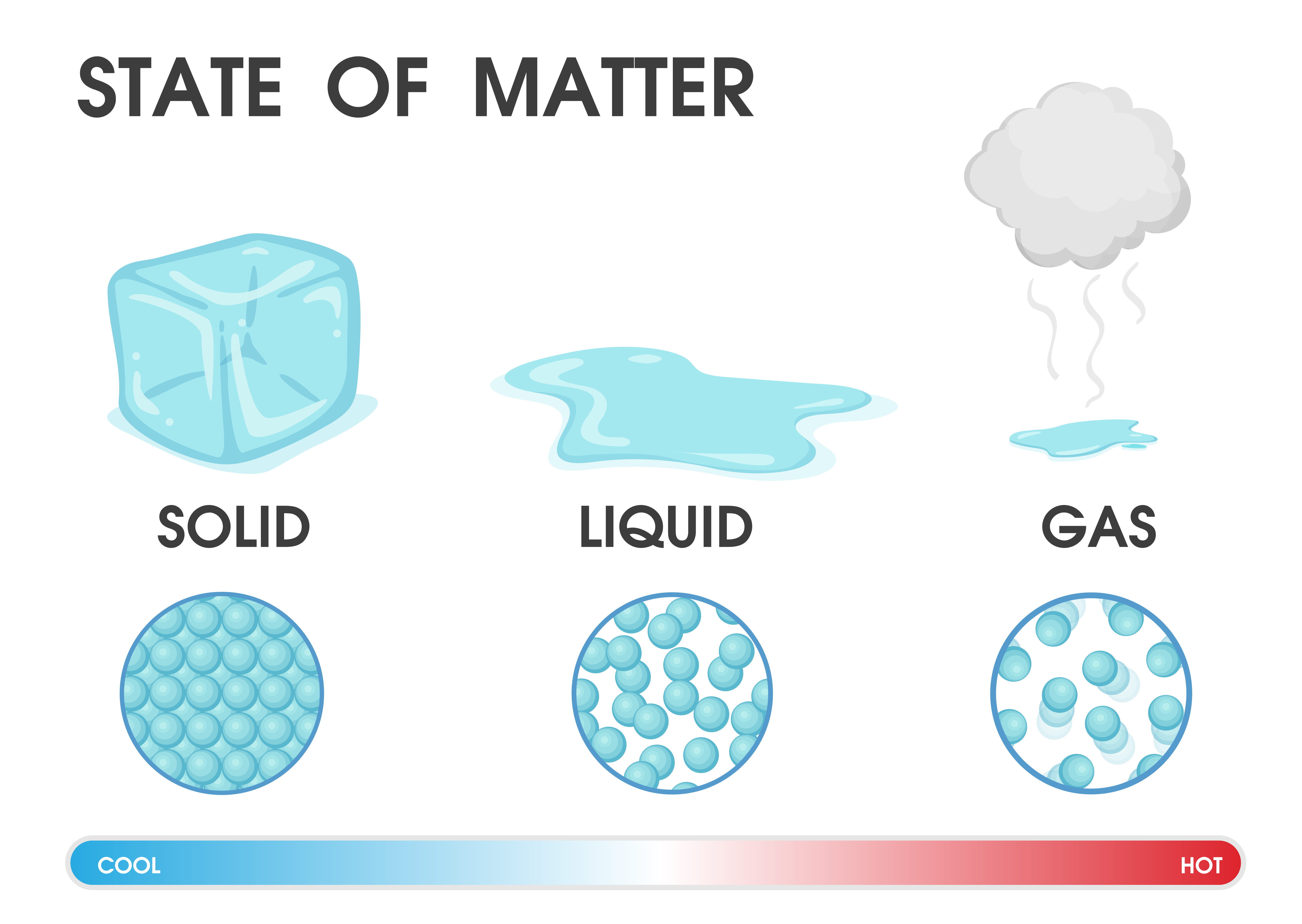
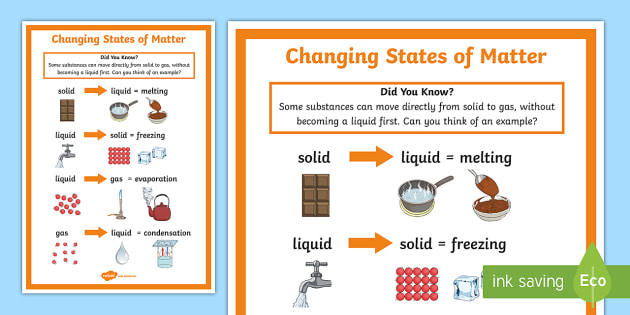
Diagram Venn Diagram Of States Of Matter Mydiagram Online A phase change or phase transition is a change between solid, liquid, gaseous, and sometimes plasma states of matter. the states of matter differ in the organization of particles and their energy. the main factors that cause phase changes are changes in temperature and pressure. at the phase transition, such as the boiling point between liquid. There are four main. changes of state. change of state a change of a substance from one physical state (solid, liquid or gas) to another. : melting the process of a solid turning into a. liquid. There are multiple different ways of modeling changes in state mathematically. the most common form is using the equations. q = m ⋅ c ⋅ Δ t and q = m ⋅ h (heat of fusion vaporization) m = mass of substance n = moles of substance c = specific heat of substance. as shown in the heating curve above, these equations are used interchangeably. The energy change associated with each common phase change is shown in figure 8.1.2 8.1. 2. Δh Δ h is positive for any transition from a more ordered to a less ordered state and negative for a transition from a less ordered to a more ordered state. previously, we defined the enthalpy changes associated with various chemical and physical.
What Is Changing State Twinkl Teaching Wiki Twinkl There are multiple different ways of modeling changes in state mathematically. the most common form is using the equations. q = m ⋅ c ⋅ Δ t and q = m ⋅ h (heat of fusion vaporization) m = mass of substance n = moles of substance c = specific heat of substance. as shown in the heating curve above, these equations are used interchangeably. The energy change associated with each common phase change is shown in figure 8.1.2 8.1. 2. Δh Δ h is positive for any transition from a more ordered to a less ordered state and negative for a transition from a less ordered to a more ordered state. previously, we defined the enthalpy changes associated with various chemical and physical. Definition: vaporization. vaporization is the change of matter from the liquid state to the gas state when it gains enough thermal energy. thermal energy also affects the space between molecules. a substance tends to get more distantly separated particles as it gains thermal energy and its state changes. there is, for example, relatively little. Ice is an example of a solid. a liquid has a defined volume, but can change its shape. water is an example of a liquid. a gas lacks either a defined shape or volume. water vapor and air are examples of gas. like a gas, plasma lacks a defined shape or volume. but, plasma particles are further apart than gas particles and they carry an electrical.

Changes Of State Ks3 Physics Revision Definition: vaporization. vaporization is the change of matter from the liquid state to the gas state when it gains enough thermal energy. thermal energy also affects the space between molecules. a substance tends to get more distantly separated particles as it gains thermal energy and its state changes. there is, for example, relatively little. Ice is an example of a solid. a liquid has a defined volume, but can change its shape. water is an example of a liquid. a gas lacks either a defined shape or volume. water vapor and air are examples of gas. like a gas, plasma lacks a defined shape or volume. but, plasma particles are further apart than gas particles and they carry an electrical.

Comments are closed.