Ventriculomegaly South West Fetal Network
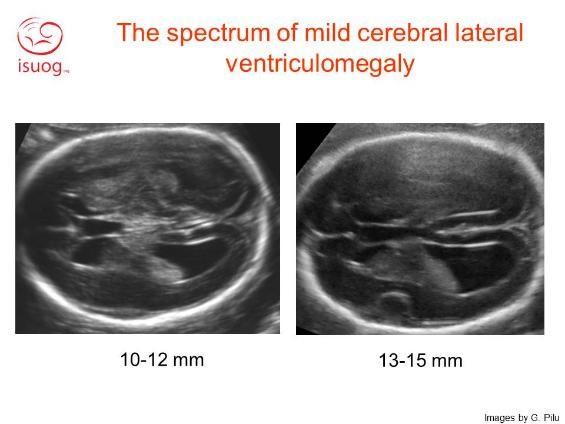
Ventriculomegaly South West Fetal Network This is a lump of tiny vessels that produce the cerebrospinal fluid. the width of the atrium of the lateral ventricles is normal up to 10 mm. a width of 10 15 mm is called ventriculomegaly. up to 12 mm we call it “mild” ventriculomegaly. if the posterior horn (atrium) measures more than 15 mm, it is known as hydrocephaly. Ventriculomegaly is defined as dilation of the fetal cerebral ventricles and is a relatively common finding on prenatal ultrasound. the purpose of this document is to review the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of mild fetal ventriculomegaly. when enlargement of the lateral ventricles (≥10 mm) is identified, a thorough evaluation should be performed, including detailed sonographic.

Ventriculomegaly Fetal Ultrasound Contact us. fetal cardiology monday – friday 8.30am – 4.30pm, 0117 342 5394. cardiac nurse specialists – monday – friday 8am – 4pm, 0117 342 8286, [email protected]. Criteria for diagnosing ventriculomegaly. the severity of fetal ventriculomegaly ranges from mild to severe based on the measurement of the ventricle. in a typical fetal brain, the ventricles are less than 10 millimeters (mm) wide — or about the width of a pea. mild: the ventricles are between 10 mm to 12 mm. Fetal cerebral ventriculomegaly is defined as an atrial diameter of ≥10 mm on prenatal ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.1–3 the terms hydrocephalus and ventriculomegaly are often used interchangeably. more often, however, the term hydrocephalus is used to describe pathologic dilation of the brain’s ventricular system because of increased cerebrospinal fluid (csf. The incidence of mild to moderate fetal ventriculomegaly is approximately 1%.4,6 asymmetry of the lateral ventricles is common, and ventriculomegaly can be unilateral or bilateral. unilateral ventriculomegaly is present in approxi mately 50e60% of cases, and bilateral ventriculomegaly occurs in approximately 40e50%.8,9 although mild ven.

Fetal Ventriculomegaly American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology Fetal cerebral ventriculomegaly is defined as an atrial diameter of ≥10 mm on prenatal ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.1–3 the terms hydrocephalus and ventriculomegaly are often used interchangeably. more often, however, the term hydrocephalus is used to describe pathologic dilation of the brain’s ventricular system because of increased cerebrospinal fluid (csf. The incidence of mild to moderate fetal ventriculomegaly is approximately 1%.4,6 asymmetry of the lateral ventricles is common, and ventriculomegaly can be unilateral or bilateral. unilateral ventriculomegaly is present in approxi mately 50e60% of cases, and bilateral ventriculomegaly occurs in approximately 40e50%.8,9 although mild ven. Ventriculomegaly is the term used to describe cerebral ventricular dilation unrelated to increased cerebrospinal fluid (csf) pressure, such as dilation due to brain dysgenesis or atrophy. hydrocephalus is the term used to describe pathologic dilation of the brain's ventricular system due to increased csf pressure; obstruction is a common. Fetal cerebral ventriculomegaly (vm) is diagnosed when the width of one or both ventricles, measured at the level of the glomus of the choroid plexus (atrium), is ≥ 10 mm. vm can result from different processes: abnormal turnover of the cerebrospinal fluid (csf), neuronal migration disorders, and destructive processes.

Fetal Ventriculomegaly American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology Ventriculomegaly is the term used to describe cerebral ventricular dilation unrelated to increased cerebrospinal fluid (csf) pressure, such as dilation due to brain dysgenesis or atrophy. hydrocephalus is the term used to describe pathologic dilation of the brain's ventricular system due to increased csf pressure; obstruction is a common. Fetal cerebral ventriculomegaly (vm) is diagnosed when the width of one or both ventricles, measured at the level of the glomus of the choroid plexus (atrium), is ≥ 10 mm. vm can result from different processes: abnormal turnover of the cerebrospinal fluid (csf), neuronal migration disorders, and destructive processes.
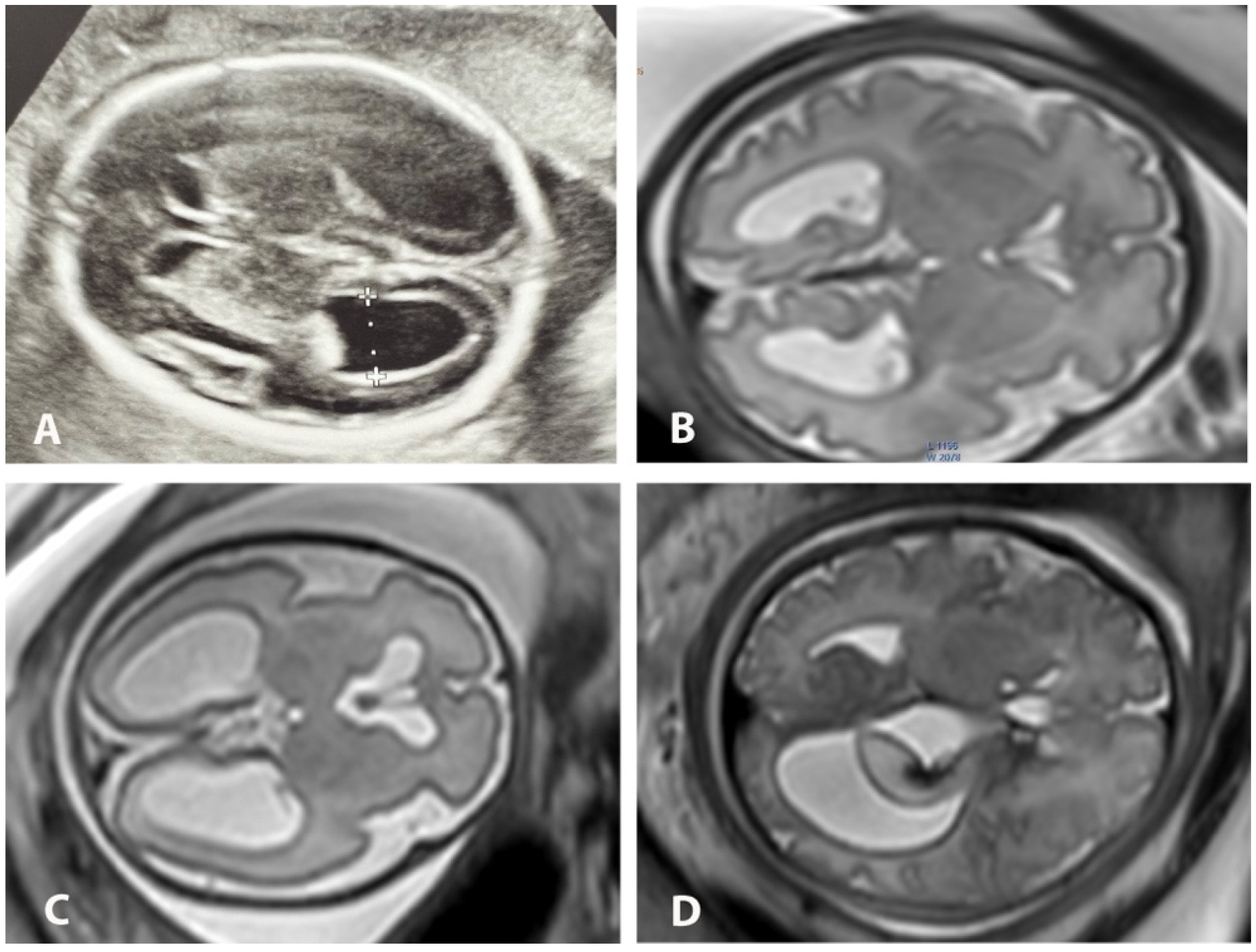
Diagnostics Free Full Text Concordance Between Us And Mri Two

Comments are closed.