Vector Data
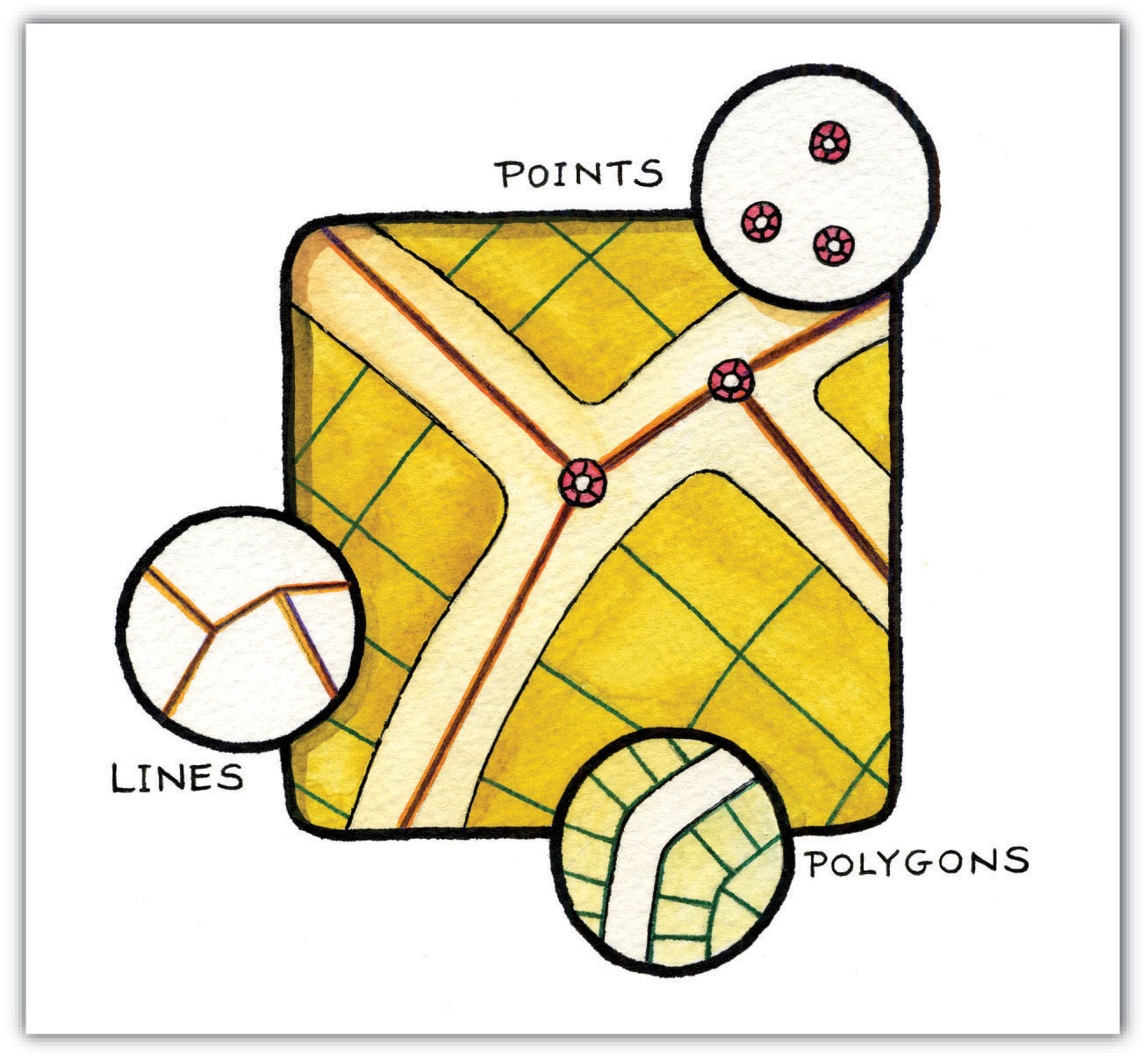
Vector Data Models Learn the basic concepts and differences between vector and raster data in a gis, two types of spatial data models. vector data are points, lines, and polygons, while raster data are pixels with values or classes. About vector data. vector data structures represent specific features on the earth’s surface, and assign attributes to those features. vectors are composed of discrete geometric locations (x, y values) known as vertices that define the shape of the spatial object. the organization of the vertices determines the type of vector that we are.
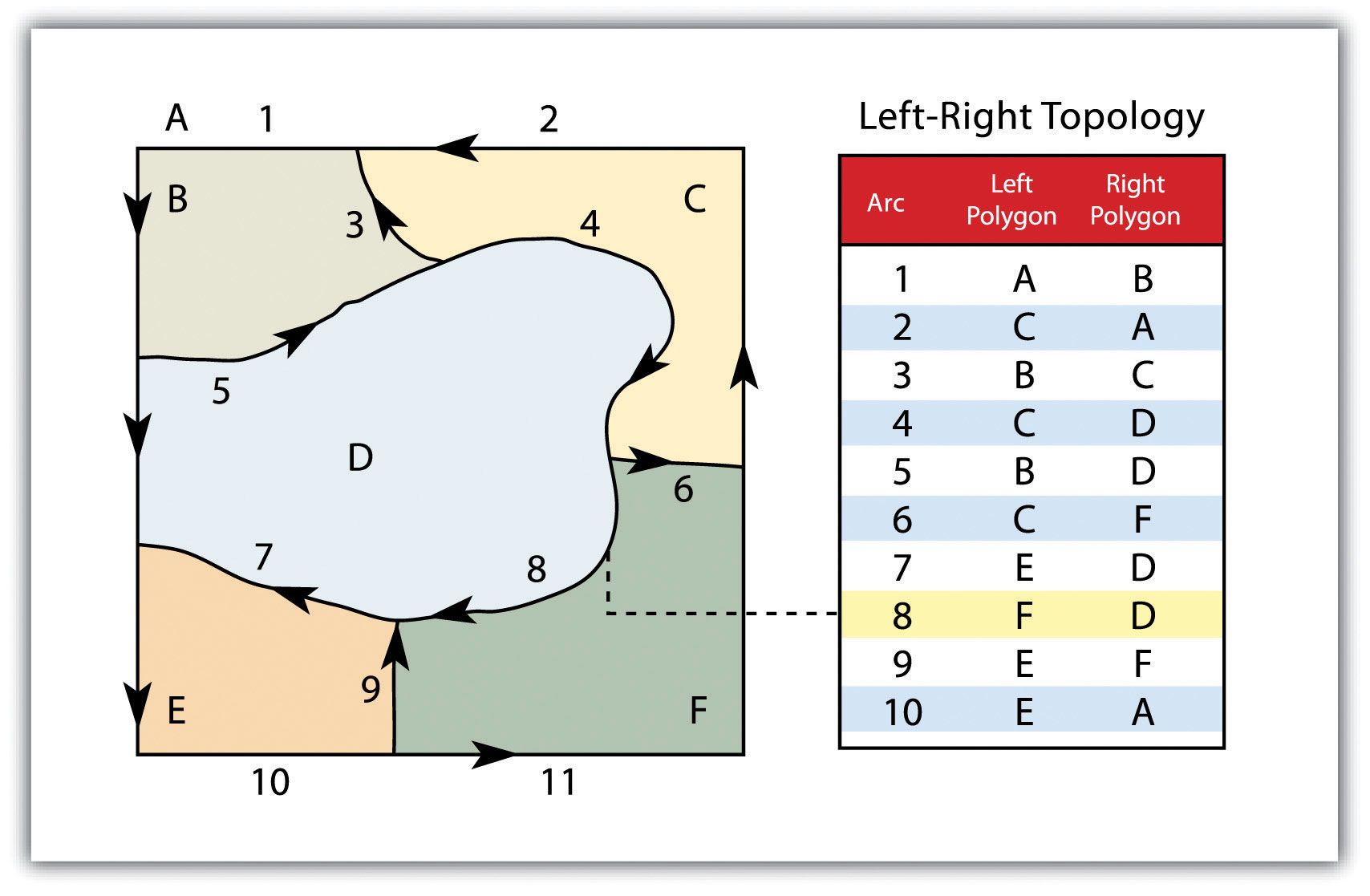
Vector Data Models Learn how vector data models are implemented in gis applications using points, lines, and polygons. compare the spaghetti and topological data models and their advantages and disadvantages. Learn how to use the data member function of the std::vector class in c to obtain a pointer to the underlying array of elements. see the syntax, parameters, return value, complexity, notes, example and defect reports of data. Learn how to represent real world features using vector data models in gis. understand the concepts of points, polylines, polygons, vertices, geometries, scale, data quality and symbology. Learn the difference between vector and raster data in gis, and how they are used to represent geographic features and surfaces. see examples of point, line, polygon, and surface raster data, and their applications in gis analysis and mapping.
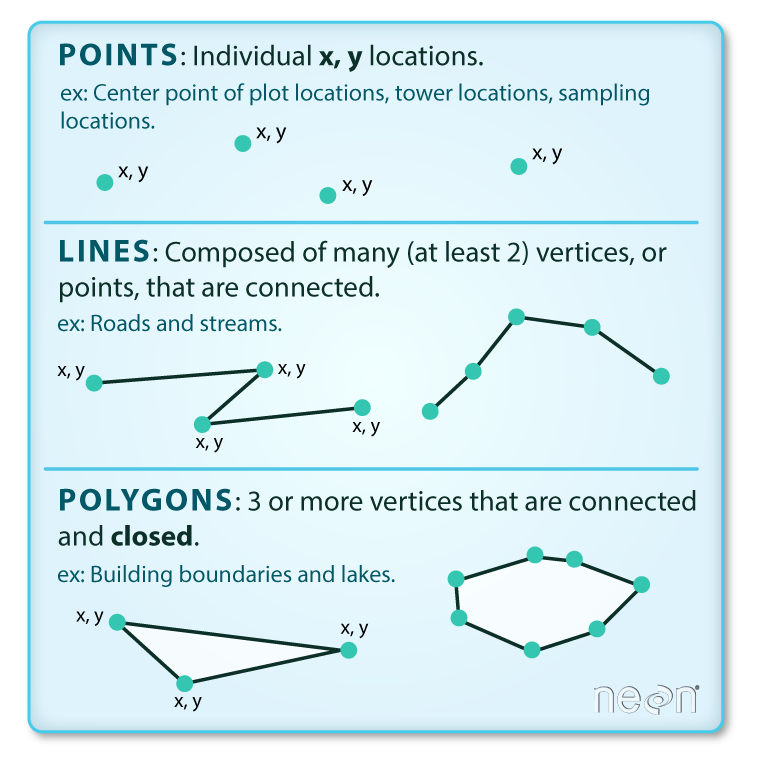
Introduction To Geospatial Concepts Introduction To Vector Data Learn how to represent real world features using vector data models in gis. understand the concepts of points, polylines, polygons, vertices, geometries, scale, data quality and symbology. Learn the difference between vector and raster data in gis, and how they are used to represent geographic features and surfaces. see examples of point, line, polygon, and surface raster data, and their applications in gis analysis and mapping. Learn what vector data is, how it differs from raster data, and when to use it in gis. vector data models geographic features as points, lines, and polygons with precise coordinates and attributes. Learn the basics of vector data, such as points, lines, and polygons, and how to work with them in arcgis pro. explore local data of logan city, utah, and yellowstone river, montana, and calculate their lengths.

Comments are closed.