Unit 4 Study Guide Key Cell Structure And Transport

Unit 4 Study Guide Key Cell Structure And Transport Youtube Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels. the transport of ions. a form of active transport of a solute through a cell membrane. maintaining a stable internal environment. protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response. equilibrium. a state of balance. Unit 4 part 1 notes cell types and structure. unit 4 part 1 notes chart (for organelle annotations) unit 4 part 1 notes chart answer key. unit 4 part 2 notes cell membrane and transport. types of cell transport chart (to complete while annotating) unit 4 part 2 in class powerpoint. unit 4 part 3 notes water potential and sa:v.
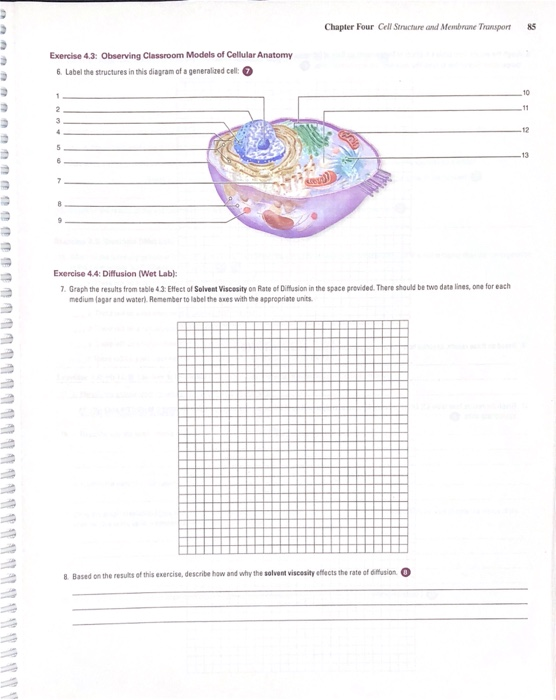
Chapter 4 Cell Structure And Membrane Transport Chegg Cell theory. this theory states: all living things are made up of cells. cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. new cells are produced from existing cells. nucleus. function: the control center of the cell. membrane bound. found in plant and animal cells. A membrane separates the cell from its surroundings. every cell features a cell membrane, which is also called the plasma membrane. the plasma membrane is a complex arrangement of several different types of molecules. the chief components are phospholipids. each phospholipid molecule is an amphipathic molecule (polar at one end and non polar at. Salt. diffusion diagrams. 1. in the figure below, draw arrows to show which way the square, triangle, and small circles would move across the membrane (dotted line). 2. if the triangles move from area 1 to area 2 across a protein channel that does not require energy, what type of transport is this? 3. Step 1: the cell performs primary active transport on a molecule, setting up a concentration gradient of that molecule across the membrane. step 2: the molecule then diffuses back down its concentration gradient through a transport channel protein.
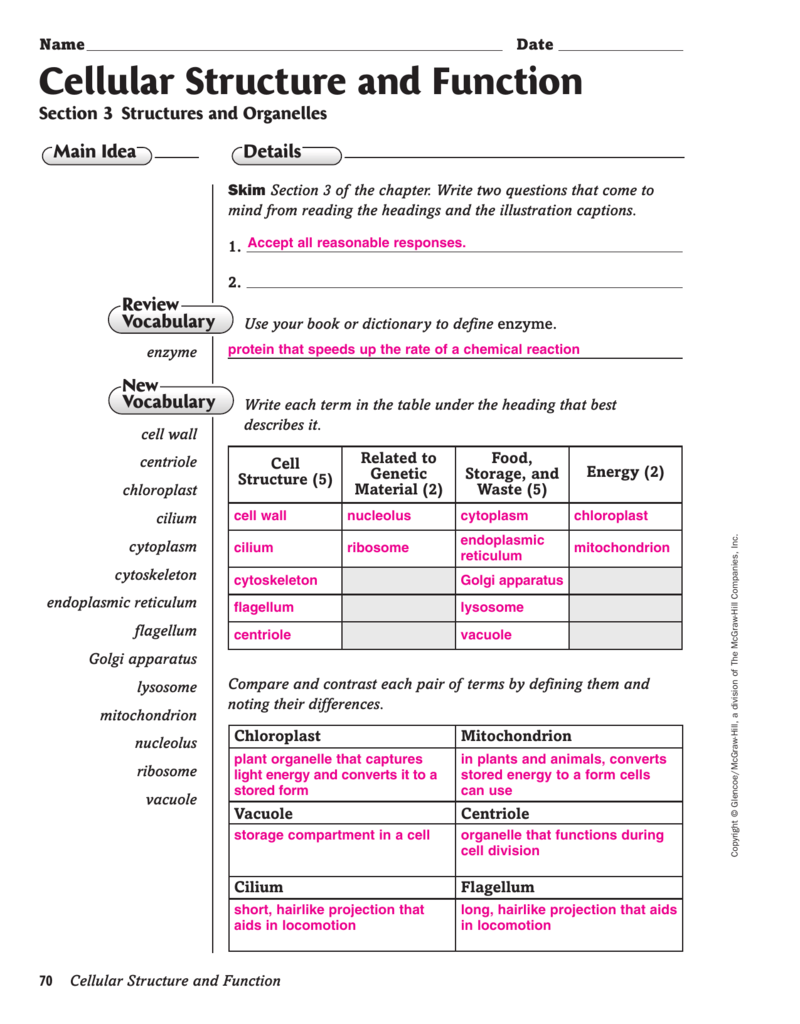
Cellular Structure And Function Salt. diffusion diagrams. 1. in the figure below, draw arrows to show which way the square, triangle, and small circles would move across the membrane (dotted line). 2. if the triangles move from area 1 to area 2 across a protein channel that does not require energy, what type of transport is this? 3. Step 1: the cell performs primary active transport on a molecule, setting up a concentration gradient of that molecule across the membrane. step 2: the molecule then diffuses back down its concentration gradient through a transport channel protein. The cell wall. if you examine figure 4.8b, the diagram of a plant cell, you will see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. fungal and protistan cells also have cell walls. Biological processes that move oxygen, water and nutrients into cells and remove waste products. active transport. uses atp to pump molecules against up the concentration gradient. low to high concentration. requires cellular energy. passive transport. movement of molecules down concentration gradient.

Comments are closed.