Unearned Income Definition Example And Taxation
Unearned Income Bookkeeping Rules Shared Economy Tax Unearned income is taxed differently than regular, or earned, income. unearned income is not subject to payroll tax, for example. however, it is included when determining adjusted gross income, or agi, which is used to calculate tax liability and eligibility for certain deductions and credits. unearned income does, therefore, contribute to an. For 2023, any unearned income above $2,500 ($2,600 for 2024) may be subject to an unearned income tax. this is known as the kiddie tax. alternatively, interest and dividend income of less than.

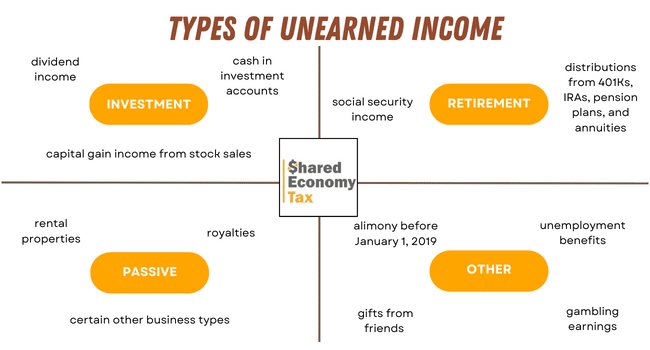
Unearned Income Definition Example And Taxation Taxes on unearned income . unearned income isn't subject to social security or medicare taxes, but it still contributes to your tax burden. it's included in the calculation of your adjusted gross income (agi), your gross income minus certain above the line deductions. Unearned income is typically reported on 1099 tax forms calculation and can come from various investment sources or government payments. here are some examples of unearned income: money earned from investments, such as interest, dividends, and capital gains. retirement account distributions and annuities. Unearned income is received from non employment sources such as investment dividends. here is how it works and how it might be taxed. Unearned income is income that isn’t made through business activities or via work. examples of unearned income include interest, inheritance, or dividends earned from investments. different tax rates are levied on unearned income when compared to earned income. unearned income can serve as supplemental income to your ordinary earned income.

Unearned Income Definition Example Top 4 Types Of Unearned Income Unearned income is received from non employment sources such as investment dividends. here is how it works and how it might be taxed. Unearned income is income that isn’t made through business activities or via work. examples of unearned income include interest, inheritance, or dividends earned from investments. different tax rates are levied on unearned income when compared to earned income. unearned income can serve as supplemental income to your ordinary earned income. Unearned income is still income, and you have to pay taxes on it. though many unearned income sources qualify for lower tax rates, others enjoy a deferred tax liability—meaning, you don’t pay taxes until later. some tax implications of unearned income include: lower tax rates than earned income: some types of unearned income are taxed at 0%. Summary: unearned income is income you get from investments and other sources that are not directly related to employment. it includes investment type income such as taxable interest, ordinary dividends, and capital gain distributions. the tax rates on unearned income are different from what you pay on earned income.

What Is Unearned Income Definition And Example Thestreet Unearned income is still income, and you have to pay taxes on it. though many unearned income sources qualify for lower tax rates, others enjoy a deferred tax liability—meaning, you don’t pay taxes until later. some tax implications of unearned income include: lower tax rates than earned income: some types of unearned income are taxed at 0%. Summary: unearned income is income you get from investments and other sources that are not directly related to employment. it includes investment type income such as taxable interest, ordinary dividends, and capital gain distributions. the tax rates on unearned income are different from what you pay on earned income.

Comments are closed.