Understanding The Laws Of Logarithms Ft The Math Sorcerer

Understanding The Laws Of Logarithms Ft The Math Sorcerer Youtube We'll take a look at some example problems that utilize the laws of logarithms and require you @themathsorcerer covers the laws of logarithms in this video. we'll take a look at some example. The math sorcerer walks us through an introduction to logarithmic functions and their graphs. we'll learn how to sketch the graph of a logarithmic function,.

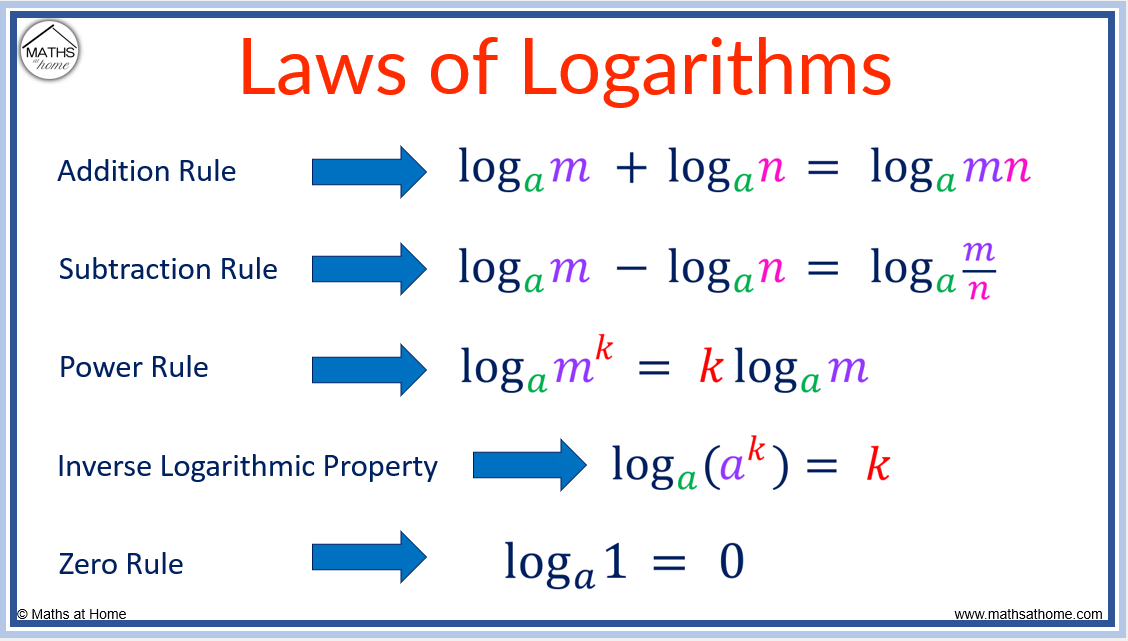
How To Graph Logarithmic Functions Ft The Math Sorcerer Youtube Math videos and all things math related. i also make videos on other things too:)bid on my math books here: ebay str themathsorcerer check ou. The logarithm of the ratio of two quantities is the logarithm of the numerator minus the logarithm of the denominator. the logarithm of an exponential number is the exponent times the logarithm of the base. the logarithm of the argument (inside the parenthesis) wherein the argument equals the base is equal to . for for b> 0 b>0. What are the laws of logarithms? the laws of logarithms are algebraic rules that allow for the simplification and rearrangement of logarithmic expressions. the 3 main logarithm laws are: the product law: log(mn) = log(m) log(n). the quotient law: log(m n) = log(m) – log(n). the power law: log(m k) = k·log(m). the three fundamental laws of. Using laws of logarithms (laws of logs) to solve log problems. the general log rule to convert log functions to exponential functions and vice versa. we know already the general rule that allows us to move back and forth between the logarithm and exponents. and we can continue to use this rule whenever it makes sense in any of these log problems.

How To Calculate Inverse Functions And Logarithms Ft The Math Sorcerer What are the laws of logarithms? the laws of logarithms are algebraic rules that allow for the simplification and rearrangement of logarithmic expressions. the 3 main logarithm laws are: the product law: log(mn) = log(m) log(n). the quotient law: log(m n) = log(m) – log(n). the power law: log(m k) = k·log(m). the three fundamental laws of. Using laws of logarithms (laws of logs) to solve log problems. the general log rule to convert log functions to exponential functions and vice versa. we know already the general rule that allows us to move back and forth between the logarithm and exponents. and we can continue to use this rule whenever it makes sense in any of these log problems. So please remember the laws of logarithms and the change of the base of logarithms. example 12: find the value of. example 13: simplify. solving equation involving indices and logarithms. a) method 1: expressing the equation to same base and compare the indices. b) method 2: expressing the equation to same indices and compare the base. Algebra 2 12 units · 113 skills. unit 1 polynomial arithmetic. unit 2 complex numbers. unit 3 polynomial factorization. unit 4 polynomial division. unit 5 polynomial graphs. unit 6 rational exponents and radicals. unit 7 exponential models. unit 8 logarithms.
Logarithm Laws Made Easy A Complete Guide With Examples Mathsathome So please remember the laws of logarithms and the change of the base of logarithms. example 12: find the value of. example 13: simplify. solving equation involving indices and logarithms. a) method 1: expressing the equation to same base and compare the indices. b) method 2: expressing the equation to same indices and compare the base. Algebra 2 12 units · 113 skills. unit 1 polynomial arithmetic. unit 2 complex numbers. unit 3 polynomial factorization. unit 4 polynomial division. unit 5 polynomial graphs. unit 6 rational exponents and radicals. unit 7 exponential models. unit 8 logarithms.

Comments are closed.