Types Of Plant Tissues And Their Functions
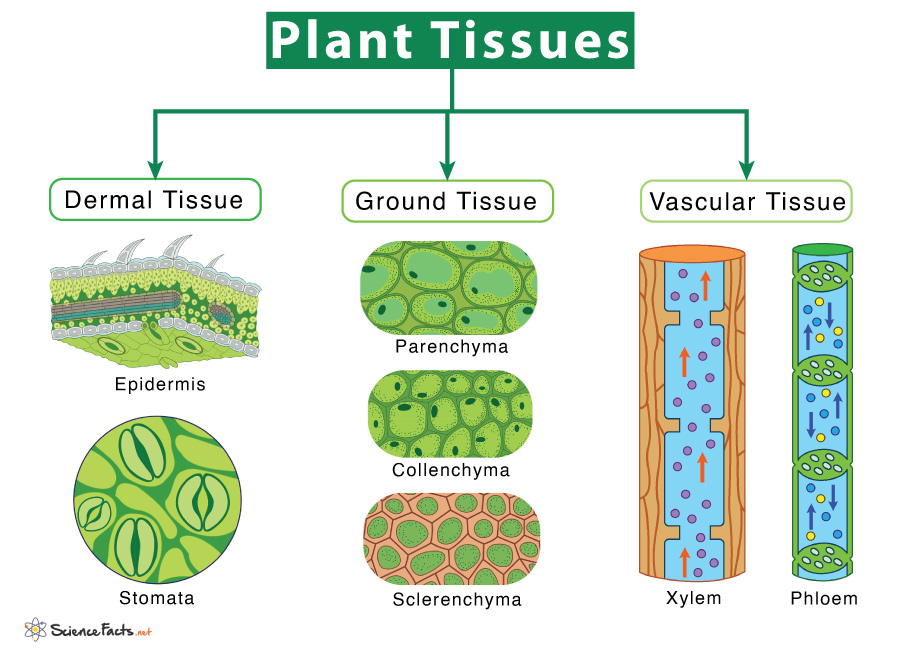
Plant Tissues Types Functions Plant tissue definition. plant tissue is a collection of similar cells performing an organized function for the plant. each plant tissue is specialized for a unique purpose, and can be combined with other tissues to create organs such as leaves, flowers, stems and roots. the following is a brief outline of plant tissues, and their functions. Protective tissues. these provide fortification to the plant. they include the cork and epidermis. epidermis – it is a layer of cell that makes up an outer casing of all the structures in the plant. the stomata perforates the epidermis at certain places. the stomata help in loss of water and gaseous exchange.
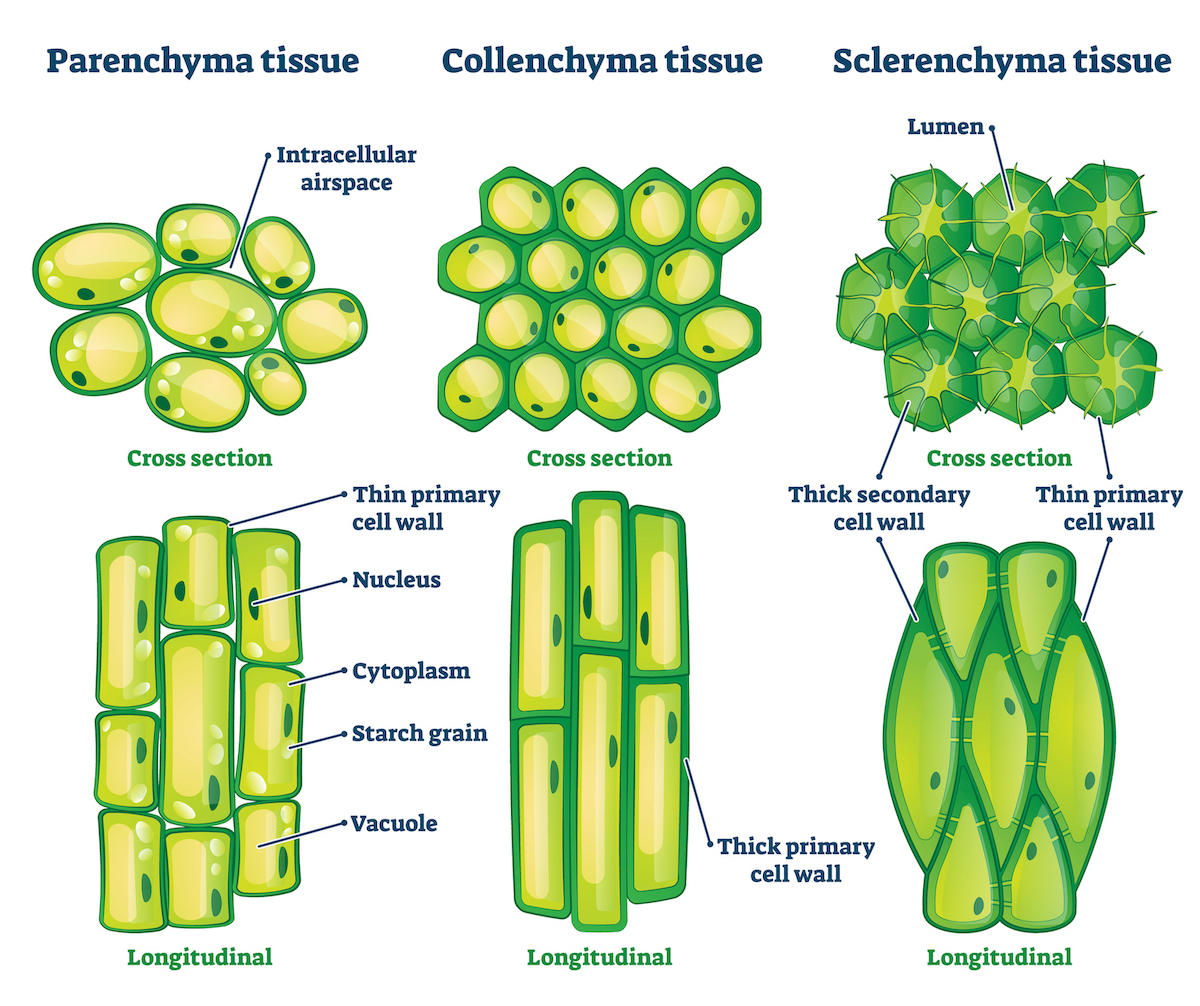
6 1 Plant Cells And Tissues The Science Of Plants The periderm functions as the plant’s first line of defense, protecting it from injury, dehydration, fire, and pathogens. 2. ground tissue. ground tissue comprises much of the interior of a plant and helps in metabolism, storage, and support. depending on location and function, ground tissues are made of three cell types: a. Plants are multicellular eukaryotes with tissue systems made of various cell types that carry out specific functions. plant tissues are composed of cells that are similar and perform a specific function. together, tissue types combine to form organs. each organ itself is also specific for a particular function. Plant tissues are either simple (composed of similar cell types) or complex (composed of different cell types). dermal tissue, for example, is a simple tissue that covers the outer surface of the plant and controls gas exchange. vascular tissue is an example of a complex tissue. it is made of two specialized conducting tissues: xylem and phloem. All animals are made of four types of tissue: epidermal, muscle, nerve, and connective tissues. plants, too, are built of tissues, but not surprisingly, their very different lifestyles derive from different kinds of tissues. all three types of plant cells are found in most plant tissues. three major types of plant tissues are dermal, ground.
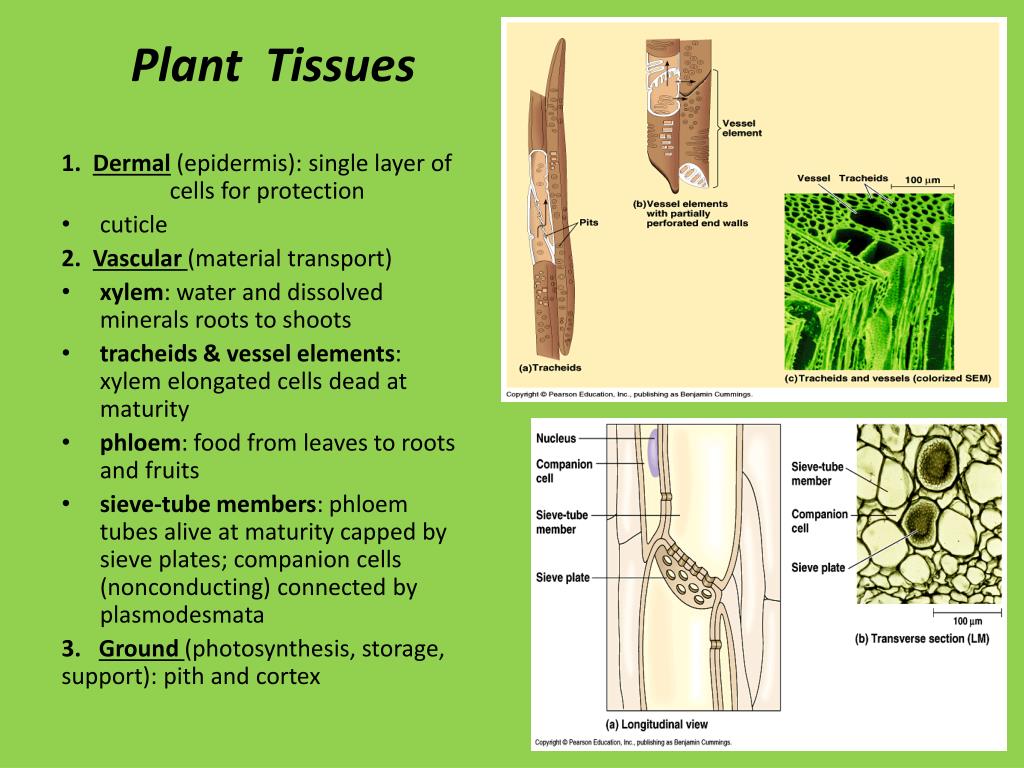
Types Of Plant Tissues And Their Functions Plant tissues are either simple (composed of similar cell types) or complex (composed of different cell types). dermal tissue, for example, is a simple tissue that covers the outer surface of the plant and controls gas exchange. vascular tissue is an example of a complex tissue. it is made of two specialized conducting tissues: xylem and phloem. All animals are made of four types of tissue: epidermal, muscle, nerve, and connective tissues. plants, too, are built of tissues, but not surprisingly, their very different lifestyles derive from different kinds of tissues. all three types of plant cells are found in most plant tissues. three major types of plant tissues are dermal, ground. 6.1 plant cells and tissues. learning objectives. by the end of this lesson you will be able to: label the parts of a plant cell. list the types of tissues in a plant and describe where they are located and the specialized cells that make up each of these tissues. summarize the key functions of those tissues. A good example of this is the three basic tissue patterns found in roots and stems which serve to delineate between woody dicot, herbaceous dicot and monocot plants. we will look at these classifications later on in the fruits flowers and seeds tutorial. different plant tissues: (1) pith, (2) protoxylem, (3) xylem, (4) phloem, (5) sclerenchyma.

Comments are closed.