Tuckman Theory Psychology Of Teams
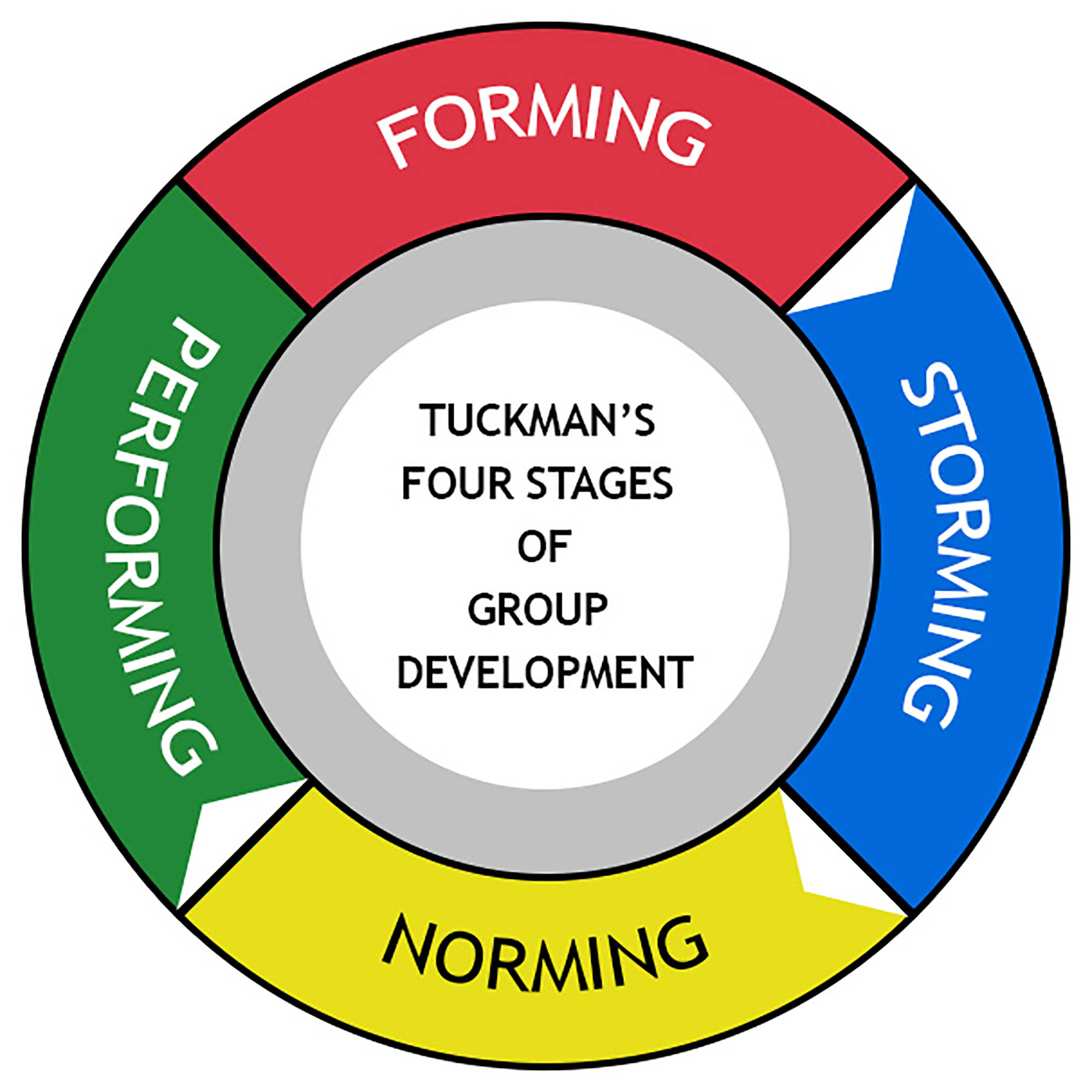
Tuckman Theory Psychology Of Teams Psychologist bruce tuckman described how teams move through stages known as forming, storming, norming, and performing, and adjourning (or mourning). you can use tuckman's model to help your team to perform better. first, identify the stage your team is at, then use our tips to move them through the stages. remember, teams can slip back a stage. Project managers can apply tuckman’s model by adjusting their leadership approach based on the team’s stage. for example: in the forming stage, the project manager provides more structure and clear direction. during storming, the focus shifts to conflict resolution. in norming, the project manager reinforces collaboration and teamwork.

From Forming To Performing Understanding Tuckman S Model Of Team The group development stages (tuckman model), also known as tuckman’s stages of group development, is a theory proposed by bruce tuckman in 1965. this model outlines the various stages that groups go through as they develop and mature. the stages include forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. Scales. administration. these stages are commonly known as: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. tuckman's model explains that as the team develops maturity and ability, relationships establish, and leadership style changes to more collaborative or shared leadership. tuckman's original work simply described the way he had. Forming. storming. norming. performing. adjourning. initially, relationships and trust are built from scratch during what is known as the forming phase. this stage is followed by the emergence of friction and conflict within the team, leading to a turbulent storming phase. once these initial conflicts are resolved and team members learn how to. Tuckman's stages of group development. the forming–storming–norming–performing model of group development was first proposed by bruce tuckman in 1965, [1] who said that these phases are all necessary and inevitable in order for a team to grow, face up to challenges, tackle problems, find solutions, plan work, and deliver results.
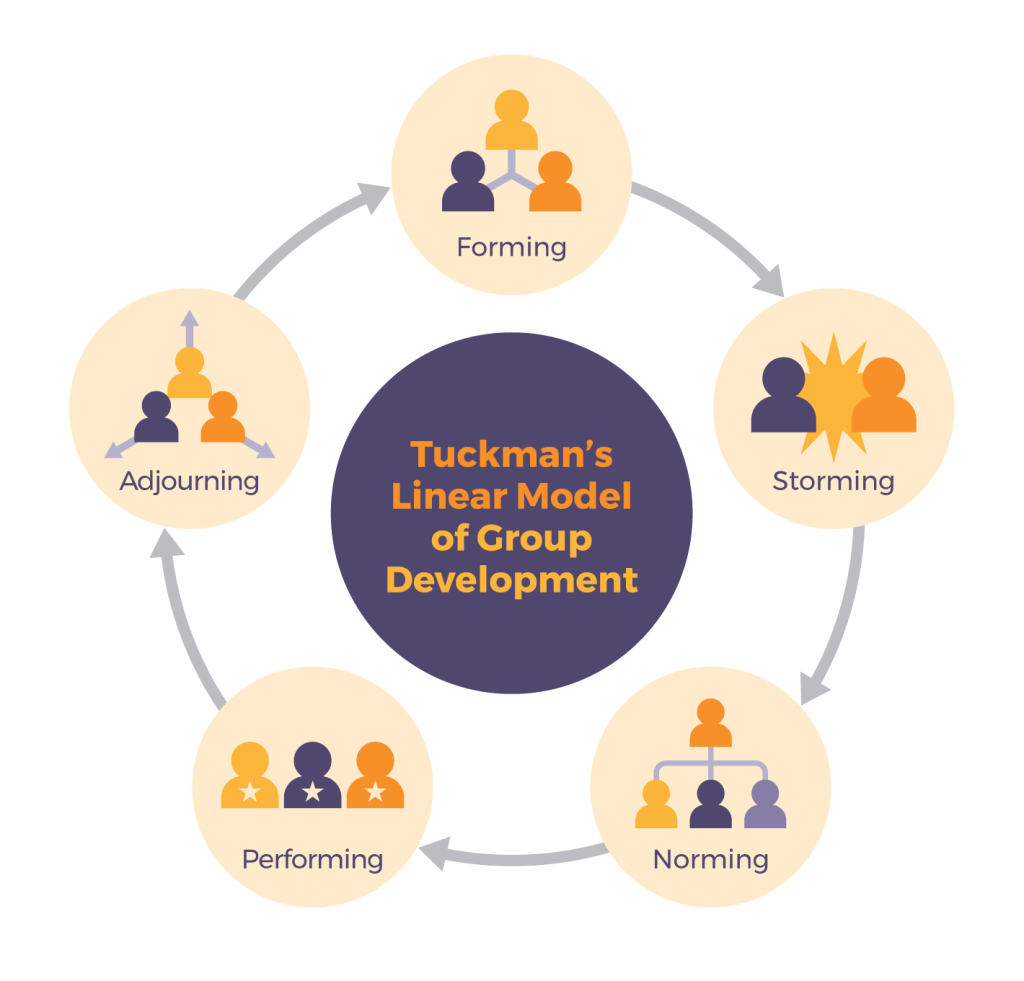
4 6 In Depth Look Tuckman S Model Five Stages Of Team Development Forming. storming. norming. performing. adjourning. initially, relationships and trust are built from scratch during what is known as the forming phase. this stage is followed by the emergence of friction and conflict within the team, leading to a turbulent storming phase. once these initial conflicts are resolved and team members learn how to. Tuckman's stages of group development. the forming–storming–norming–performing model of group development was first proposed by bruce tuckman in 1965, [1] who said that these phases are all necessary and inevitable in order for a team to grow, face up to challenges, tackle problems, find solutions, plan work, and deliver results. Tuckman’s stages of team development. the first four stages of team growth were initially developed by bruce wayne tuckman and published in 1965. his theory titled ‘tuckman’s stages’ was based on research conducted on team dynamics. he believed (as is still a common belief today) these stages were an inevitable part of the process if a. On the other hand, there's a sense of sadness and loss. team members, who've spent considerable time together, now prepare to part ways. the team, much like a group of graduating students, disbands, with each member moving on to new projects or roles. for managers, the 'adjourning' stage requires sensitivity and understanding.

Tuckman Team Development Model Agile Coach Journal Tuckman’s stages of team development. the first four stages of team growth were initially developed by bruce wayne tuckman and published in 1965. his theory titled ‘tuckman’s stages’ was based on research conducted on team dynamics. he believed (as is still a common belief today) these stages were an inevitable part of the process if a. On the other hand, there's a sense of sadness and loss. team members, who've spent considerable time together, now prepare to part ways. the team, much like a group of graduating students, disbands, with each member moving on to new projects or roles. for managers, the 'adjourning' stage requires sensitivity and understanding.

Comments are closed.