Trig Sections 1 1 Angles And Their Measures X Y Angles And Their
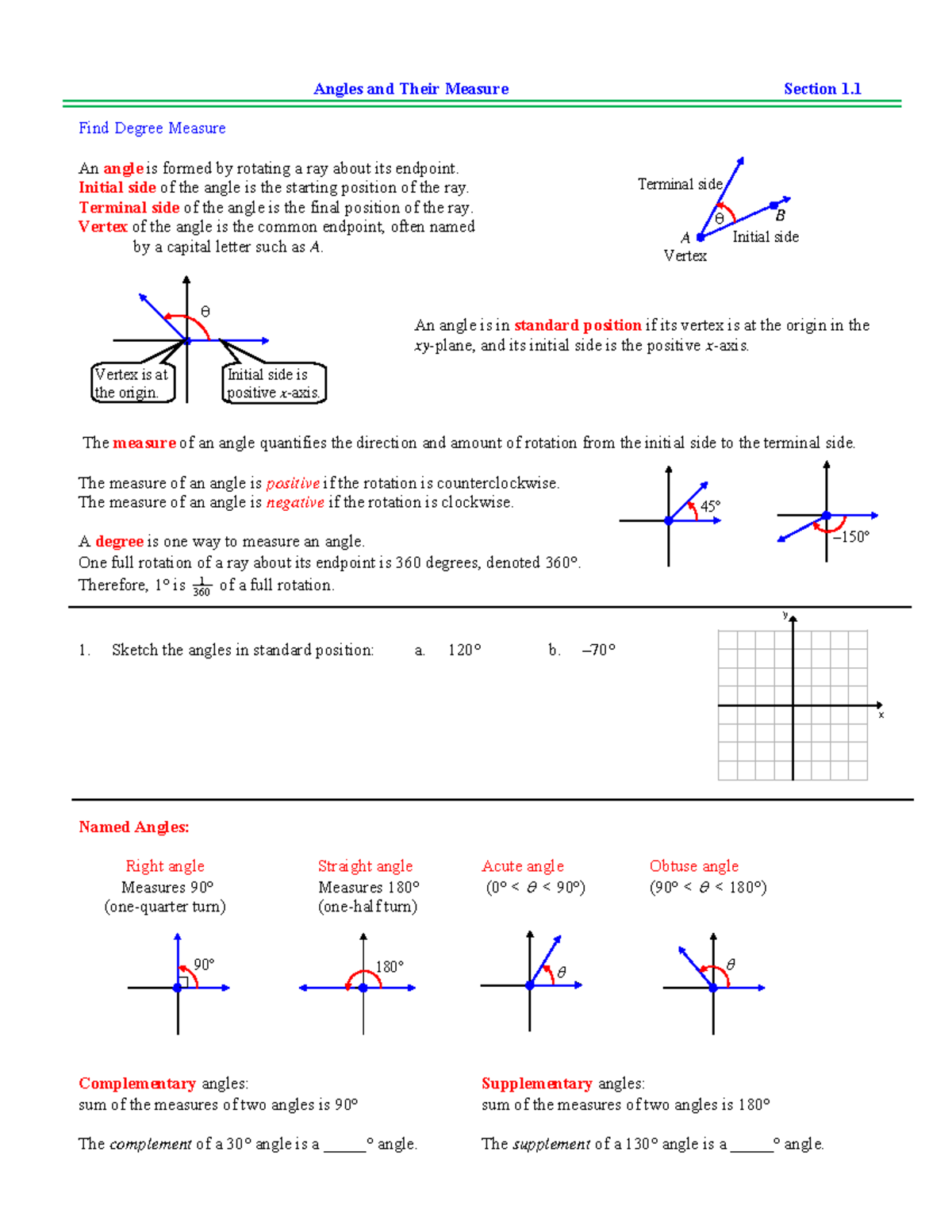
Trig Sections 1 1 Angles And Their Measures X Y Angles And Their An angle obtained by one complete counterclockwise revolution has a measure of 360 degrees, written 360 . an angle of measure x degree refers to x 360 complete counterclockwise revolutions. a negative value of x refers to an angle obtained by aclockwise revolution. short notation: = 60 refers to an angle whose measure is 60 . we also refer to. 1 radian=180 π degrees. converting degrees to radians. 1 degree=π 180 radian. 1 revolution. 2π radians. 180°. π radians. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like arc length, area of a sector, linear speed and more.
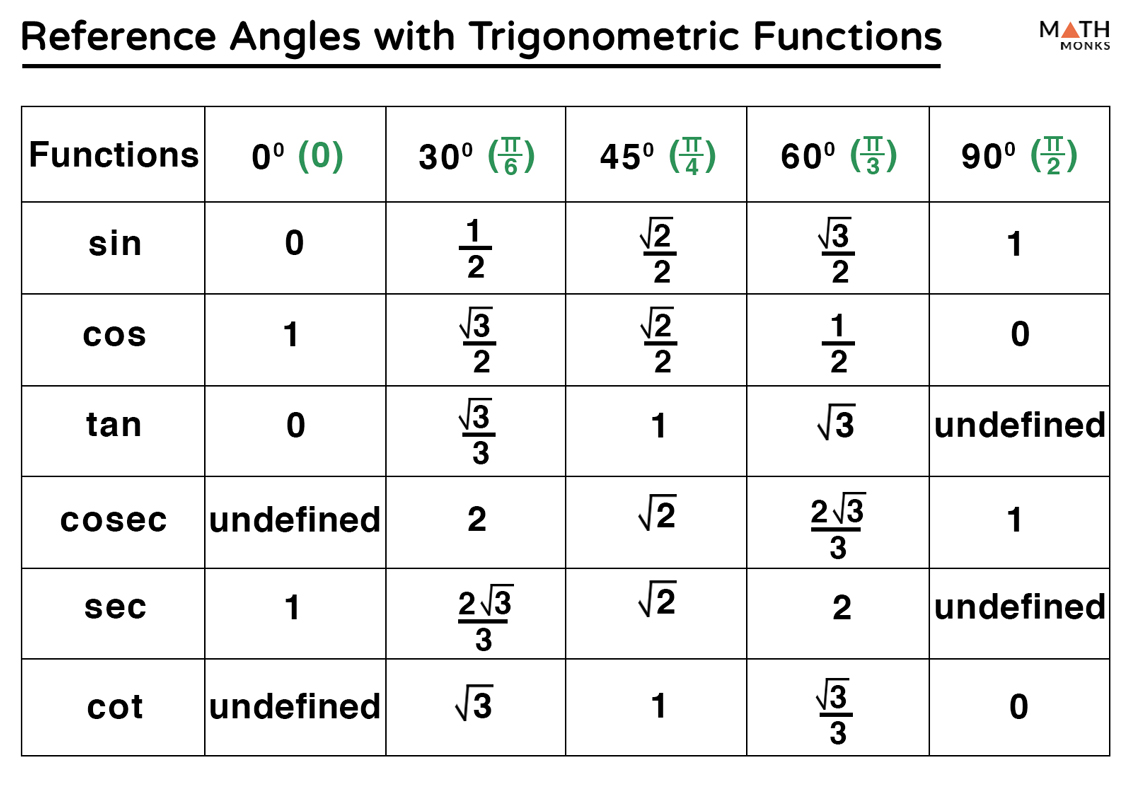
Trig Reference Angle Chart X. y. angles and their measure section 1. find degree measure. an angle is formed by rotating a ray about its endpoint. initial side of the angle is the starting position of the ray. terminal side of the angle is the final position of the ray. vertex of the angle is the common endpoint, often named by a capital letter such as a. The numbers involved are, admittedly, much more complicated than degree measure. the answer lies in how easily angles in radian measure can be identified with real numbers. consider the unit circle, \(x^2 y^2 = 1\), as drawn below, the angle \(\theta\) in standard position and the corresponding arc measuring \(s\) units in length. Trigonometry reviewt. jesuit high school math department. table of contents. subject. page. worksheet. 1.1 angles and their measure 1.2 angles and their measure – degrees 1.3 angles and their measure – radians 1.4 angles and their measure – arc length 1.5 angles and their measure – sector area 2.1 unit circle approach 2.2 familiar. Example 1. draw each of the following angles in standard position: a. 45° b. 225° c. 90° d. 270° e. − 135 ° f. 405°. we refer to angles with the same initial and terminal sides, like examples a. and f., as coterminal angles. an angle of x ° is coterminal with angles of x ° k ⋅ 360 ° where k is an integer. example 2.

Trig 1 1 Angles Youtube Trigonometry reviewt. jesuit high school math department. table of contents. subject. page. worksheet. 1.1 angles and their measure 1.2 angles and their measure – degrees 1.3 angles and their measure – radians 1.4 angles and their measure – arc length 1.5 angles and their measure – sector area 2.1 unit circle approach 2.2 familiar. Example 1. draw each of the following angles in standard position: a. 45° b. 225° c. 90° d. 270° e. − 135 ° f. 405°. we refer to angles with the same initial and terminal sides, like examples a. and f., as coterminal angles. an angle of x ° is coterminal with angles of x ° k ⋅ 360 ° where k is an integer. example 2. Historically, trigonometry began as the study of triangles and their properties. let’s review some definitions and facts from geometry. we measure angles in degrees. one full rotation is [latex]360^ {\circ} [ latex] as shown below. half a full rotation is [latex]180^ {\circ} [ latex] and is called a straight angle. 1.1 degree and radian measure of angles 1.2 right triangle trigonometry 1.3 the unit circle 1.4 the six trigonometric functions 1.5 trigonometric identities 1.6 beyond the unit circle introduction chances are good that you have some experience with geometry, which is the study of shapes and surfaces (generally in 1, 2, or 3 dimensions).
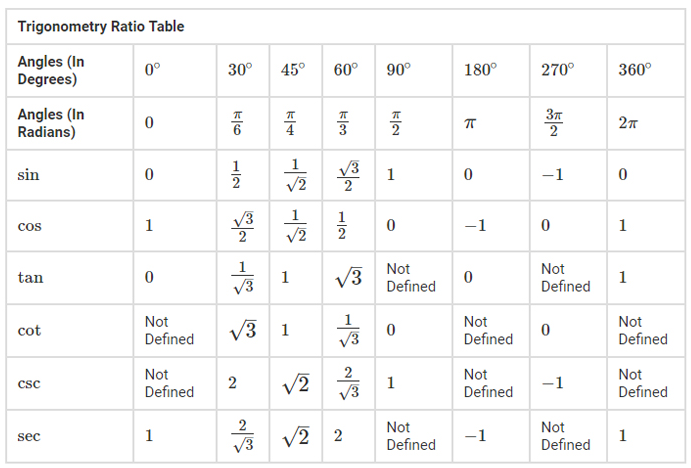
Trigonometric Table Of All Angles In Radians Historically, trigonometry began as the study of triangles and their properties. let’s review some definitions and facts from geometry. we measure angles in degrees. one full rotation is [latex]360^ {\circ} [ latex] as shown below. half a full rotation is [latex]180^ {\circ} [ latex] and is called a straight angle. 1.1 degree and radian measure of angles 1.2 right triangle trigonometry 1.3 the unit circle 1.4 the six trigonometric functions 1.5 trigonometric identities 1.6 beyond the unit circle introduction chances are good that you have some experience with geometry, which is the study of shapes and surfaces (generally in 1, 2, or 3 dimensions).

How To Remember The Trigonometric Table 5 Steps With Pictures

Comments are closed.