Trapezius Muscle Diagram
/GettyImages-147219941-56a05efe3df78cafdaa14c5f.jpg)
Trapezius Muscle Anatomy Function Pain Causes The trapezius muscle is a large, triangular, paired muscle located on the posterior aspect of the neck and thorax. when viewed together, this pair forms a diamond or trapezoid shape, hence its name. the trapezius has many attachment points, extending from the skull and vertebral column to the shoulder girdle. The trapezius muscle is a large muscle in your back. it starts at the back of your head and neck, extends across your shoulders, and down the middle of your back, forming a trapezoid. also known as traps, the trapezius muscles play an important role in posture. they move the shoulders, lift arms out to the side, and protect the neck and spine.
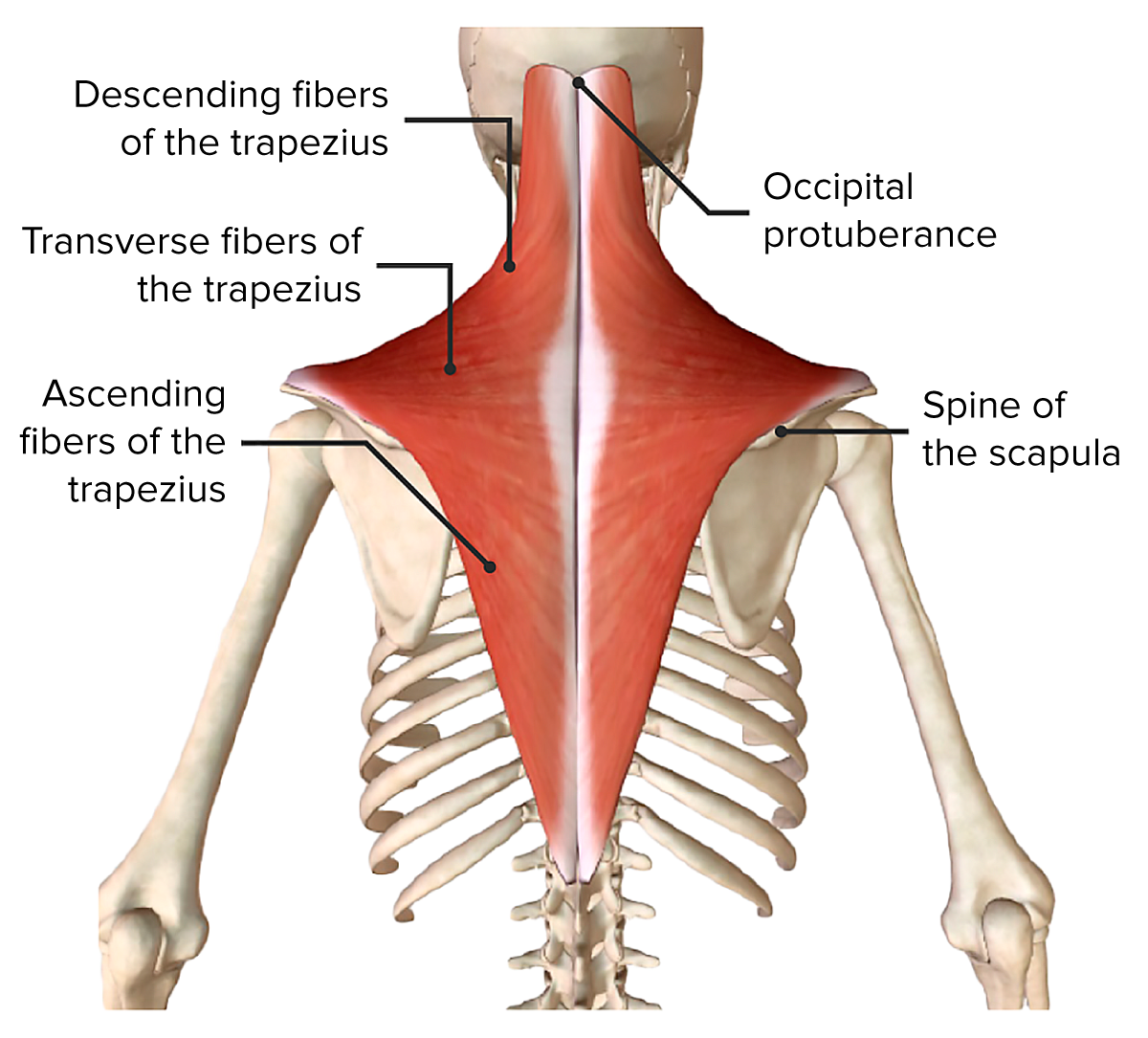
Trapezius Muscle Diagram The trapezius is an extrinsic muscle of the shoulder. it is a broad, flat and triangular shape – forming a trapezoid shape in combination with the contralateral side. attachments: originates from the skull, nuchal ligament and the spinous processes of c7 t12. the fibres attach to the clavicle, acromion, and the scapula spine. Like the rest of your back muscles, your trapezius muscles support your body and help you move. your traps help you do many motions, including: tilting your head up and down. turning your head to either side. maintaining and adjusting your posture (including standing up straight or bending your upper back forward). twisting your torso. Origin. the trapezius muscle has a broad origin from the superior nuchal line (on the occipital bone) and the external occipital protuberance to the spinous processes of the 7th cervical and all the thoracic vertebrae. a part of the superior fibers arises from the nuchal ligament, which extends over the 1st to 7th cervical vertebrae. This muscle is named for its trapezoid shape. the trapezius muscle is a postural and active movement muscle, used to tilt and turn the head and neck, shrug, steady the shoulders, and twist the.
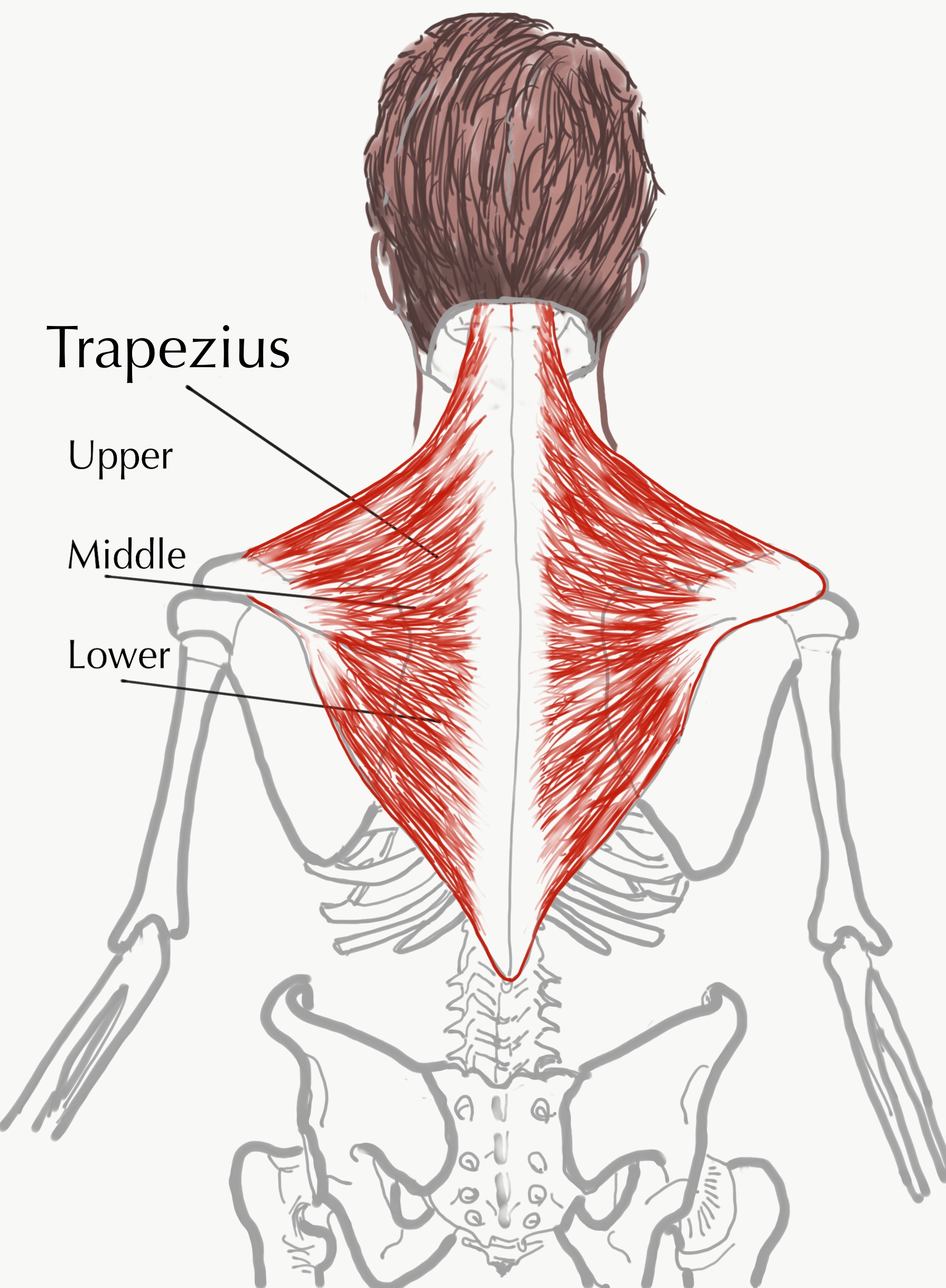
Trapezius The Bodywork Institute Origin. the trapezius muscle has a broad origin from the superior nuchal line (on the occipital bone) and the external occipital protuberance to the spinous processes of the 7th cervical and all the thoracic vertebrae. a part of the superior fibers arises from the nuchal ligament, which extends over the 1st to 7th cervical vertebrae. This muscle is named for its trapezoid shape. the trapezius muscle is a postural and active movement muscle, used to tilt and turn the head and neck, shrug, steady the shoulders, and twist the. Explore the anatomy, function, and role of the trapezius muscle with innerbody's interactive 3d model. the trapezius is one of the major muscles of the back and is responsible for moving, rotating, and stabilizing the scapula (shoulder blade) and extending the head at the neck. it is a wide, flat, superficial muscle that covers most of the. The trapezius is a broad, flat, superficial muscle extending from the cervical to thoracic region on the posterior aspect of the neck and trunk. the human trapezius muscle has an origin that is more extensive than that of any other body muscle. [1] the muscle is divided into three parts: descending (superior), ascending (inferior), and middle [2].

The Trapezius Muscle Its Attachments And Actions Yoganatomy Explore the anatomy, function, and role of the trapezius muscle with innerbody's interactive 3d model. the trapezius is one of the major muscles of the back and is responsible for moving, rotating, and stabilizing the scapula (shoulder blade) and extending the head at the neck. it is a wide, flat, superficial muscle that covers most of the. The trapezius is a broad, flat, superficial muscle extending from the cervical to thoracic region on the posterior aspect of the neck and trunk. the human trapezius muscle has an origin that is more extensive than that of any other body muscle. [1] the muscle is divided into three parts: descending (superior), ascending (inferior), and middle [2].
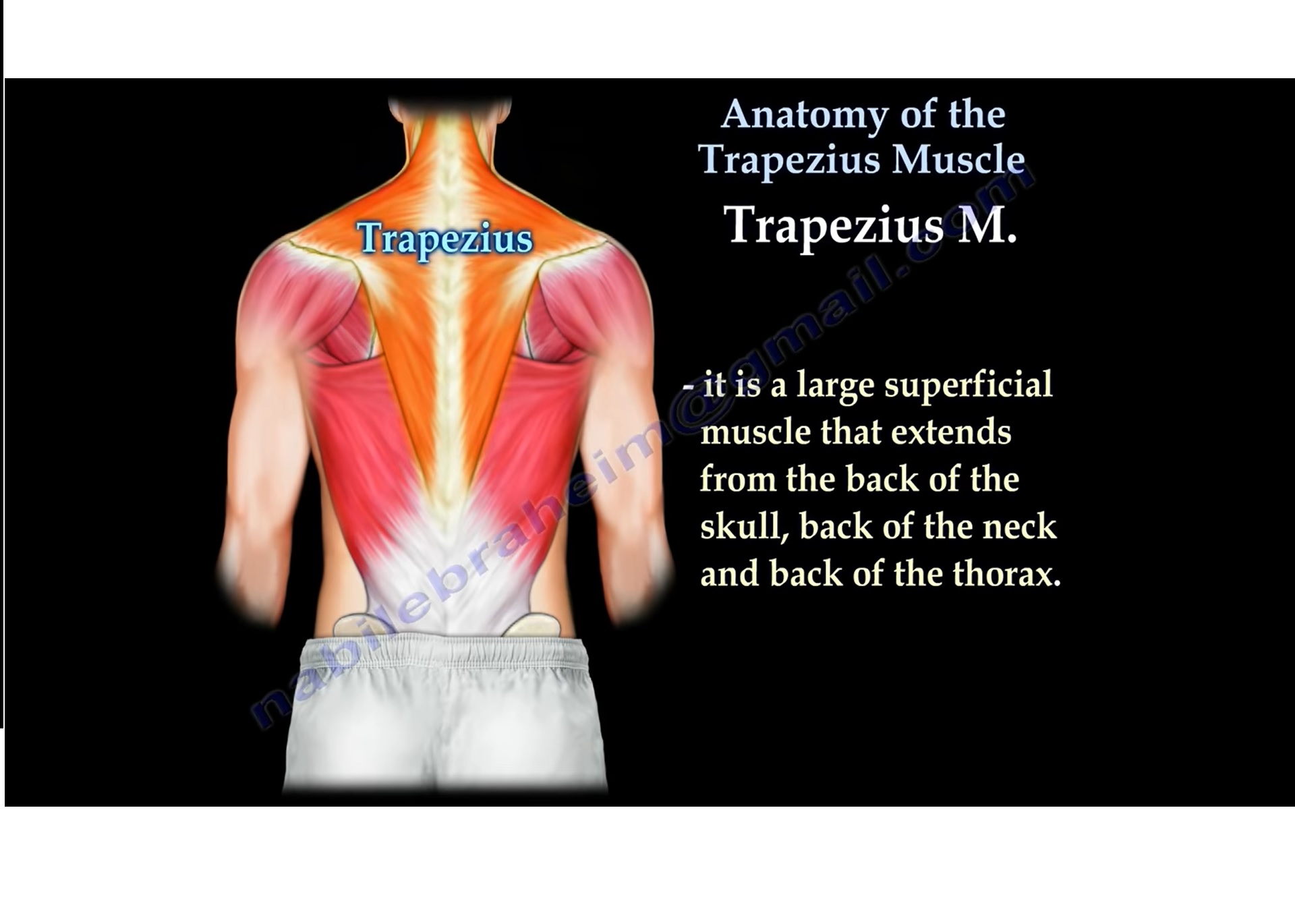
The Trapezius Muscle Orthopaedicprinciples

The Trapezius Muscle Its Attachments And Actions Yoganatomy

Comments are closed.