Transfer Processing Of Heat Energy Heat World Of Physics

Transfer Processing Of Heat Energy Heat World Of Physics Heat transfer is the movement of heat due to a temperature difference between a system and its surroundings. the energy transfer is always from higher temperature to lower temperature, due to the second law of thermodynamics. the units of heat transfer are the joule (j), calorie (cal), and kilocalorie (kcal). the unit for the rate of heat. A practical approximation for the relationship between heat transfer and temperature change is: q = mcΔt, (1.5.2) (1.5.2) q = m c Δ t, where q q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is the mass of the substance, and Δt Δ t is the change in temperature. the symbol c stands for the specific heat (also called.
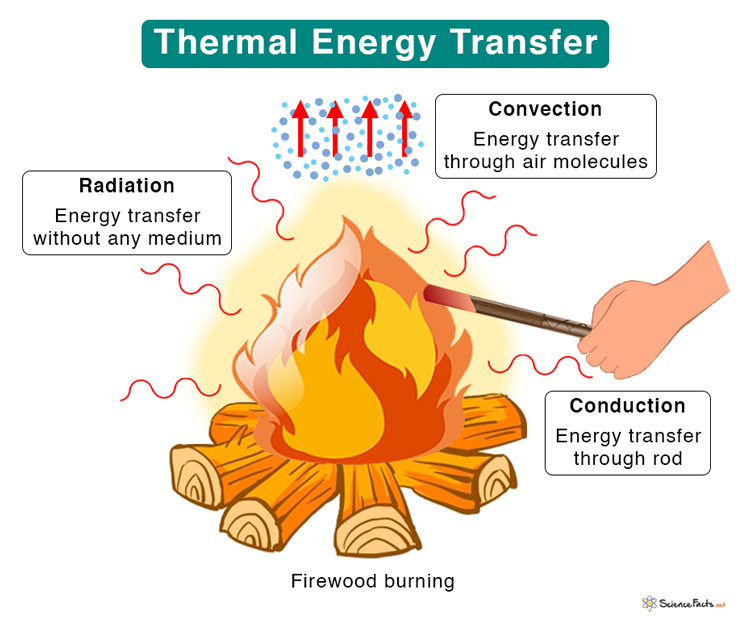
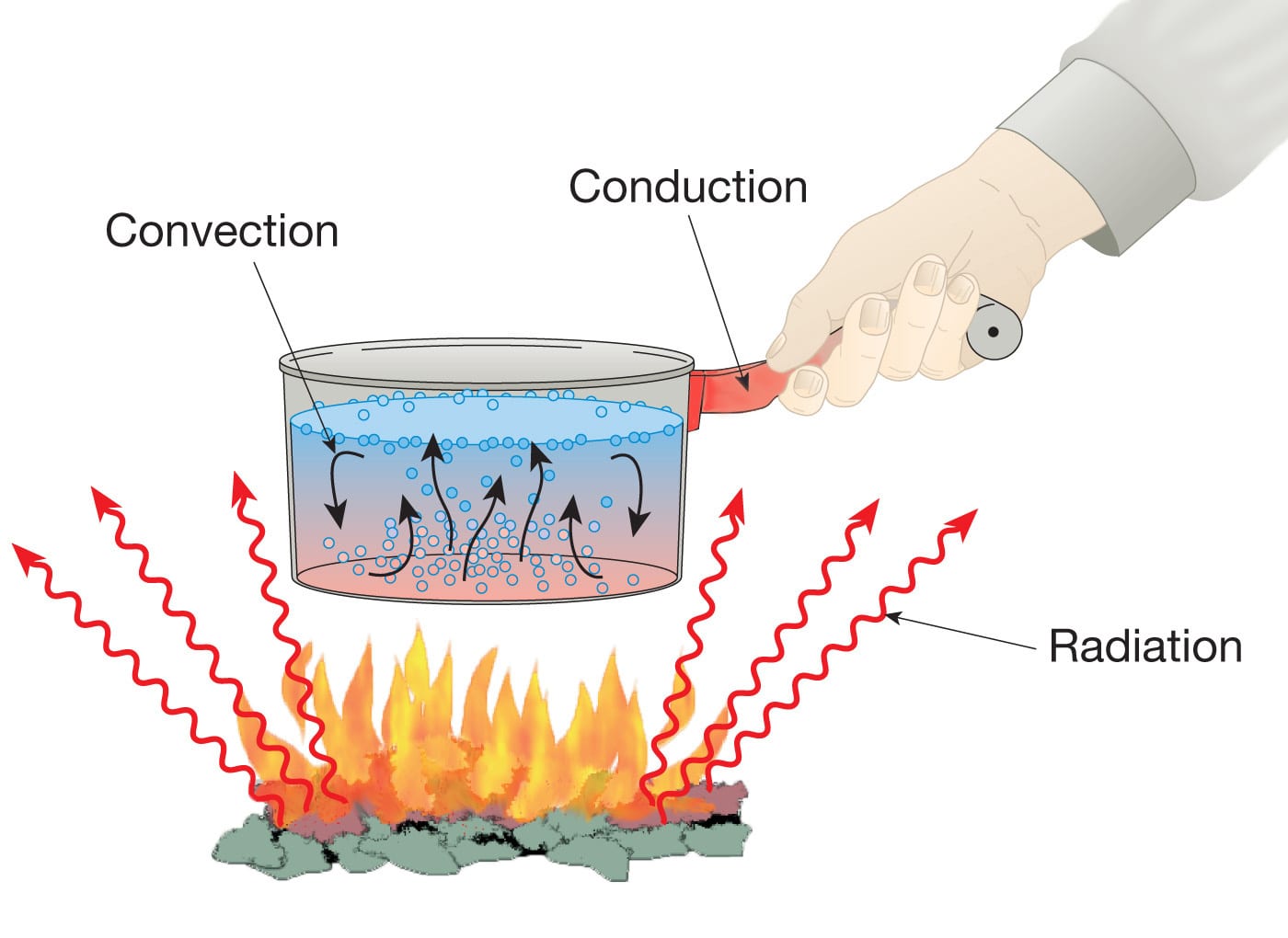
Thermal Heat Energy Definition Examples Equations And Units Figure 1.7.1: in a fireplace, heat transfer occurs by all three methods: conduction, convection, and radiation. radiation is responsible for most of the heat transferred into the room. heat transfer also occurs through conduction into the room, but much slower. Every process involving heat transfer takes place by only three methods: heat is transferred by three different methods: conduction, convection, and radiation. 14.5: conduction. heat conduction is the transfer of heat between two objects in direct contact with each other. the rate of heat transfer q t q t (energy per unit time) is. Figure 11.6 convection plays an important role in heat transfer inside this pot of water. once conducted to the inside fluid, heat transfer to other parts of the pot is mostly by convection. the hotter water expands, decreases in density, and rises to transfer heat to other regions of the water, while colder water sinks to the bottom. In conclusion, heat transfer is a fundamental concept in physics that has various practical applications in our daily lives. we covered the three main types of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation, as well as the laws and formulas that govern it. we also explored how heat transfer is used in real world scenarios, from buildings.

Heat Transfer Physics Figure 11.6 convection plays an important role in heat transfer inside this pot of water. once conducted to the inside fluid, heat transfer to other parts of the pot is mostly by convection. the hotter water expands, decreases in density, and rises to transfer heat to other regions of the water, while colder water sinks to the bottom. In conclusion, heat transfer is a fundamental concept in physics that has various practical applications in our daily lives. we covered the three main types of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation, as well as the laws and formulas that govern it. we also explored how heat transfer is used in real world scenarios, from buildings. High school physics—ngss (deprecated) course: high school physics—ngss (deprecated) > unit 4. lesson 4: thermodynamics. heat transfer. specific heat and latent heat of fusion and vaporization. specific heat capacity. understand: thermodynamics. apply: thermodynamics. Heat transfer physics: principal energy carriers • the macroscopic conduction, convection, and radiation heat transfer can be understood and analyzed using the four underlying atomic level (principal) energy carriers. • phonon (lattice vibration, cause of thermal conduction in electric insulators, and participant in.
What Is Heat Transfer Heat Flow Complete Guide Simscale High school physics—ngss (deprecated) course: high school physics—ngss (deprecated) > unit 4. lesson 4: thermodynamics. heat transfer. specific heat and latent heat of fusion and vaporization. specific heat capacity. understand: thermodynamics. apply: thermodynamics. Heat transfer physics: principal energy carriers • the macroscopic conduction, convection, and radiation heat transfer can be understood and analyzed using the four underlying atomic level (principal) energy carriers. • phonon (lattice vibration, cause of thermal conduction in electric insulators, and participant in.

Igcse Physics Thermal Energy Transfer Youtube

Comments are closed.