Torque And Equilibrium Engineering Science Physics Mechanics

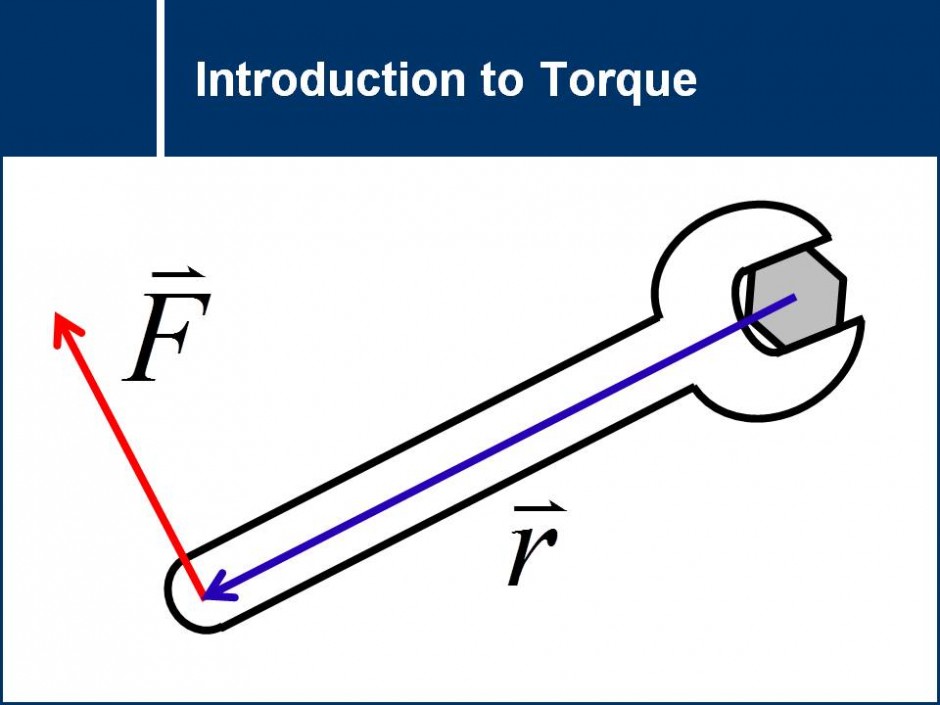
Torque And Equilibrium Physics Mechanics Engineering Science How to visualize the torque equation. a wrench produces a torque on a nut if a force is applied to it correctly (see figure 1). the equation for torque is: τ = r f sin θ. figure 1. variables of the torque equation shown for a wrench and nut. the nut’s center is the pivot point. to produce a torque, the force f must be applied at some. Torque. a torque is an influence which tends to change the rotational motion of an object. one way to quantify a torque is. torque = force applied x lever arm . the lever arm is defined as the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force. example in u.s. common units. ok, this is a ridiculously large wrench.

Torque And Equilibrium Physics Classroom Physics And Mathematics Figure 10.7.1: torque is the turning or twisting effectiveness of a force, illustrated here for door rotation on its hinges (as viewed from overhead). torque has both magnitude and direction. (a) a counterclockwise torque is produced by a force →f acting at a distance r from the hinges (the pivot point). The greatest weight correct. the person on the right is supporting the greatest weight. they are supporting the same weight. “assume r for f1(person on the left to the log) is 1 4r, then after calculation i get f1=2f2”. “the guy on the left has to support more weight because he is further in and has to support more of the board. Mechanics: newton’s three laws of motion. second law: a particle of mass “m” acted upon by an unbalanced force “f” experiences an acceleration “a” that has the same direction as the force and a magnitude that is directly proportional to the force. f = ma. second law forms the basis for most of the analysis in dynamics. 2. decompose f into components parallel and perpendicular to r, and take: t = rf. ┴. if rotation is clockwise, torque is negative, and if rotation is counterclockwise torque is positive. note: if f and r are parallel or antiparallel, the torque is 0. (e.g., can’t open a door if pushing or pulling toward the hinges).
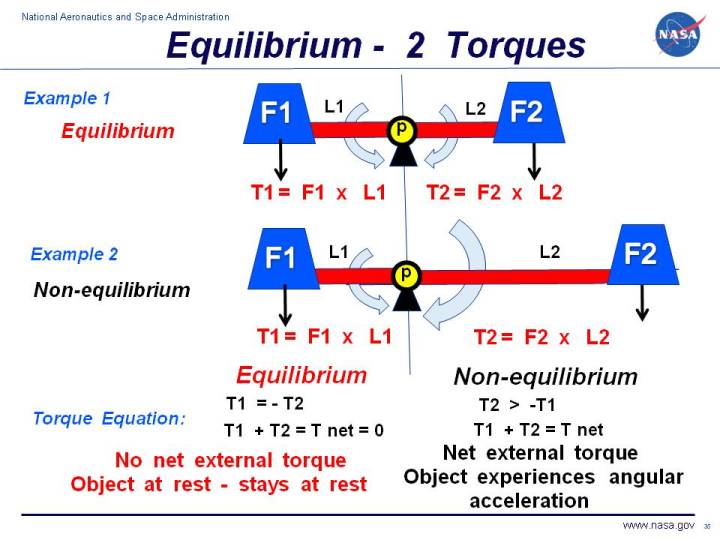
Equilibrium Of Torques Mechanics: newton’s three laws of motion. second law: a particle of mass “m” acted upon by an unbalanced force “f” experiences an acceleration “a” that has the same direction as the force and a magnitude that is directly proportional to the force. f = ma. second law forms the basis for most of the analysis in dynamics. 2. decompose f into components parallel and perpendicular to r, and take: t = rf. ┴. if rotation is clockwise, torque is negative, and if rotation is counterclockwise torque is positive. note: if f and r are parallel or antiparallel, the torque is 0. (e.g., can’t open a door if pushing or pulling toward the hinges). Understanding torque in classical mechanics. torque, a fundamental concept in classical mechanics, plays a pivotal role in explaining how forces cause rotational motion. also known as the moment of force, torque provides a deeper understanding of the principles behind the turning effect of forces on objects. principles of torque. torque is the. Introduction to engineering mechanics: statics, for those who love to learn. concepts include: particles and rigid body equilibrium equations, distributed loads, shear and moment diagrams, trusses, method of joints and sections, & inertia. about the contributors authors. elizabeth (libby) osgood, university of prince edward island.
Torque And Equilibrium Mstltt Understanding torque in classical mechanics. torque, a fundamental concept in classical mechanics, plays a pivotal role in explaining how forces cause rotational motion. also known as the moment of force, torque provides a deeper understanding of the principles behind the turning effect of forces on objects. principles of torque. torque is the. Introduction to engineering mechanics: statics, for those who love to learn. concepts include: particles and rigid body equilibrium equations, distributed loads, shear and moment diagrams, trusses, method of joints and sections, & inertia. about the contributors authors. elizabeth (libby) osgood, university of prince edward island.

Comments are closed.