Tissues Part 4 Nervous Tissue

Types Of Tissue Part 4 Nervous Tissue Youtube Tissue – an organized group of cells that carries out a certain function. nervous system – the organ system responsible for controlling and coordinating body movements and functions. action potential – a sudden rise and fall in the electrical membrane potential of a neuron that leads to a signal being transmitted to other neurons or the. Nervous tissue is characterized as being excitable and capable of sending and receiving electrochemical signals that provide the body with information. two main classes of cells make up nervous tissue: the neuron and neuroglia (figure 4.5.1 the neuron). neurons propagate information via electrochemical impulses, called action potentials, which.
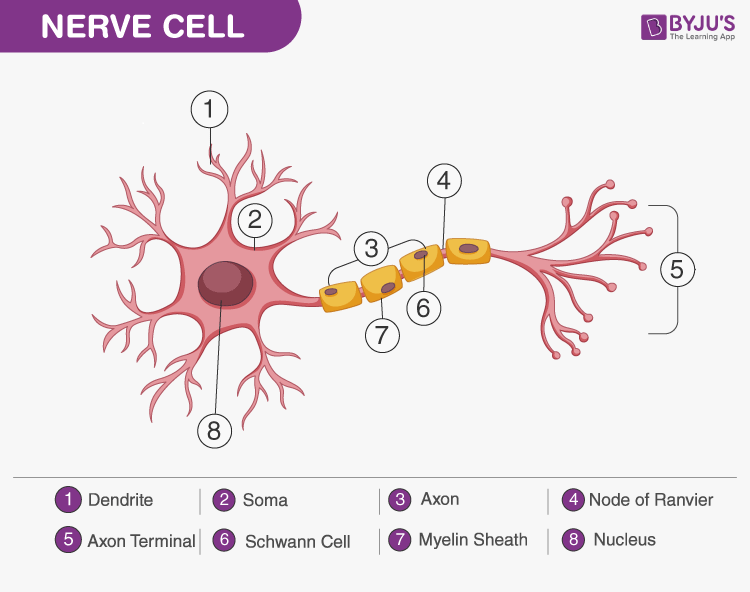
Nervous Tissue Characteristics Structure Function It monitors and regulates the functions of the body. nervous tissue consists of two cells: nerve cells or neurons and glial cells, which helps transmit nerve impulses and also provides nutrients to neurons. brain, spinal cord, and nerves are composed of nervous tissue, they are specialized for being stimulated to transmit stimulus from one to. Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and supporting cells called neuroglia, or ” glial cells.”. there are six types of neuroglia. four are found in the central nervous system, while two are found in the peripheral nervous system. the four types of neuroglia found in the central nervous system are astrocytes, microglial cells, ependymal. Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. neurons are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. they are electrically active and release chemical signals to communicate between each other and with target cells. glial cells, or glia or neuroglia, are much smaller than. An important part of the function of neurons is in their structure, or shape. the three dimensional shape of these cells makes the immense numbers of connections within the nervous system possible. parts of a neuron. as you learned in the first section, the main part of a neuron is the cell body, which is also known as the soma (soma = “body”).
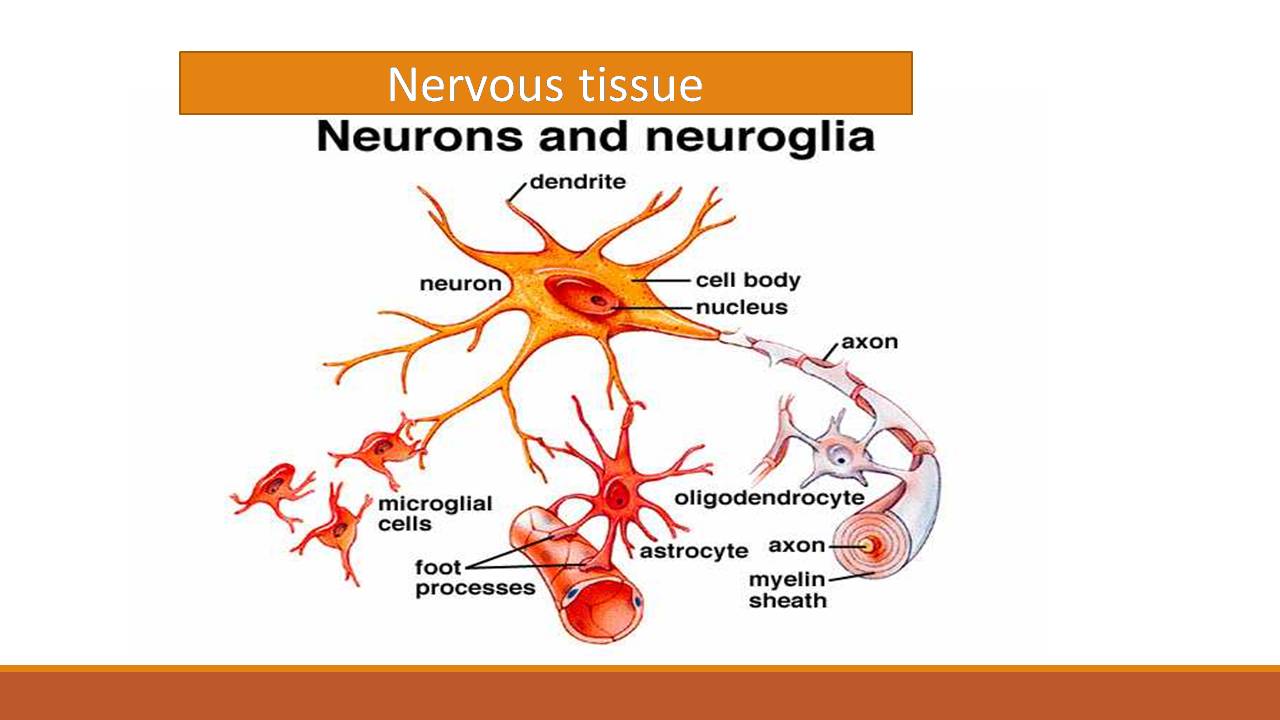
Labeled Neuron Nervous Tissue Cells Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. neurons are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. they are electrically active and release chemical signals to communicate between each other and with target cells. glial cells, or glia or neuroglia, are much smaller than. An important part of the function of neurons is in their structure, or shape. the three dimensional shape of these cells makes the immense numbers of connections within the nervous system possible. parts of a neuron. as you learned in the first section, the main part of a neuron is the cell body, which is also known as the soma (soma = “body”). The peripheral nervous system lies outside the skull and spinal canal and includes all neural tissue outside the cns. peripheral nerves carry impulses from the cns to the organs and from the organs back to the cns. peripheral nerves are composed of axons and schwann cells, which collectively form bundles of nerve fibers encased in connective. Nervous tissue is made up of different types of neurons, all of which have an axon. an axon is the long stem like part of the cell that sends action potentials to the next cell. bundles of axons make up the nerves in the pns and tracts in the cns. functions of the nervous system are sensory input, integration, control of muscles and glands.
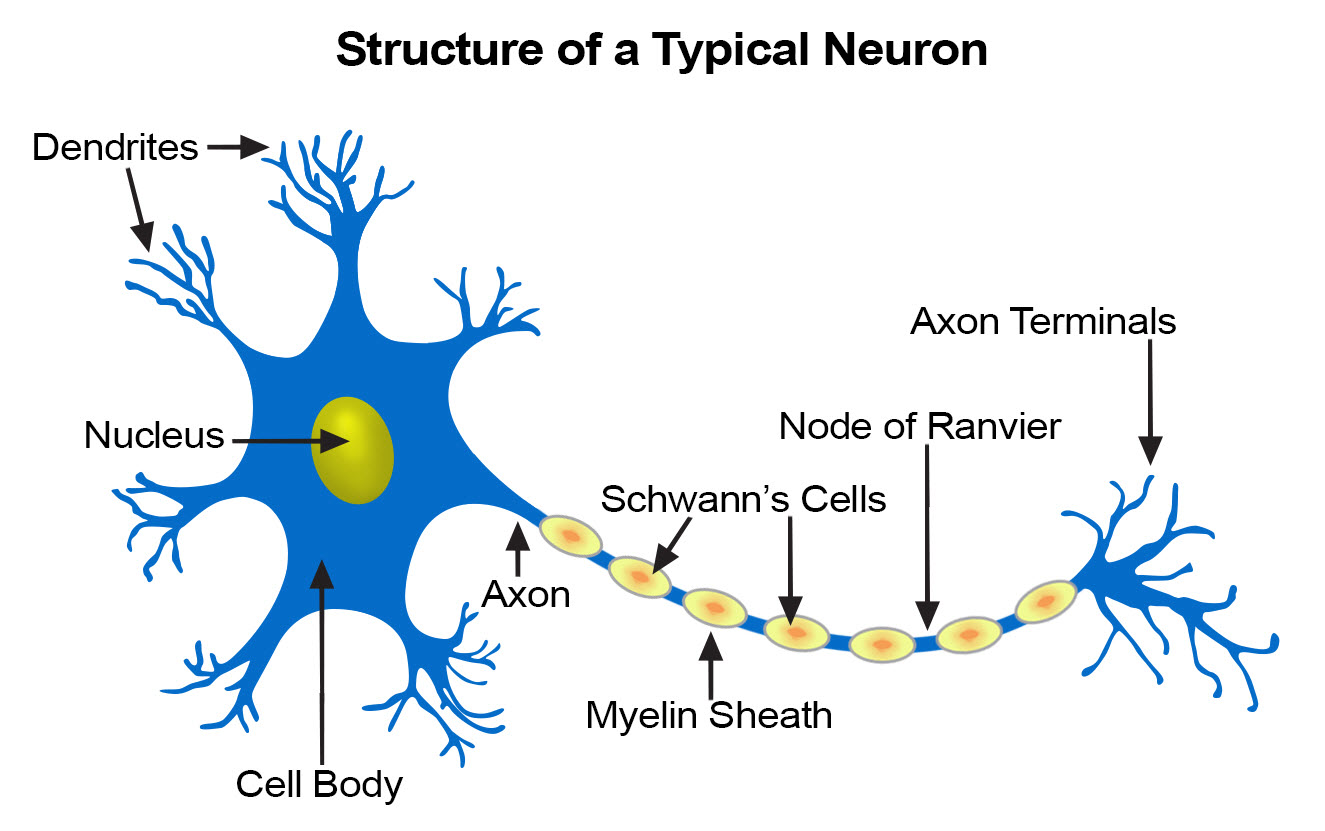
Nerve Tissue Seer Training The peripheral nervous system lies outside the skull and spinal canal and includes all neural tissue outside the cns. peripheral nerves carry impulses from the cns to the organs and from the organs back to the cns. peripheral nerves are composed of axons and schwann cells, which collectively form bundles of nerve fibers encased in connective. Nervous tissue is made up of different types of neurons, all of which have an axon. an axon is the long stem like part of the cell that sends action potentials to the next cell. bundles of axons make up the nerves in the pns and tracts in the cns. functions of the nervous system are sensory input, integration, control of muscles and glands.

Comments are closed.