Time Restricted Feeding Improves Digestion And The Microbiome

Time Restricted Feeding Improves Digestion And The Microbiome The gut microbiome can help in producing vitamins, hormones, and other active metabolites that support the immune system; harvest energy from food; aid in digestion; protect against pathogens; improve gut transit and function; send signals to the brain and other organs; oscillate the circadian rhythm; and coordinate with the host metabolism. Time restricted feeding or changes in dietary macronutrient composition could … declining health, gut dysbiosis, and cognitive impairments are hallmarks of advanced age. while caloric restriction is known to robustly extend the healthspan and alter gut microbiome composition, it is difficult maintain.

Time Restricted Feeding Improves Digestion And The Microbiome Through a 12 week isocaloric restricted feeding trial with 28 week post intervention follow up, li et al. demonstrate the efficacy of hlcd and tre in weight management beyond caloric restriction among adults with overweight or obesity. they also identify that both hlcd and tre yield profound alterations in the gut microbiome and metabolome. Individuals are encouraged to eat probiotic foods, to plant beneficial bacteria in the gut , and prebiotic foods, to feed gut bacteria [24,32]. time restricted feeding is also suggested, which involves fasting for twelve hours between dinner and breakfast, to allow the gut time to stimulate gut bacteria regrowth overnight [14,33]. Time restricted feeding ( [trf] in animals) or time restricted eating ( [tre] in humans) is a type of intermittent fasting (if) that can potentially improve metabolic health. if involves restricting caloric intake to specific hours of the day or to specific days of the week or month. Diet is a key factor influencing gut microbiota (gm) composition and functions, which in turn affect host health. among dietary regimens, time restricted (tr) feeding has been associated to.
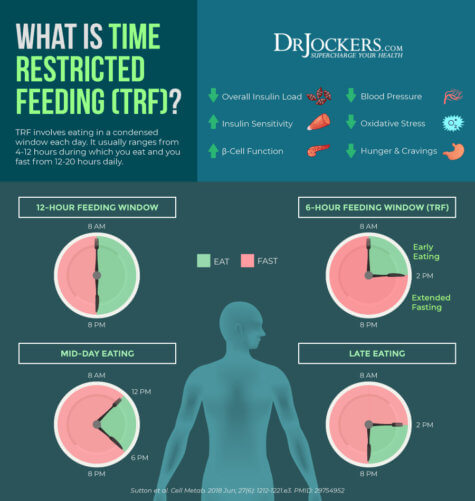
Time Restricted Feeding Improves Digestion And The Microbiome Time restricted feeding ( [trf] in animals) or time restricted eating ( [tre] in humans) is a type of intermittent fasting (if) that can potentially improve metabolic health. if involves restricting caloric intake to specific hours of the day or to specific days of the week or month. Diet is a key factor influencing gut microbiota (gm) composition and functions, which in turn affect host health. among dietary regimens, time restricted (tr) feeding has been associated to. Many functions of gastrointestinal system are time dependent. body clock works in synchrony with organs of the body and even gut microbiota . recent attention for intermittent fasting dramatically increased in majority . rodent studies indicate that the gut microbiome is highly variable, changing daily cyclical fluctuations in diversity (3,4. During trf, food is restricted for a specific period and affects the gut microbiome, as diet is the critical determinant of gut microbiota. this feeding rhythm may contribute to increases in microbiome diversity and influence the host metabolism and nutritional status of the individuals.

Time Restricted Feeding Improves Digestion And The Microbiome Youtube Many functions of gastrointestinal system are time dependent. body clock works in synchrony with organs of the body and even gut microbiota . recent attention for intermittent fasting dramatically increased in majority . rodent studies indicate that the gut microbiome is highly variable, changing daily cyclical fluctuations in diversity (3,4. During trf, food is restricted for a specific period and affects the gut microbiome, as diet is the critical determinant of gut microbiota. this feeding rhythm may contribute to increases in microbiome diversity and influence the host metabolism and nutritional status of the individuals.

Time Restricted Feeding Improves Digestion And The Microbiome

Comments are closed.