The Undeniable Link Between Early Childhood Stress And Chronic Illness Traumahealing Nervoussystem

The Undeniable Link Between Early Childhood Stress And Chronic Illness The seminal adverse childhood experiences study connected early adversity, abuse, and childhood neglect with the onset of adult illness of many kinds. i’ll b. This is not just about managing them, it is about getting to the root cause so that deep healing that is long lasting can take shape. that’s what we’ll cover in this week’s video share— the undeniable link between early childhood stress and chronic illness and the essential ingredients you need for deep healing. * * *.

The Undeniable Link Between Early Childhood Stress And Chronic Illness Background chronic and or extreme stress in early life, often referred to as early adversity, childhood trauma, or early life stress, has been associated with a wide range of adverse effects on development. however, while early life stress has been linked to negative effects on a number of neural systems, the specific mechanisms through which early life stress influences development and. The hpa axis, early life stress and psychiatric conditions. early life stress (els) due to childhood abuse and or neglect has been linked to increased risk of psychiatric illness onset and recurrence, increased disease severity and poor treatment response (pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy) (148, 149). Psychological trauma is a significant risk factor for physical and mental health development distortion. this paper presents the results of longitudinal epidemiological surveys and naturalistic observations. it also reviews the results of the most important neurobiological findings in the field of impact of early life trauma on cognitive and. Experience of early life stress (els) and trauma is highly prevalent in the general population and has a high public health impact, as it can trigger a health related risk cascade and lead to impaired homeostatic balance and elevated cacostatic load even decades later. the prolonged neuropsychobiological impact of els can, thus, be conceptualized as a common developmental risk factor for.
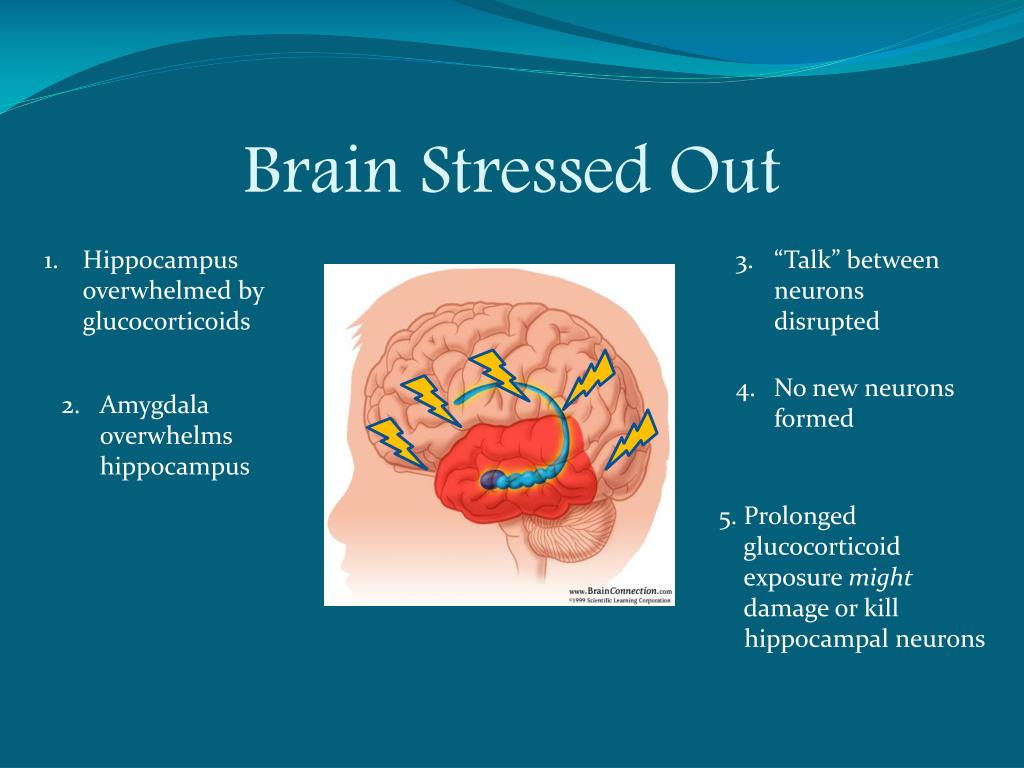
Ppt Childhood Trauma Chronic Stress Powerpoint Presentation Id Psychological trauma is a significant risk factor for physical and mental health development distortion. this paper presents the results of longitudinal epidemiological surveys and naturalistic observations. it also reviews the results of the most important neurobiological findings in the field of impact of early life trauma on cognitive and. Experience of early life stress (els) and trauma is highly prevalent in the general population and has a high public health impact, as it can trigger a health related risk cascade and lead to impaired homeostatic balance and elevated cacostatic load even decades later. the prolonged neuropsychobiological impact of els can, thus, be conceptualized as a common developmental risk factor for. Hyperarousal of the sympathetic nervous system with sustained allostatic load along the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (hpa) axis and its connections has been theorized as the basis for adult psychopathology following early childhood trauma. in this review we synthesize current understandings and hypotheses concerning the neurobiological link. The link between stress and impaired adaptive immune function has been well established using both human and animal studies; stress impairs wound healing, reduces antibody response to vaccinations, and increases susceptibility to illness such as the common cold (e.g., cohen et al., 1991; glaser et al., 2005). major cell components of the.

Figure 3 Chronic Stress And Effect On Brain Development In Childhood Hyperarousal of the sympathetic nervous system with sustained allostatic load along the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (hpa) axis and its connections has been theorized as the basis for adult psychopathology following early childhood trauma. in this review we synthesize current understandings and hypotheses concerning the neurobiological link. The link between stress and impaired adaptive immune function has been well established using both human and animal studies; stress impairs wound healing, reduces antibody response to vaccinations, and increases susceptibility to illness such as the common cold (e.g., cohen et al., 1991; glaser et al., 2005). major cell components of the.

Ppt Childhood Trauma Chronic Stress Powerpoint Presentation Id

Stress And Early Brain Growth Infograph

Comments are closed.