The Sensory Motor Pathway

Sensory Nervous System Organs And Functions Other cranial nerves contain both sensory and motor axons, including the trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves (however, the vagus nerve is not associated with the somatic nervous system). the general senses of somatosensation for the face travel through the trigeminal system. sensory pathways. The ascending and descending tracts are the first two articles, which cover the anatomy of the sensory and motor pathways of the central nervous system respectively. there are also articles on the visual pathways and auditory pathways to help you understand the intricacies of these important senses. the ascending tracts refer to the neural.
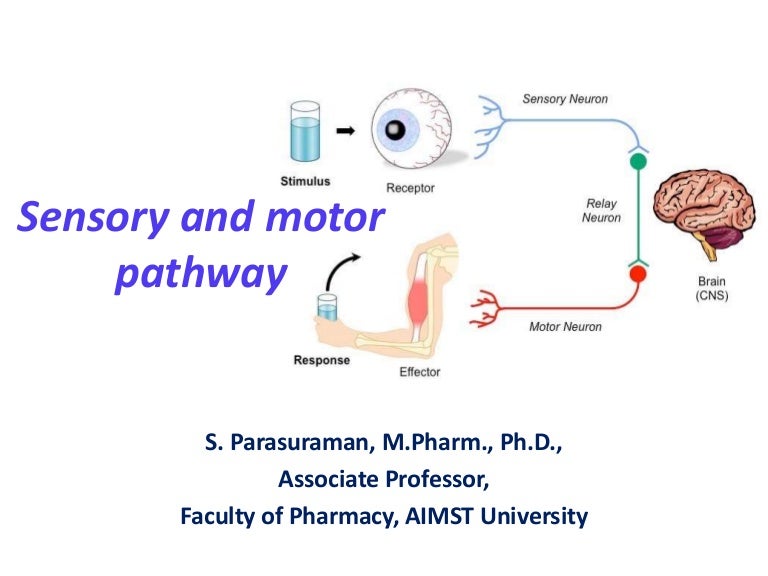
Sensory And Motor Pathways Neural pathways that connect the brain and the spinal cord are called the ascending and descending tracts. they are responsible for carrying sensory and motor messages to and from the periphery. for example; this is how sensation from your fingertips reaches your brain and how conscious and reflexive actions return to your fingers. The sensory pathway ends when the signal reaches the cerebral cortex. after integration with neurons in other parts of the cerebral cortex, a motor command is sent from the precentral gyrus of the frontal cortex. the upper motor neuron sends an action potential down to the spinal cord. the target of the upper motor neuron is the dendrites of. Extrapyramidal tracts – these tracts originate in the brain stem, carrying motor fibres to the spinal cord. they are responsible for the involuntary and automatic control of all musculature, such as muscle tone, balance, posture and locomotion. there are no synapses within the descending pathways. The sensory system follows two ascending pathways from the periphery to the central nervous system. primary somatosensory neurons in both pathways are pseudounipolar. sensory cell bodies are located in the dorsal root ganglion, with one peripheral axon that receives sensory input and one central axon that travels to the spinal cord.
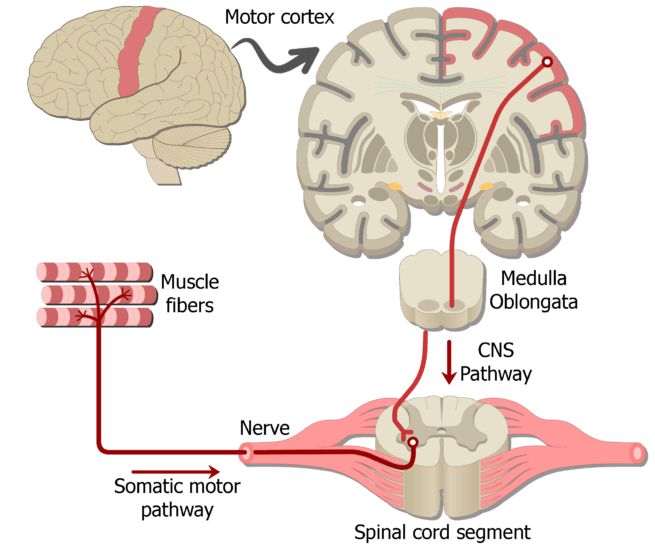
Examples Of Somatic Nervous System Pathways Getbodysmart Extrapyramidal tracts – these tracts originate in the brain stem, carrying motor fibres to the spinal cord. they are responsible for the involuntary and automatic control of all musculature, such as muscle tone, balance, posture and locomotion. there are no synapses within the descending pathways. The sensory system follows two ascending pathways from the periphery to the central nervous system. primary somatosensory neurons in both pathways are pseudounipolar. sensory cell bodies are located in the dorsal root ganglion, with one peripheral axon that receives sensory input and one central axon that travels to the spinal cord. Like the motor system, the sensory pathway plays an important role in the transmission and interpretation of environmental stimuli. without adequate sensory input, appropriate motor responses could not be generated. the two systems work synergistically to provide optimum perception and response to the ever changing external environment. The spinothalamic tract is a sensory pathway originating in the spinal cord. it transmits information to the thalamus about pain, temperature, itch, and crude touch. the pathway decussates at the level of the spinal cord. somatosensory organization is divided into the dorsal column–medial lemniscus tract (the touch proprioception vibration.
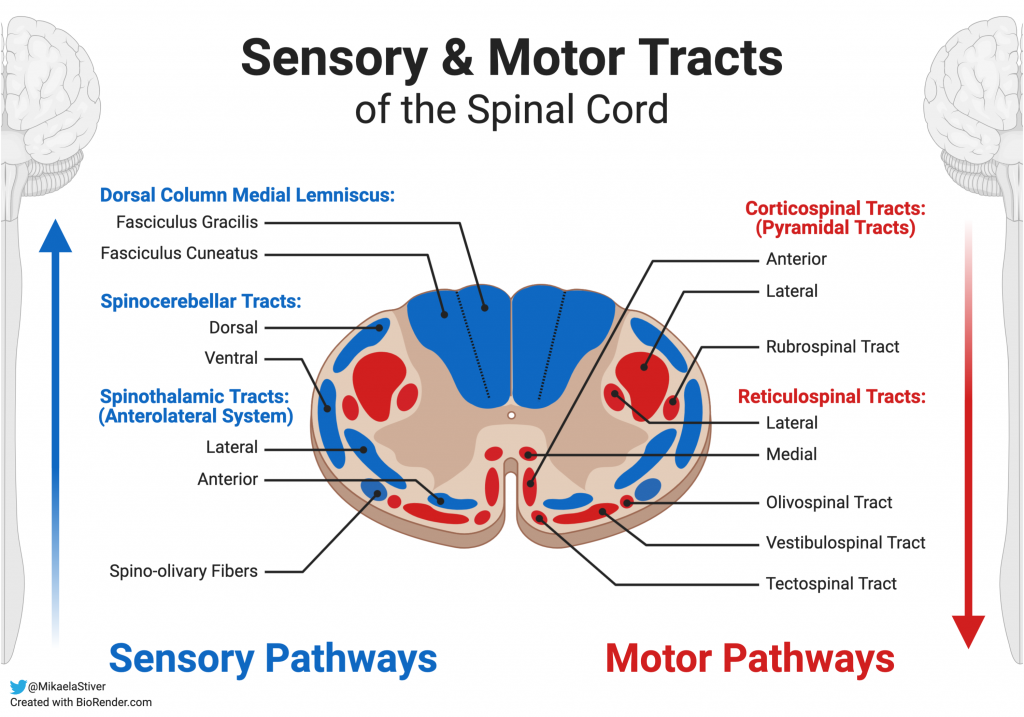
Sensory And Motor Nerves Diagram Like the motor system, the sensory pathway plays an important role in the transmission and interpretation of environmental stimuli. without adequate sensory input, appropriate motor responses could not be generated. the two systems work synergistically to provide optimum perception and response to the ever changing external environment. The spinothalamic tract is a sensory pathway originating in the spinal cord. it transmits information to the thalamus about pain, temperature, itch, and crude touch. the pathway decussates at the level of the spinal cord. somatosensory organization is divided into the dorsal column–medial lemniscus tract (the touch proprioception vibration.

Comments are closed.