The Science Of Emotion Exploring The Basics Of Emotional The
The Science Of Emotion Exploring The Basics Of Emotional Psychology The james lange theory of emotion is one of the earliest emotion theories of modern psychology. developed by william james and carl lange in the 19th century, the theory hypothesizes that physiological stimuli (arousal) causes the autonomic nervous system to react which in turn causes individuals to experience emotion. The author of this . . . text on the science of emotion examines each of the 4 major theoretical points of view representing most contemporary research on the subject: darwinian, jamesian, cognitive, and social constructivist. he describes the major premises of each tradition, compares them to one another, briefly details the major research defining each point of view, and concludes each.

The Science Of Emotion Exploring The Basics Of Emotional The Measuring emotion means capturing when and how mere physical changes are categorized so as to serve the psychological functions of an emotion (as opposed to other times when the same physical changes are not understood as an emotion and therefore serve some other psychological function; barrett, 2012). 4.3. The scientific study of emotion is nearly 150 years old. it is a field ripe with zeitgeist altering empirical advances, and at the same time it is rich with theoretical debate. herein we briefly review the nature of emotions through the lens of basic emotion theory (bet), the most central narrative in emotion psychology to date. The science of emotion: research and tradition in the psychology of emotion. originally published in contemporary psychology: apa review of books, 1997, vol 42 (3), 269. this introductory text (see record 1996 97076 000) introduces readers to four major theoretical perspectives on emotion: darwinian, jamesian, cognitive, and social constructivist. The science of emotion is muddled with a multitude of hypotheses and assumptions about what emotions are and how they work. the standard narrative framework used in the science of emotion conceals meaningful variation within scientific traditions and obfuscates similarities, depriving both newcomers and scientists of effective conceptual tools for making scientific progress.

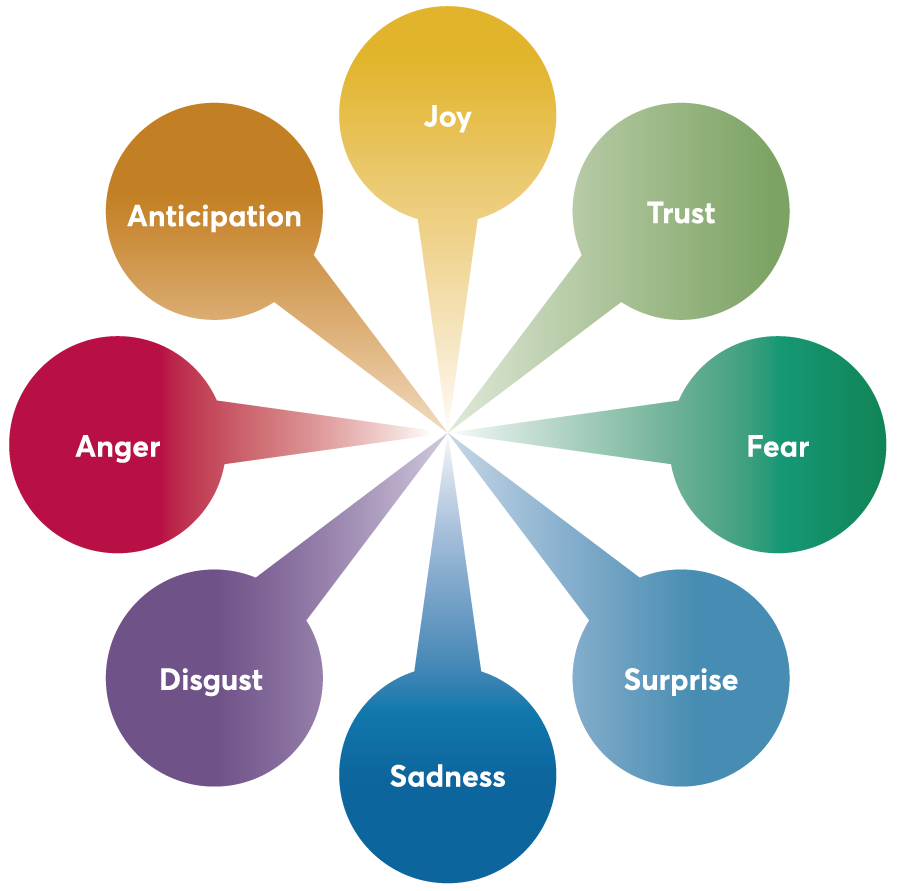
6 Types Of Basic Emotions And Their Effect On Our Behavior The science of emotion: research and tradition in the psychology of emotion. originally published in contemporary psychology: apa review of books, 1997, vol 42 (3), 269. this introductory text (see record 1996 97076 000) introduces readers to four major theoretical perspectives on emotion: darwinian, jamesian, cognitive, and social constructivist. The science of emotion is muddled with a multitude of hypotheses and assumptions about what emotions are and how they work. the standard narrative framework used in the science of emotion conceals meaningful variation within scientific traditions and obfuscates similarities, depriving both newcomers and scientists of effective conceptual tools for making scientific progress. Within the last few decades, the emotions have re emerged more generally as a topic of great philosophical interest and importance. philosophers, along with psychologists, cognitive scientists, and neuroscientists have engaged in inter and intra disciplinary debates concerning the ontology and phenomenology of emotions, the epistemic and cognitive dimensions of emotions, the rationality of. A subfield of affective science is affective neuroscience, the study of the emotional brain.this revised second edition of psychology of emotion reviews both theory and methods in emotion science, discussing findings about the brain; the function, expression, and regulation of emotion; similarities and differences due to gender and culture; the.

Comments are closed.