The Science Behind Engine Cooling Systems How Your Car Stays Cool

The Science Behind Engine Cooling Systems How Your Car Stays Cool The job of the car’s cooling system is to allow the engine to quickly attain its maximum temperature, maintain that temperature during its use and release the excess heat into the air. the cooling system is composed of various parts: the radiator, pressure cap, fan, pump, thermostat, hoses and overflow tank. the pump sends cooling fluid to. Diagram of a cooling system: how the plumbing is connected. want to learn more? check out these car engine pictures. . hsw . although gasoline engines have improved a lot, they are still not very efficient at turning chemical energy into mechanical power. most of the energy in the gasoline (perhaps 70%) is converted into heat, and it is the job of the cooling system to take care of that.
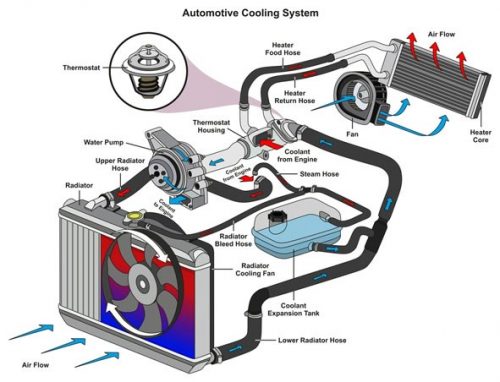
How Engine Cooling System Works Blue Driving School Coolant. at the core of the cooling system is the coolant, a specially formulated mixture of water and antifreeze. this fluid circulates through the engine and absorbs heat from the combustion process. acting as a heat exchange medium, the coolant undergoes a transformation from liquid to vapor and back, carrying away the excess heat. In the video, we learn about the general structure and operating principle of one of the subsystems of a car engine the engine cooling system. the video br. Engine cooling systems play a pivotal role in preventing engine overheating, a potentially catastrophic issue. when an engine overheats, its internal components may suffer damage, leading to costly repairs or even engine failure. the cooling system helps dissipate excess heat, maintaining the engine’s temperature within a safe range. When the engine warms up, the wax melts, expands and pushes the valve open, allowing coolant to flow through the radiator. when the engine stops and cools, the valve closes again. water expands when it freezes, and if the water in an engine freezes it can burst the block or radiator. so antifreeze usually ethylene glycol is added to the water.
How Automotive Cooling Systems Work Bg Find A Shop Engine cooling systems play a pivotal role in preventing engine overheating, a potentially catastrophic issue. when an engine overheats, its internal components may suffer damage, leading to costly repairs or even engine failure. the cooling system helps dissipate excess heat, maintaining the engine’s temperature within a safe range. When the engine warms up, the wax melts, expands and pushes the valve open, allowing coolant to flow through the radiator. when the engine stops and cools, the valve closes again. water expands when it freezes, and if the water in an engine freezes it can burst the block or radiator. so antifreeze usually ethylene glycol is added to the water. In order for the system to work, the coolant needs to move throughout the system. the water pump uses power from the crankshaft and serpentine belt to force coolant into the engine and through the rest of the cooling system. allow your engine to run for a few minutes before inspecting your water pump. visually check for leaks around the unit. Pressure generated by the water pump maintains the flow of coolant through the radiator. once heat has dissipated, the core tubes join again at the other end of the radiator, pumping cold coolant through the coolant jacket again. it’s a continuous cycle of heating and cooling that occurs the entire time your engine is running.
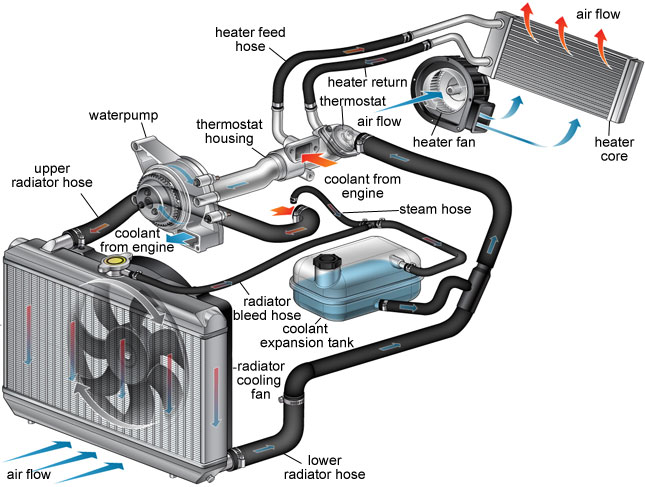
What You Need To Know About Your Automotive Cooling System Toytechs In order for the system to work, the coolant needs to move throughout the system. the water pump uses power from the crankshaft and serpentine belt to force coolant into the engine and through the rest of the cooling system. allow your engine to run for a few minutes before inspecting your water pump. visually check for leaks around the unit. Pressure generated by the water pump maintains the flow of coolant through the radiator. once heat has dissipated, the core tubes join again at the other end of the radiator, pumping cold coolant through the coolant jacket again. it’s a continuous cycle of heating and cooling that occurs the entire time your engine is running.

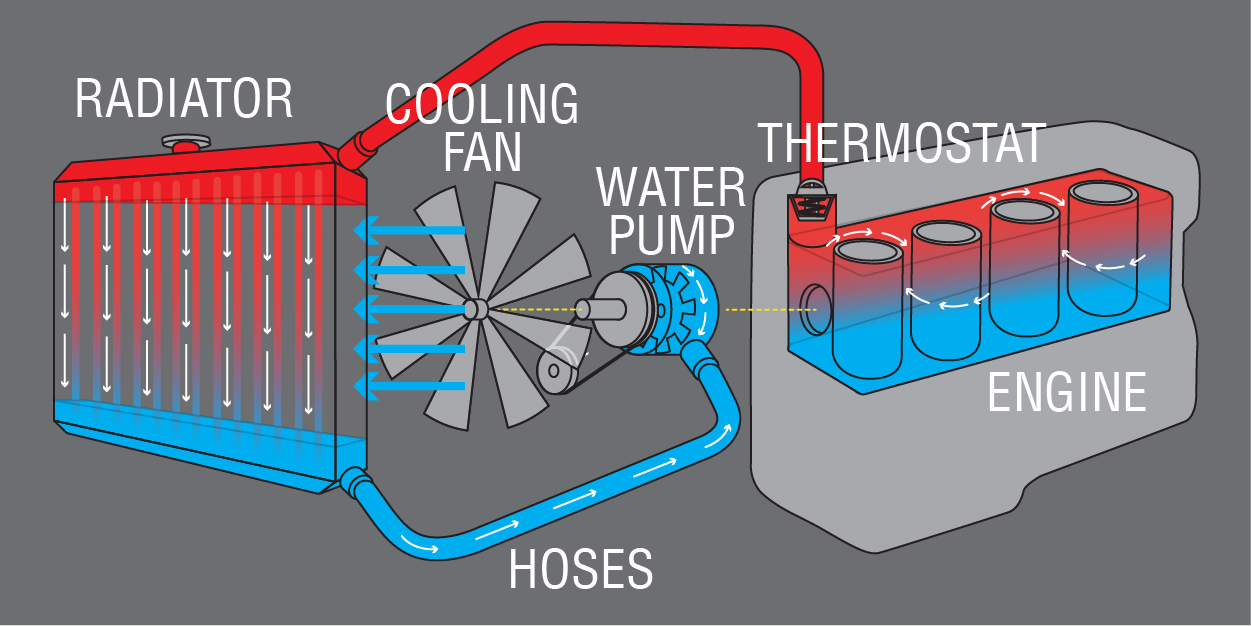
How An Engine Cooling System Works How A Car Works
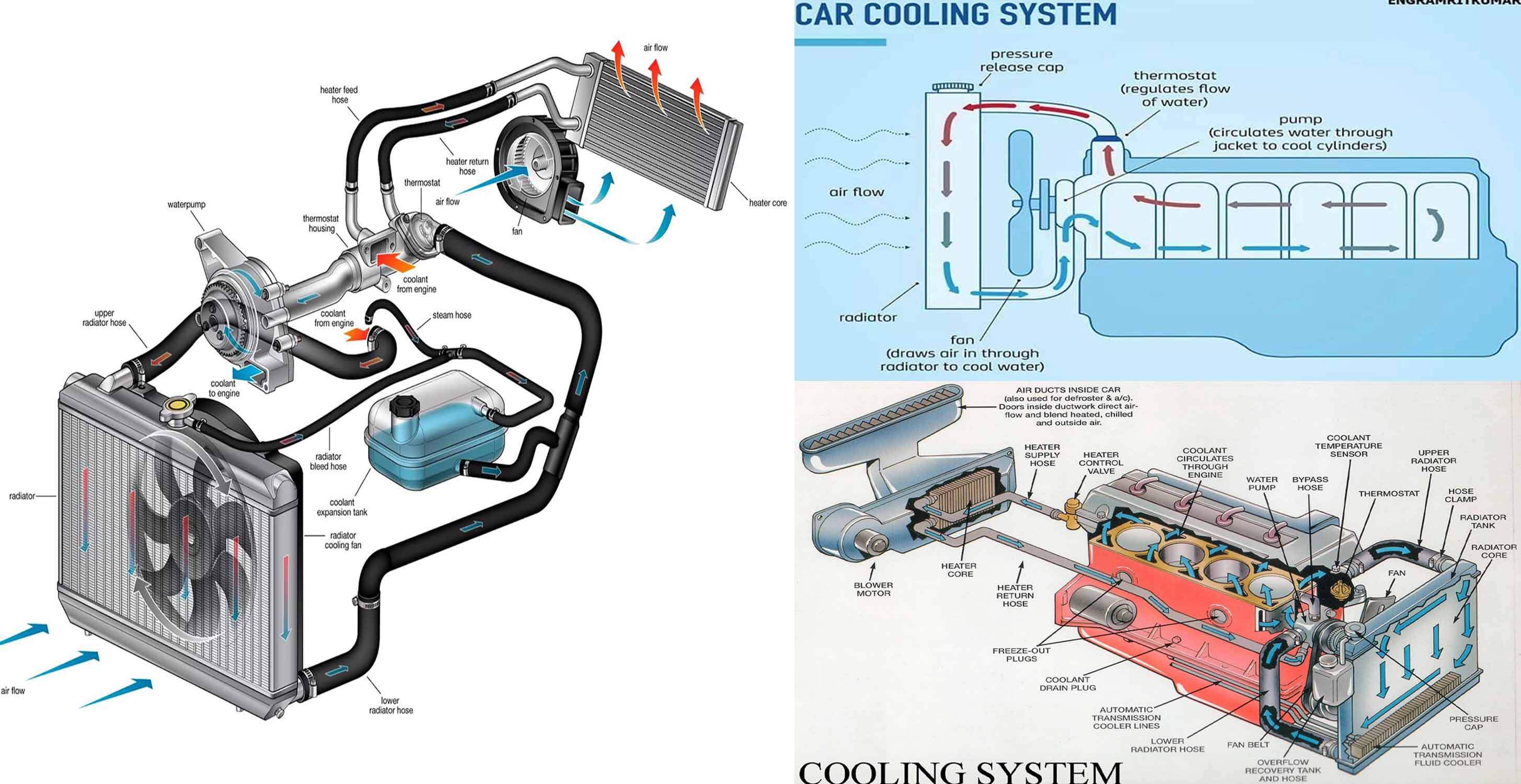
How Engine Cooling System Works Engineering Discoveries

Comments are closed.