The Role Of Producers Consumers And Decomposers In A Habitat

The Role Of Producers Consumers And Decomposers In A Habitat Producers are also called autotrophs. auto means self, while troph means food. they are organisms that create their food from inorganic molecules such as water, co2, nitrogen, and phosphate. most. Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat.

Food Chain Producers Consumers Decomposers Food Chain In Pond Aquatic animal that strains nutrients from water. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. Decomposers are involved in virtually all of the nutrient cycles on the planet. the plants in the consumer level rely on decomposers to break down dead organic material to release the nutrients and elements like carbon, oxygen and phosphorus back into the soil. this along with energy from the sun powers the process of photosynthesis in plants. Decomposers. when organisms die, they leave behind energy and matter in their remains. decomposers break down the remains and other wastes and release simple inorganic molecules back to the environment. producers can then use the molecules to make new organic compounds. the stability of decomposers is essential to every ecosystem. Post and review the following directions: 1. as a group, read and look at the picture cards. 2. as a group, categorize the organisms on the picture cards as producers, primary consumers, or secondary consumers. 3. individually record your findings in the three column chart in your student science notebook.

What Are The Roles Of Producers Consumers And Decomposers In An Decomposers. when organisms die, they leave behind energy and matter in their remains. decomposers break down the remains and other wastes and release simple inorganic molecules back to the environment. producers can then use the molecules to make new organic compounds. the stability of decomposers is essential to every ecosystem. Post and review the following directions: 1. as a group, read and look at the picture cards. 2. as a group, categorize the organisms on the picture cards as producers, primary consumers, or secondary consumers. 3. individually record your findings in the three column chart in your student science notebook. This tutorial will introduce the main types of biotic (living) factors in ecosystems as producers, consumers, and decomposers. students will learn how producers (e.g., plants) and consumers (e.g., animals) interact in the environment and the role they play in sustaining healthy ecosystems. watch the video to learn more. Producers are the foundation of every food web in every ecosystem—they occupy what is called the first tropic level of the food web. the second trophic level consists of primary consumers —the herbivores, or animals that eat plants. at the top level are secondary consumers —the carnivores and omnivores who eat the primary consumers.

Producers Decomposers Consumers Examples This tutorial will introduce the main types of biotic (living) factors in ecosystems as producers, consumers, and decomposers. students will learn how producers (e.g., plants) and consumers (e.g., animals) interact in the environment and the role they play in sustaining healthy ecosystems. watch the video to learn more. Producers are the foundation of every food web in every ecosystem—they occupy what is called the first tropic level of the food web. the second trophic level consists of primary consumers —the herbivores, or animals that eat plants. at the top level are secondary consumers —the carnivores and omnivores who eat the primary consumers.
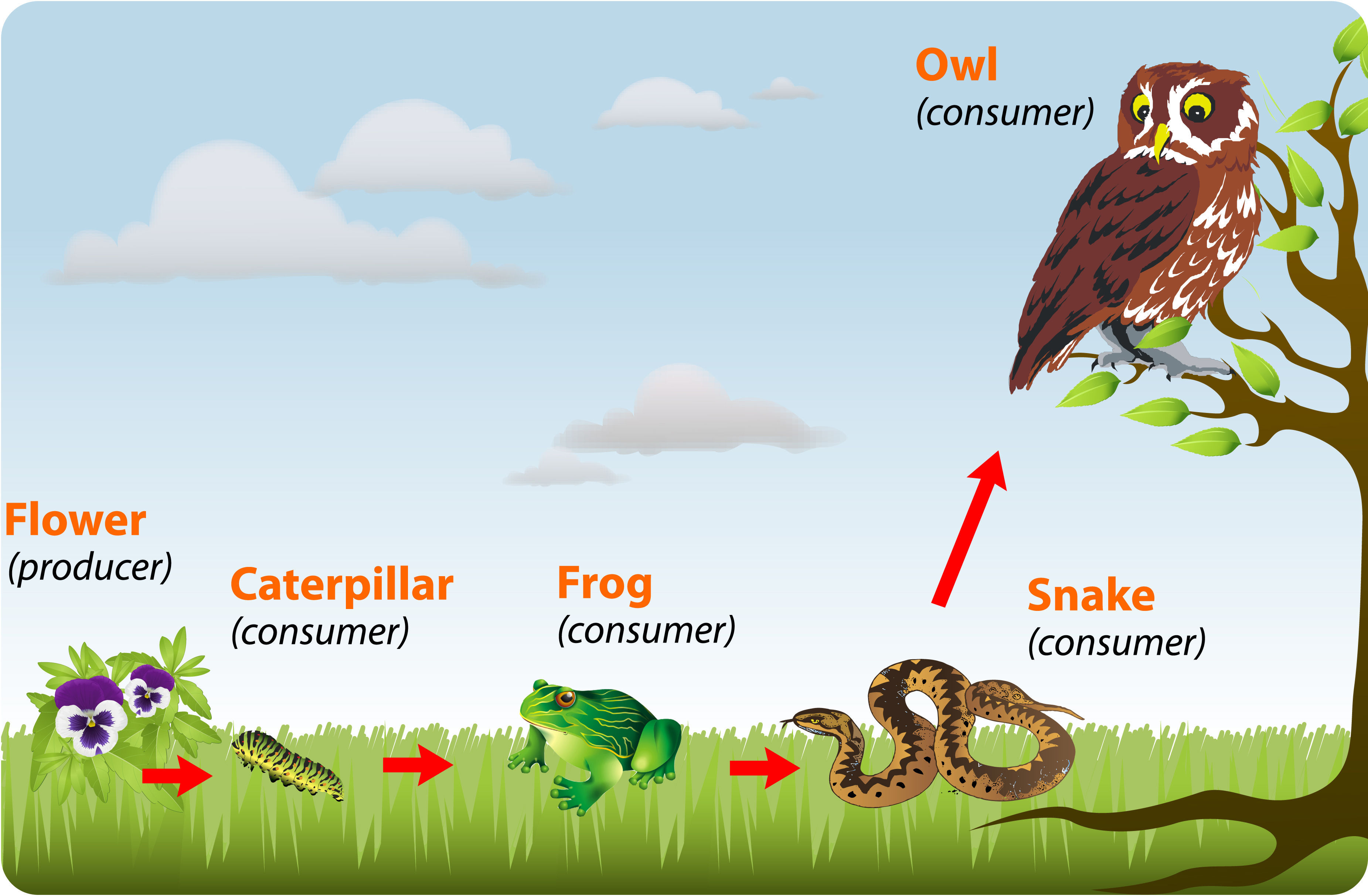
What Are The Relationships Between Producers Consumers And Decomposers

Comments are closed.