The Role Of Neuroinflammation In Alzheimer Disease Ad Microglia

The Role Of Neuroinflammation In Alzheimer Disease Ad Microglia Neuroinflammation has demonstrated a key role in the pathogenesis of alzheimer disease (ad), the most prevalent form of dementia. neuroinflammation encompasses a variety of inflammatory events in. However, this hypothesis falls short of explaining many aspects of ad pathogenesis. recently, there has been mounting evidence that neuroinflammation plays a key role in the pathophysiology of ad and causes neurodegeneration by over activating microglia and releasing inflammatory mediators.
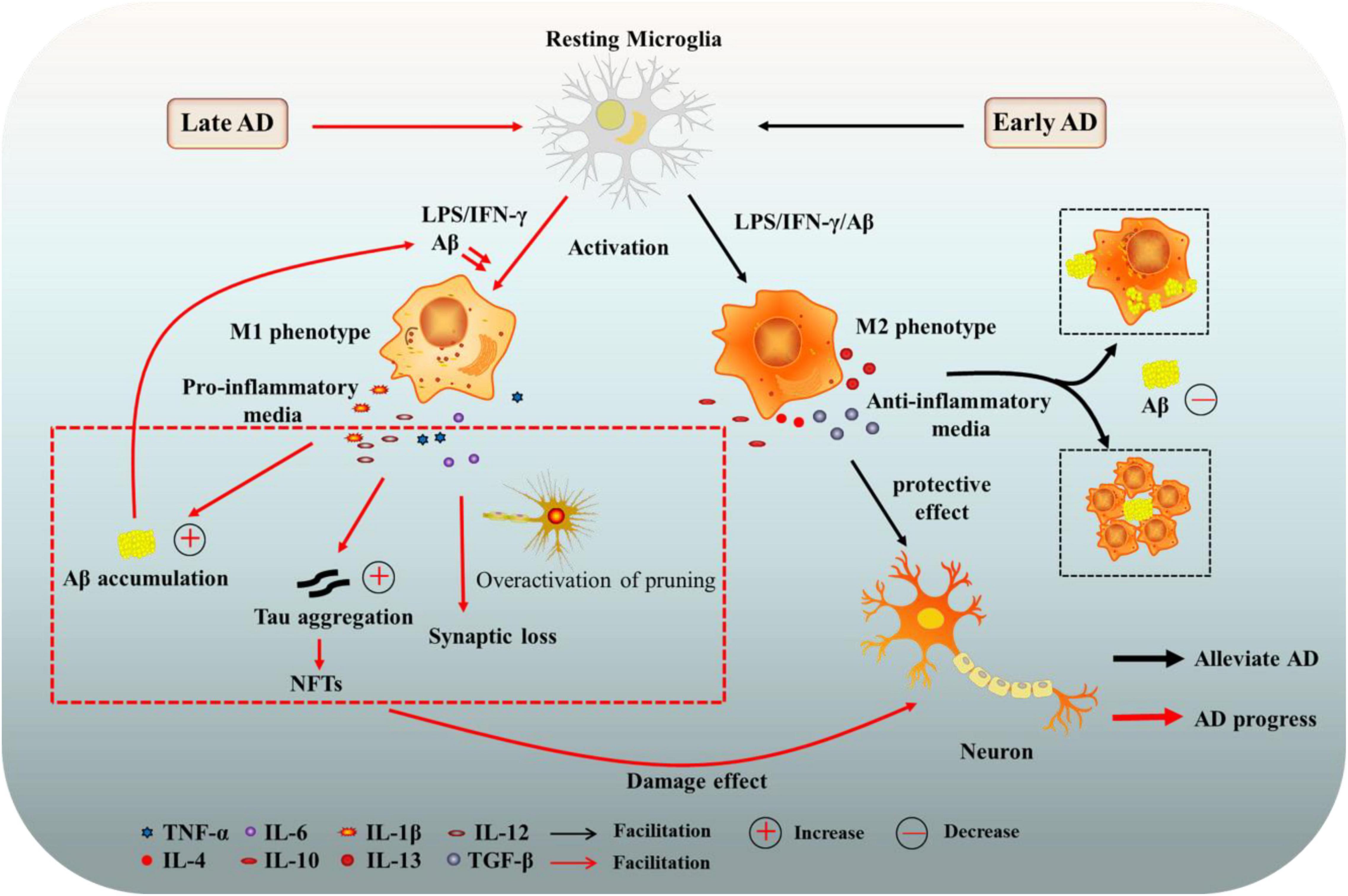
Frontiers The Role Of Microglia In Alzheimer S Disease From The 1 background. alzheimer's disease (ad); a toxic neurodegenerative disorder is the most common cause of dementia and is becoming more common in the elderly. 1 the world health organization (who) projects that 132 million people worldwide will have dementia by the year 2050. 2, 3 progressive neuropathological processes in ad include neurodegeneration and loss of neuronal synapses, which are. Keywords: alzheimer’s disease, microglial cells, neuroinflammation, anti neuroinflammation, molecular therapy. 1 introduction. alzheimer’s disease (ad) is the most common neurodegenerative disease, beginning with gradual memory and cognitive impairment, abnormal behavior, and progressive social dysfunction. Alzheimer disease (ad) is the most common form of neurodegenerative disease, estimated to contribute 60 70% of all cases of dementia worldwide. according to the prevailing amyloid cascade hypothesis, amyloid β (aβ) deposition in the brain is the initiating event in ad, although evidence is accumulat …. Keywords: alzheimer's disease, inflammation, microglia, cytokines, microglia receptors. 1. overview. alzheimer's disease (ad) is a neurodegenerative disorder that is the most common cause of dementia and is characterized by the decline in cognitive and function and neuronal loss.
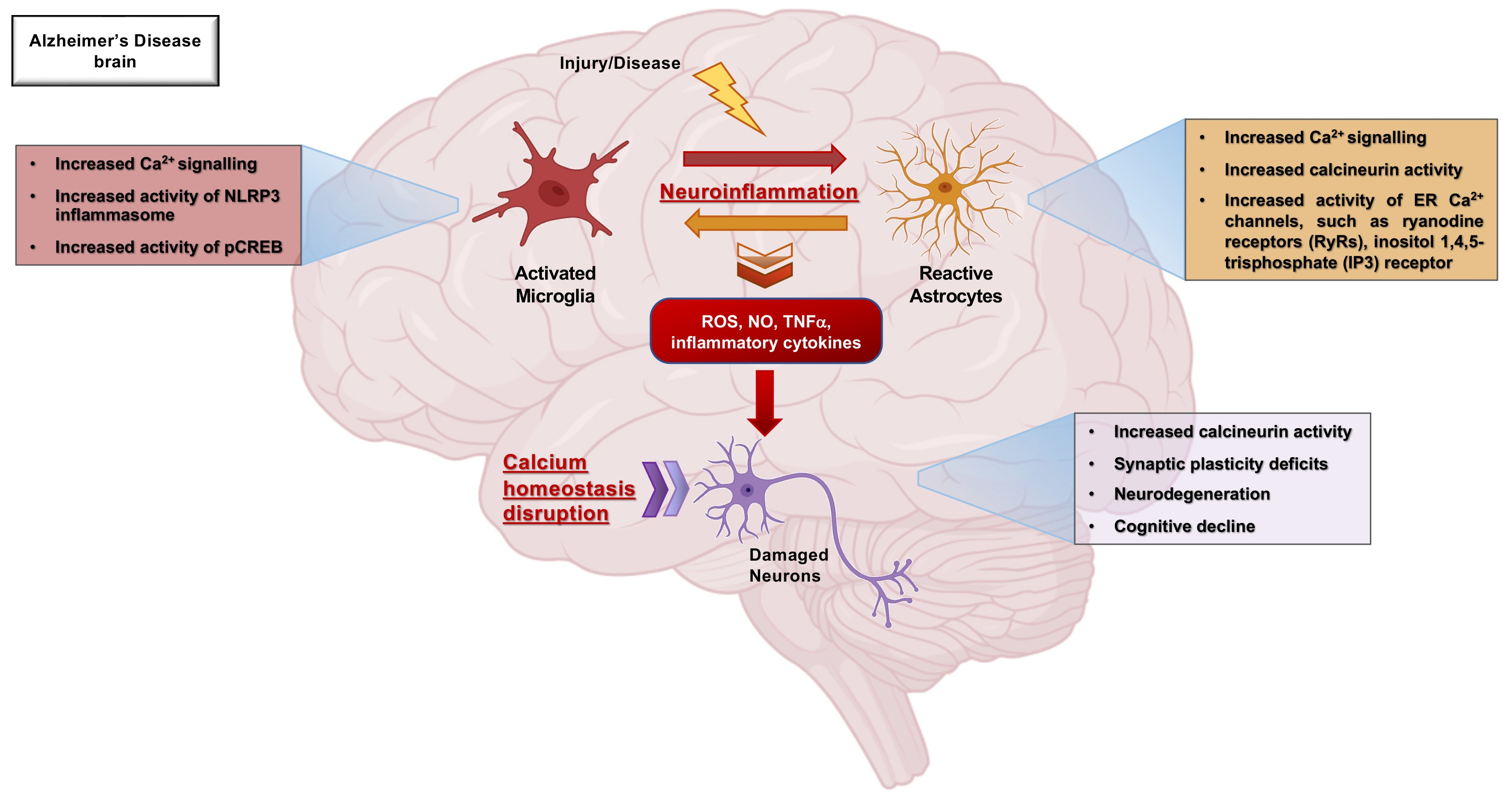
Cells Free Full Text Role Of Microglia And Astrocytes In Alzheimer Alzheimer disease (ad) is the most common form of neurodegenerative disease, estimated to contribute 60 70% of all cases of dementia worldwide. according to the prevailing amyloid cascade hypothesis, amyloid β (aβ) deposition in the brain is the initiating event in ad, although evidence is accumulat …. Keywords: alzheimer's disease, inflammation, microglia, cytokines, microglia receptors. 1. overview. alzheimer's disease (ad) is a neurodegenerative disorder that is the most common cause of dementia and is characterized by the decline in cognitive and function and neuronal loss. Alzheimer’s disease (ad) is the most common neurodegenerative disease in the world. neuronal calcium dysfunction and microglial mediated neuroinflammation are closely associated with the development of ad. however, it remains unknown whether calcium dysfunction contributes to microglial activation and, in turn, ad pathology in vivo. Here we comprehensively review the biology of microglia and the roles of microglia in neurodegenerative diseases, including alzheimer’s disease, parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy.
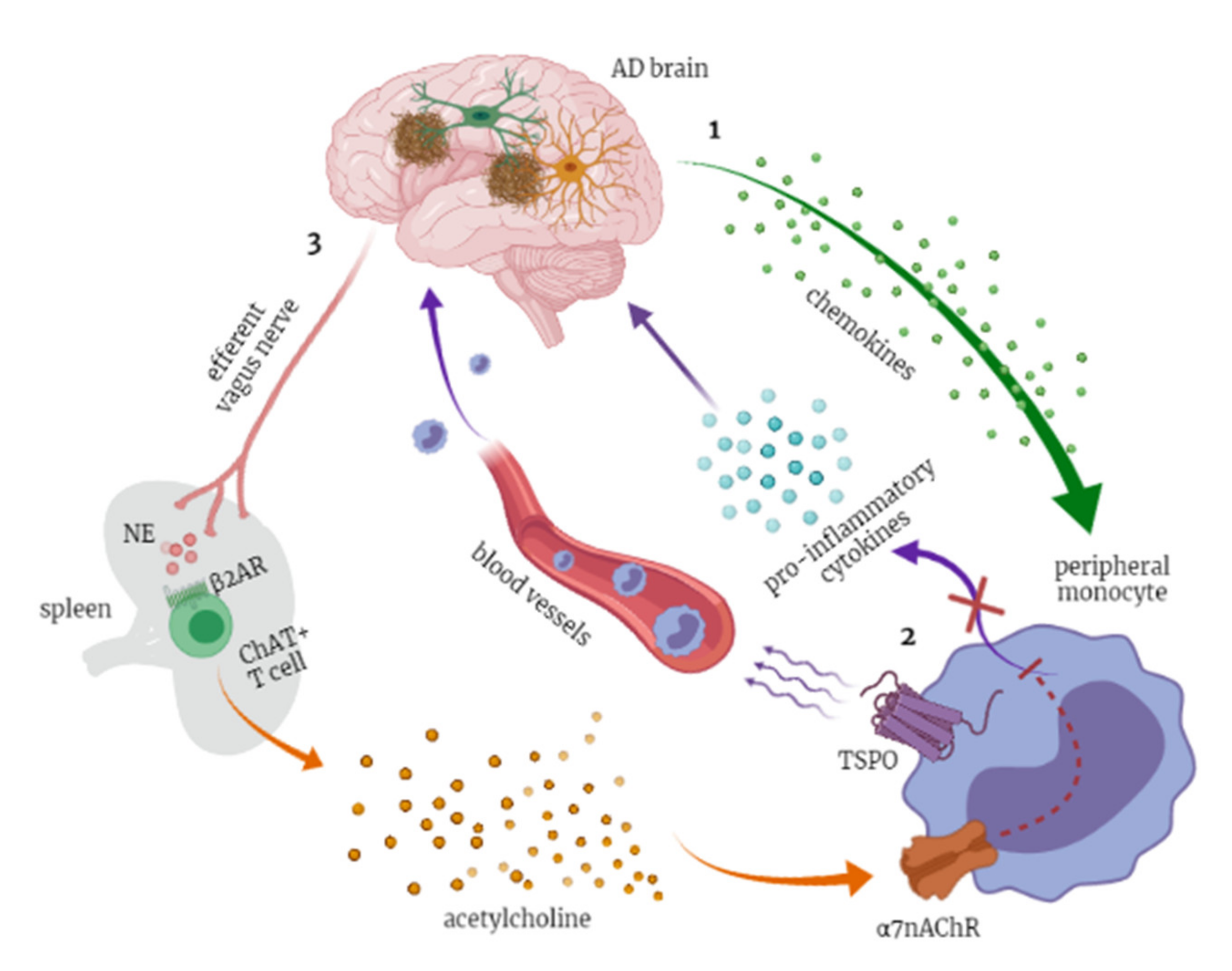
Diagnostics Free Full Text Blood Based Biomarkers Of Alzheimer’s disease (ad) is the most common neurodegenerative disease in the world. neuronal calcium dysfunction and microglial mediated neuroinflammation are closely associated with the development of ad. however, it remains unknown whether calcium dysfunction contributes to microglial activation and, in turn, ad pathology in vivo. Here we comprehensively review the biology of microglia and the roles of microglia in neurodegenerative diseases, including alzheimer’s disease, parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy.

Comments are closed.