The Progression Of Alzheimer S Disease From Brain Changes Download

The Progression Of Alzheimer S Disease From Brain Changes Download Mgh abbvie ad progression study. alzheimer’s disease neuropathological changes (adnc) are accompanied by prominent morphological and functional changes in astrocytes, collectively termed reactive astrogliosis. while transcriptomic studies have begun to unveil the molecular underpinnings of reactive astrocytes, whether astrocyte gene. Alzheimer’s disease (ad) is characterized by the progressive alterations seen in brain images which give rise to the onset of various sets of symptoms. the variability in the dynamics of changes.

Progression Of Alzheimer S Disease Through Different Stages Alzheimer's disease tends to develop slowly and gradually worsens over several years. eventually, alzheimer's disease affects most areas of your brain. memory, thinking, judgment, language, problem solving, personality and movement can all be affected by the disease. there are five stages associated with alzheimer's disease. they include:. At a glance. researchers constructed an atlas of cellular changes in the brain during alzheimer’s disease. the findings revealed two distinct phases of disease progression and suggest potential treatment targets. researchers discovered that these brain cell types may be harmed first by alzheimer’s disease. the allen institute, seattle. Alzheimer’s disease (ad) is a disorder that causes degeneration of the cells in the brain and it is the main cause of dementia, which is characterized by a decline in thinking and independence in personal daily activities. ad is considered a multifactorial disease: two main hypotheses were proposed as a cause for ad, cholinergic and amyloid. Time course of brain volume changes in the preclinical phase of alzheimer’s disease. alzheimer’s & dementia 10 , 143–151. e141 (2014). article google scholar.
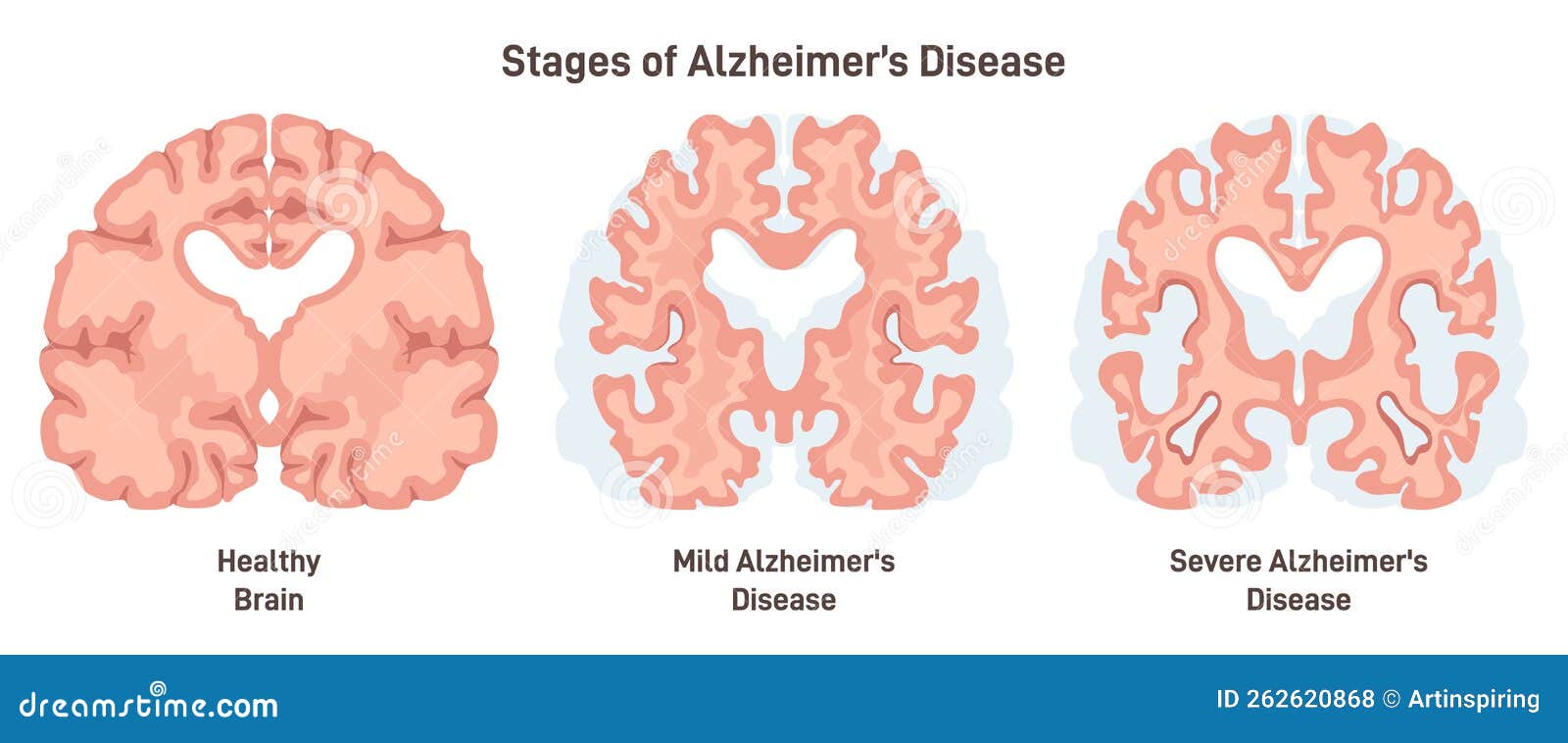
Alzheimer S Disease Stages Human Brain Cross Section Affected With Alzheimer’s disease (ad) is a disorder that causes degeneration of the cells in the brain and it is the main cause of dementia, which is characterized by a decline in thinking and independence in personal daily activities. ad is considered a multifactorial disease: two main hypotheses were proposed as a cause for ad, cholinergic and amyloid. Time course of brain volume changes in the preclinical phase of alzheimer’s disease. alzheimer’s & dementia 10 , 143–151. e141 (2014). article google scholar. The current model of alzheimer’s disease progression is mainly based on the braak staging of alzheimer’s disease tauopathy. 3 this scheme was initially built on the concatenation of post mortem pathological brain examinations from donors at all the stages of disease progression. ongoing longitudinal tau pet imaging studies support the braak. Abstract. the anticipation of progression of alzheimer’s disease (ad) is crucial for evaluations of secondary prevention measures thought to modify the disease trajectory. however, it is.

Alzheimer S Brain Progression Illustration Stock Image F031 9395 The current model of alzheimer’s disease progression is mainly based on the braak staging of alzheimer’s disease tauopathy. 3 this scheme was initially built on the concatenation of post mortem pathological brain examinations from donors at all the stages of disease progression. ongoing longitudinal tau pet imaging studies support the braak. Abstract. the anticipation of progression of alzheimer’s disease (ad) is crucial for evaluations of secondary prevention measures thought to modify the disease trajectory. however, it is.

Comments are closed.