The Pelvis Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141
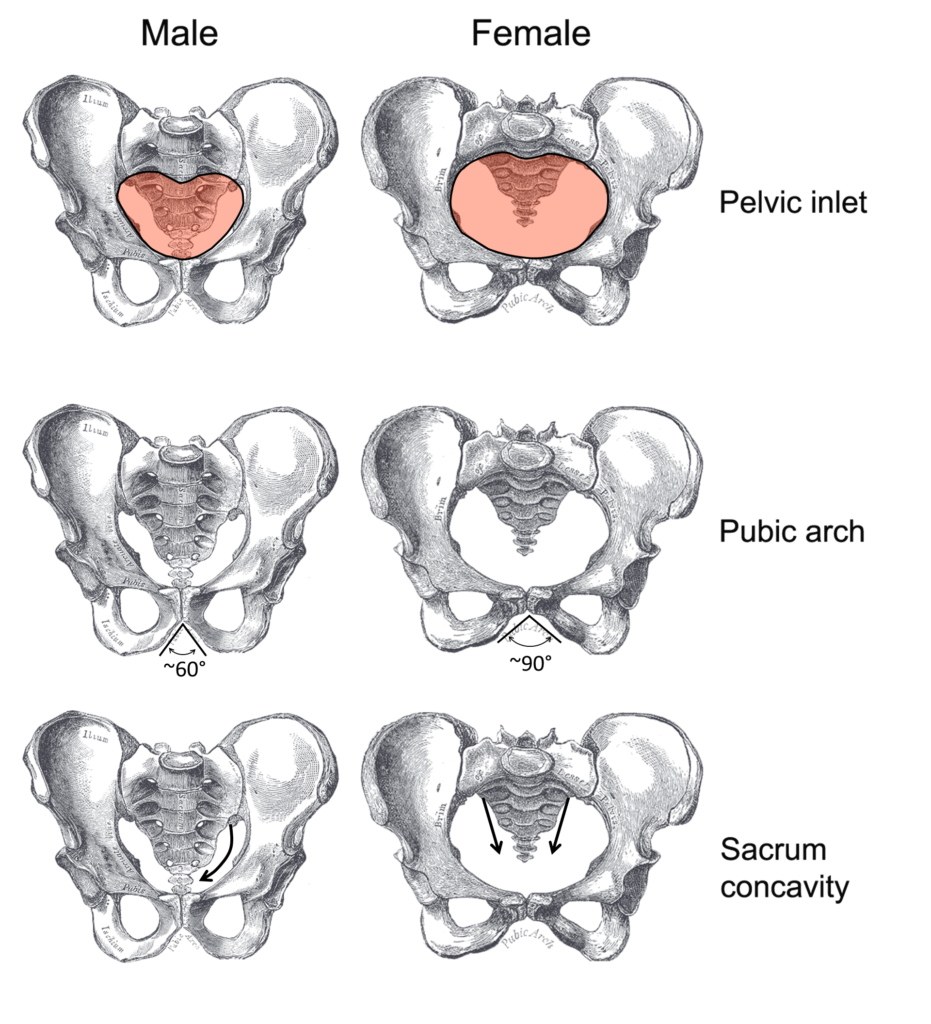
The Pelvis Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141 Study Guides The pelvis is the bowl shaped structure generated by the two coxal bones articulated with the sacrum and coccyx bones. on the anterior side of the pelvis, the pubis portions of the two coxal bones do not articulate with each other, but instead are joined with a small piece of cartilage called the pubic symphysis (“pyoo bick sim fiss is. Colloquially, these are known as the “hip bones”. the pelvic girdle is just the two coxal bones, but the pelvis itself is the bowl like structure created by the two coxal bones joined in the anterior by the sacrum, and coccyx. (“pelvis “comes from the latin word for “basin”.) at birth, each coxal bone starts out as three separate.

The Pelvis Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141 The thoracic cage the ribs and sternum. the appendicular skeleton. the pectoral girdles. the upper limbs. the pelvic girdle. the pelvis. the lower limbs. module 8: muscles of the head and trunk. lab 8 overview. 1. hormone is the single most important stimulus for epiphyseal plate activity during infancy and childhood. 2. the membranous areas between the cranial bones of the fetal skull are called sutures. 3. the striations of a skeletal muscle cell is due to a difference in the thickness of the sarcolemma. 4. Human anatomy & physiology i lab 1 anatomical language & organs learning outcomes. identify anatomical position and be able to reference it when describing anatomical locations. Human anatomy & physiology i lab 4 microscopy i – basics of microscopy lab exercises 4. there is a compound microscope for each student. carry out the activities listed below and fill in the blanks as you do so. pick up your microscope and physically move it to a new location.

Pelvic Bone Anatomy Male Human anatomy & physiology i lab 1 anatomical language & organs learning outcomes. identify anatomical position and be able to reference it when describing anatomical locations. Human anatomy & physiology i lab 4 microscopy i – basics of microscopy lab exercises 4. there is a compound microscope for each student. carry out the activities listed below and fill in the blanks as you do so. pick up your microscope and physically move it to a new location. Coccyx: the coccyx is the small, triangular bone located at the bottom of the vertebral column, formed by the fusion of 3 5 small vertebrae. it serves as an attachment point for several muscles and ligaments, and plays a role in various bodily functions and anatomical structures covered in the topics of bone classification, the skeletal system, the vertebral column, the pelvic girdle and. Hu a & p i lab (bsb 141l) syllabus –fall 2024 page 2 at the end of this course, the student should be able to: •successfully apply scientific methods to the problems in natural sciences. •use anatomical terms to describe body organs, body sections, body regions, and relative positions. •identify the major body organs, body cavities and.
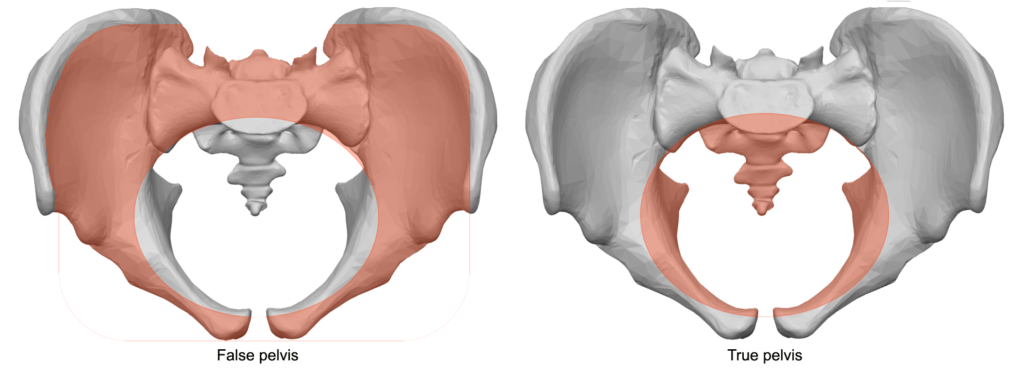
The Pelvis Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141 Study Guides Coccyx: the coccyx is the small, triangular bone located at the bottom of the vertebral column, formed by the fusion of 3 5 small vertebrae. it serves as an attachment point for several muscles and ligaments, and plays a role in various bodily functions and anatomical structures covered in the topics of bone classification, the skeletal system, the vertebral column, the pelvic girdle and. Hu a & p i lab (bsb 141l) syllabus –fall 2024 page 2 at the end of this course, the student should be able to: •successfully apply scientific methods to the problems in natural sciences. •use anatomical terms to describe body organs, body sections, body regions, and relative positions. •identify the major body organs, body cavities and.

Comments are closed.