The Limbic System Amygdala The Reign Of The Brain
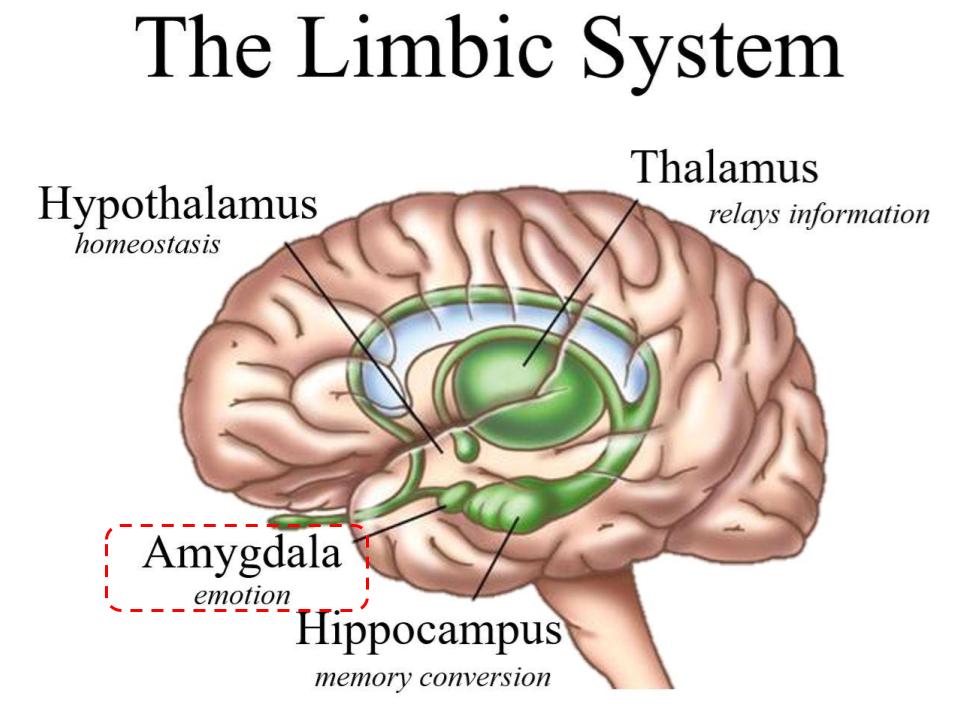
The Limbic System Amygdala The Reign Of The Brain Next on our trip throughout the limbic system is the amygdala! a fun fact about the amygdala: its name originates from the fact that it looks like an almond, and almond in greek sounds like amygdala! the amygdala's main purpose is to control your emotions. of those emotions, the amygdala especially deals with your feeling of fear. The limbic system is a complex set of brain structures involved in emotion, motivation, memory, and behavior regulation. key components include the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cingulate gyrus. it's central to emotional processing, memory formation, and various autonomic functions, bridging higher cognitive processes and primal emotions.

Limbic System Description Components Function History Of Study The limbic system is one of the oldest structures of your brain. it produces natural instincts that your ancestors used to survive by triggering behaviors needed to: eat and drink. reproduce. care for young. react to surroundings (fight or flight response). there are many components to your limbic system that give it a lot of responsibilities. The amygdala is an almond shaped structure located deep in the temporal lobe of the brain. it is part of the limbic system and is made up of over a dozen different nuclei, which are clusters of neurons with specialized functions. the amygdala sits in front of the hippocampus and has connections to brain regions involved in sensory perception. The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain. [1] its various components support a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long term memory, and olfaction. The limbic system is a group of structures in the brain that governs emotions, motivation, olfaction, and behavior. it is also involved in the formation of long term memory. the limbic system consists of several interconnected components, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, and amygdala. a dysfunctional limbic system is associated with several.

Amygdala Function Location What Happens When Amygdala Is Damaged The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain. [1] its various components support a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long term memory, and olfaction. The limbic system is a group of structures in the brain that governs emotions, motivation, olfaction, and behavior. it is also involved in the formation of long term memory. the limbic system consists of several interconnected components, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, and amygdala. a dysfunctional limbic system is associated with several. The region of the brain believed to be responsible for these activities formed a physical border between the hypothalamus and the cerebrum. therefore, it was called the limbic system; arising from the latin word limbus, meaning edge. the limbic system is considered to be the epicentre of emotional and behavioral expression. The limbic system is vital for one's normal functioning. this system acts as the center of emotions, behavior, and memory. it is also a contributor to the control of reactions to stress, attention, and sexual instincts. it comprises a set of complex structures anatomically divided into the limbic cortex, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, hippocampal formation, dentate gyrus, hippocampus.

Amygdala Function Location What Happens When Amygdala Is Damaged The region of the brain believed to be responsible for these activities formed a physical border between the hypothalamus and the cerebrum. therefore, it was called the limbic system; arising from the latin word limbus, meaning edge. the limbic system is considered to be the epicentre of emotional and behavioral expression. The limbic system is vital for one's normal functioning. this system acts as the center of emotions, behavior, and memory. it is also a contributor to the control of reactions to stress, attention, and sexual instincts. it comprises a set of complex structures anatomically divided into the limbic cortex, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, hippocampal formation, dentate gyrus, hippocampus.
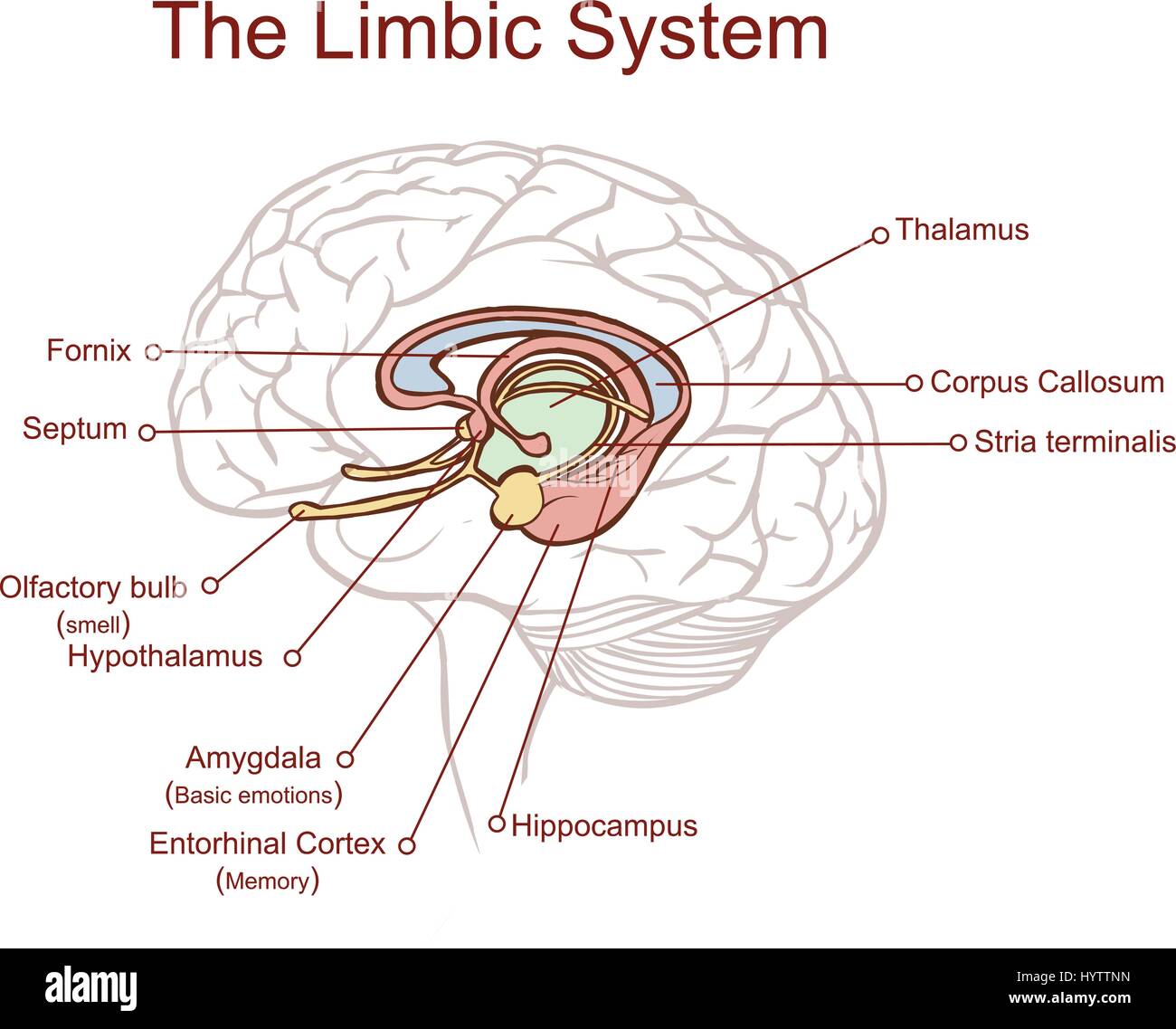
Cross Section Through The Brain Showing The Limbic System And All Stock

Comments are closed.