The Incredible Stages Of A Stars Life Cycle
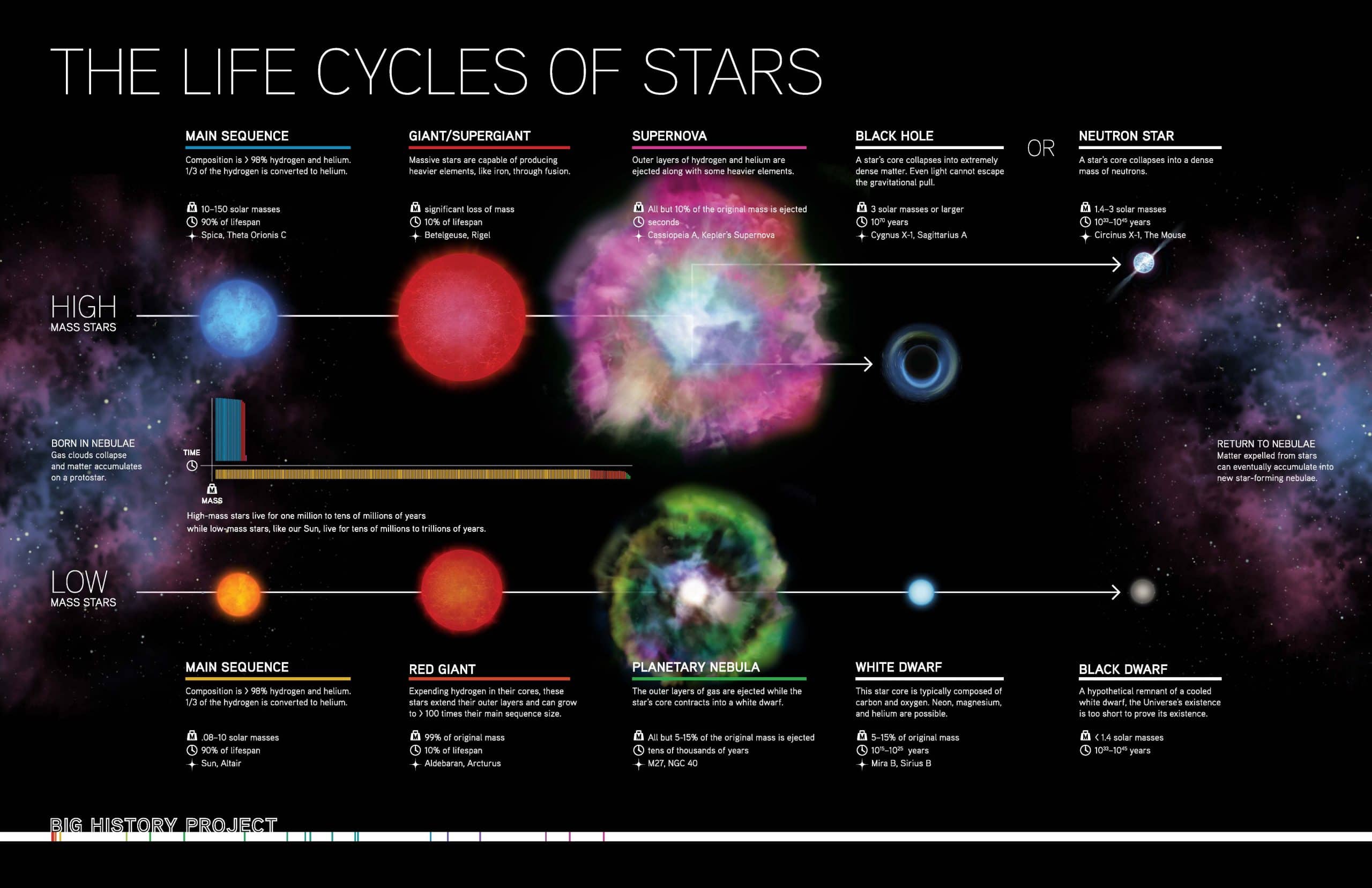
The Incredible Life Of Stars Daily Infographic At the first stage of their lives, stars are formed by the gravitational collapse of giant clouds of dust and gas called nebulae. this stage is the start of their life cycle. 2. protostar. a protostar is the result of the gravitational collapse of a nebula. it is the formative phase of a star. Stars are composed primarily of hydrogen and helium gases. they vary dramatically in size, luminosity and temperature, and live for billions of years, transitioning through several stages. our own sun is a typical star, one of hundreds of billions that litter the milky way. the life cycle of a star consists of a number of well defined stages.
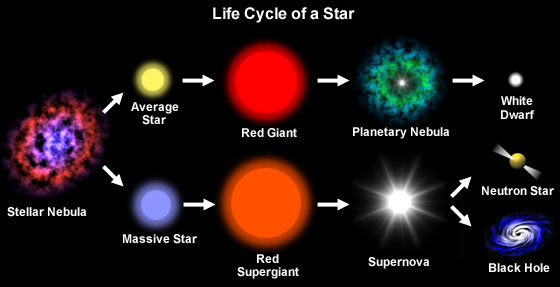
Life Cycle Of A Star The Schools Observatory The early stage of a star, still gathering material: main sequence: the prime of a star’s life, powered by hydrogen fusion: red giant: the transitional stage when a star expands and cools: supernova: the explosive death of a massive star: stellar remnant: the final stage of a star, such as a white dwarf or black hole. Stars approximately the size of our sun are considered small stars, but they aren't as small as red dwarves, which have a mass about half that of the sun and are as close to being eternal as a star can get. the life cycle of a low mass star like the sun, which is classified as a g type, main sequence star (or a yellow dwarf), lasts about 10. Life cycle of a star. all stars form in nebulae, which are huge clouds of gas and dust. though they shine for many thousands, and even millions of years, stars do not last forever. the changes that occur in a star over time and the final stage of its life depend on a star's size. nuclear reactions at the centre (or core) of a star provides. Massive stars transform into supernovae, neutron stars and black holes while average stars like the sun, end life as a white dwarf surrounded by a disappearing planetary nebula. all stars, irrespective of their size, follow the same 7 stage cycle, they start as a gas cloud and end as a star remnant. 1. giant gas cloud.
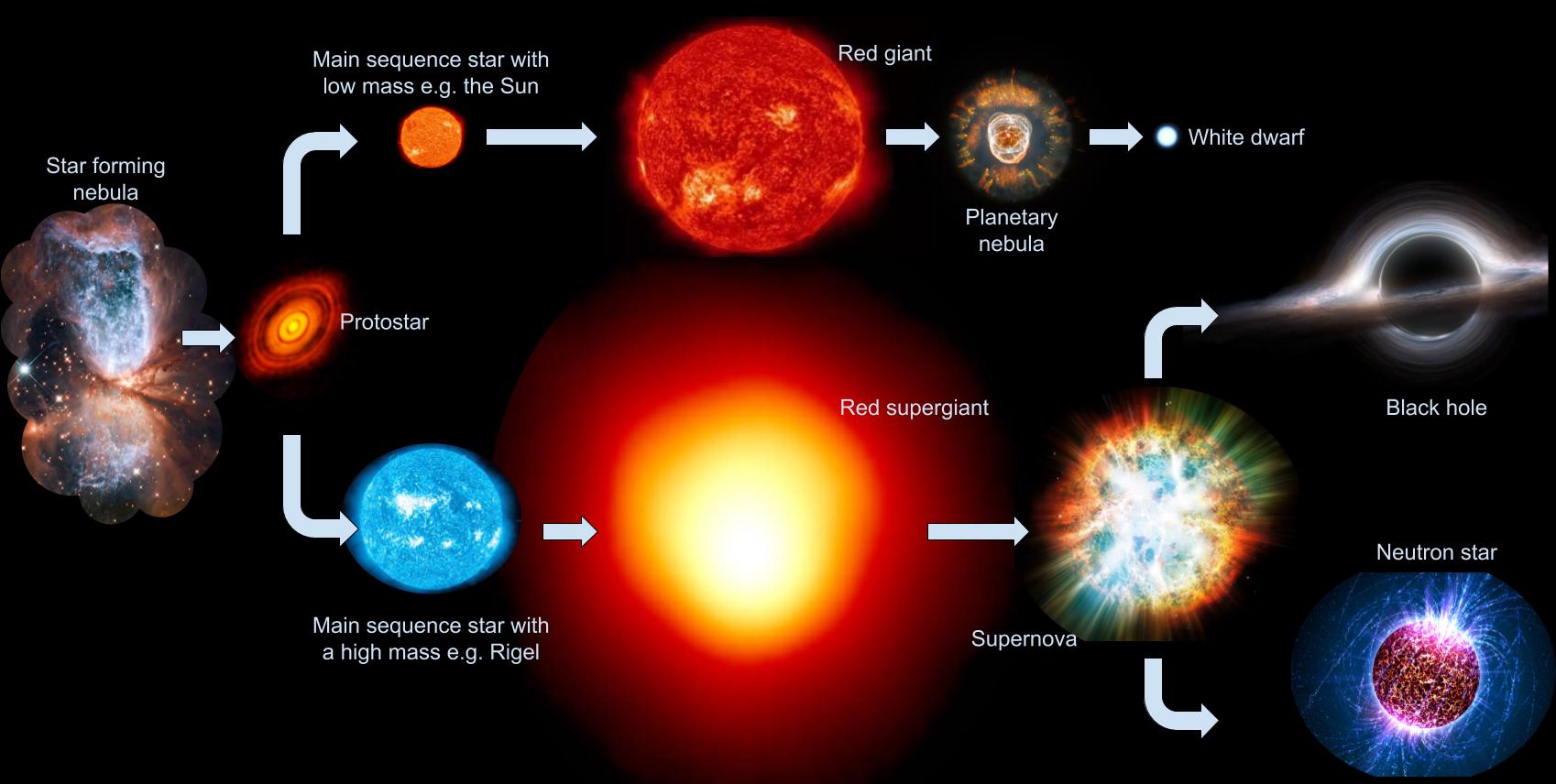
Mr Toogood Physics Life Cycle Of Stars Supernovae Black Holes And Life cycle of a star. all stars form in nebulae, which are huge clouds of gas and dust. though they shine for many thousands, and even millions of years, stars do not last forever. the changes that occur in a star over time and the final stage of its life depend on a star's size. nuclear reactions at the centre (or core) of a star provides. Massive stars transform into supernovae, neutron stars and black holes while average stars like the sun, end life as a white dwarf surrounded by a disappearing planetary nebula. all stars, irrespective of their size, follow the same 7 stage cycle, they start as a gas cloud and end as a star remnant. 1. giant gas cloud. All life on earth contains the element carbon, and all carbon was originally formed in the core of a star. stars populate the universe with elements through their “lifecycle”—an ongoing process of formation, burning fuel, and dispersal of material when all the fuel is used up. different stars take different paths, however, depending on. The life cycle of a star is a tale of birth, life, and death on a cosmic scale. from their humble beginnings in vast nebulae to their final resting places as white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes, stars play a central role in shaping the universe and the elements that comprise it. as we delve deeper into the mysteries of these celestial.
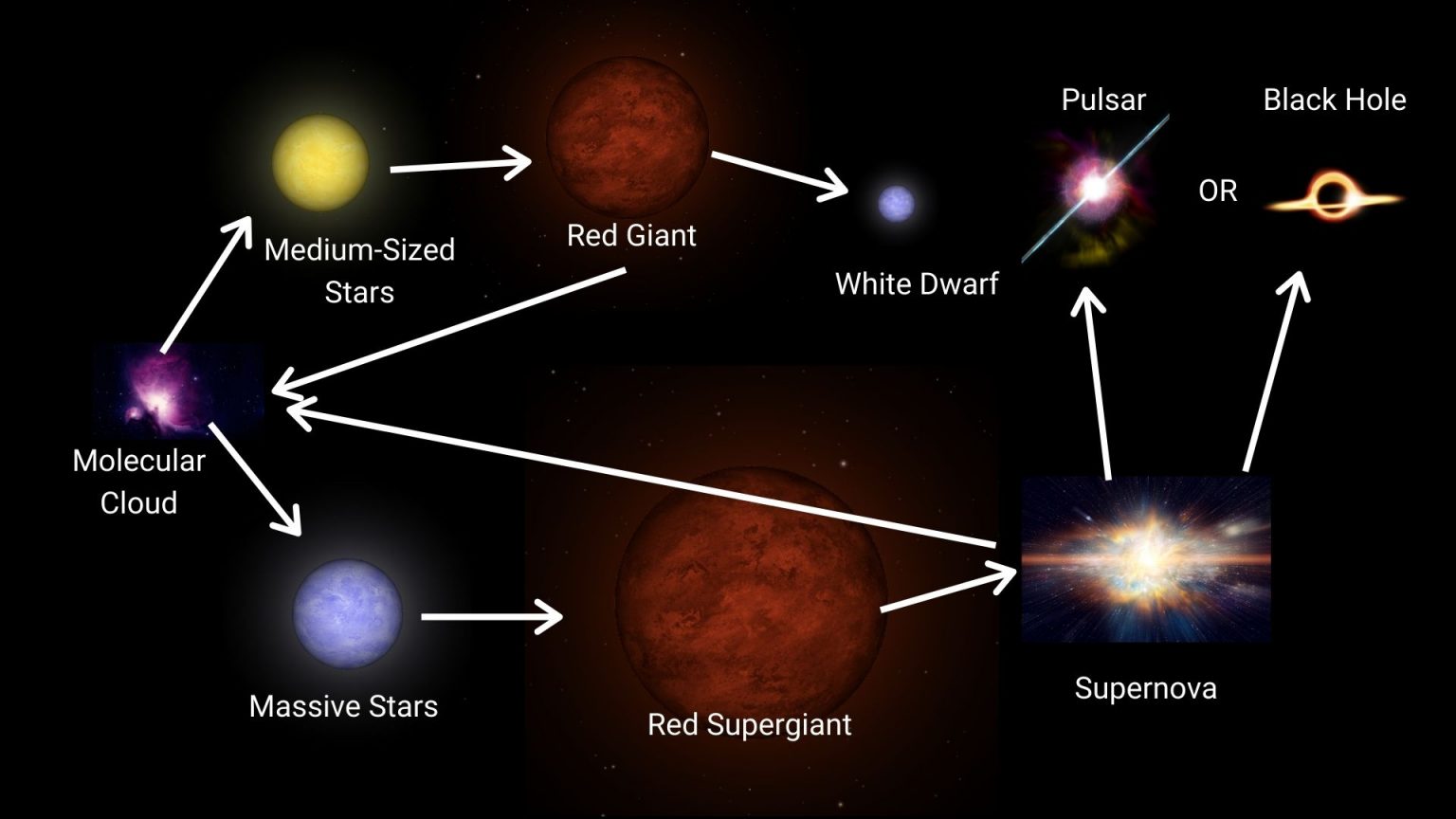
The Main Stages Of The Life Cycle Of A Star Central Galaxy All life on earth contains the element carbon, and all carbon was originally formed in the core of a star. stars populate the universe with elements through their “lifecycle”—an ongoing process of formation, burning fuel, and dispersal of material when all the fuel is used up. different stars take different paths, however, depending on. The life cycle of a star is a tale of birth, life, and death on a cosmic scale. from their humble beginnings in vast nebulae to their final resting places as white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes, stars play a central role in shaping the universe and the elements that comprise it. as we delve deeper into the mysteries of these celestial.

Comments are closed.