The Human Skeletal System Functions Bones And Classification

Human Skeleton Skeletal System Function Human Bones Describe the function of each category of bones. the 206 bones that compose the adult skeleton are divided into five categories based on their shapes (figure 6.2.1). like other structure function relationships in the body, their shapes and their functions are related such that each categorical shape of bone has a distinct function. figure 6.2.1. They are usually classified into five types of bones that include the flat, long, short, irregular, and sesamoid bones. the human bones have a number of important functions in the body. most importantly, they are responsible for somatic rigidity, structural outline, erect posture and movement (e.g. bipedal gait).

Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Skeletal System Anatomy The only short bones in the human skeleton are in the carpals of the wrists and the tarsals of the ankles. short bones provide stability and support as well as some limited motion. flat bones. the term “ flat bone ” is somewhat of a misnomer because, although a flat bone is typically thin, it is also often curved. examples include the. Part 2: bone classification. the 206 bones that compose the adult skeleton can be divided into five categories based on their shapes (figure 10.4). their shapes and their functions are related such that each categorical shape of bone has a distinct function. long bones: a long bone is cylindrical in shape, with a diameter smaller than its. In the areas of the skeleton where bones move (for example, the ribcage and joints), cartilage, a semi rigid form of connective tissue, provides flexibility and smooth surfaces for movement. the skeletal system is the body system composed of bones and cartilage and performs the following critical functions for the human body: supports the body. Ligaments. some bones protect your internal organs. for example, your skull safely encloses your brain, and your ribcage shields your heart, lungs and other organs near your chest. bones contain and protect your bone marrow. bone marrow is a soft, fatty tissue that produces critical cells, including: advertisement.

Functions Skeletal System In the areas of the skeleton where bones move (for example, the ribcage and joints), cartilage, a semi rigid form of connective tissue, provides flexibility and smooth surfaces for movement. the skeletal system is the body system composed of bones and cartilage and performs the following critical functions for the human body: supports the body. Ligaments. some bones protect your internal organs. for example, your skull safely encloses your brain, and your ribcage shields your heart, lungs and other organs near your chest. bones contain and protect your bone marrow. bone marrow is a soft, fatty tissue that produces critical cells, including: advertisement. An introduction to bones. we discuss their function, the different types of bones in the human body, and the cells that are involved. below is a 3d map of the skeletal system. click to explore. Main bones of the skeletal system. we’ll begin by looking at the skeletal system. as the name implies, the structural and functional unit is bone–a highly specialized and hard connective tissue. bones can be classified according to two major criteria, yielding different types of bones: compact and spongy bone (according to strength).
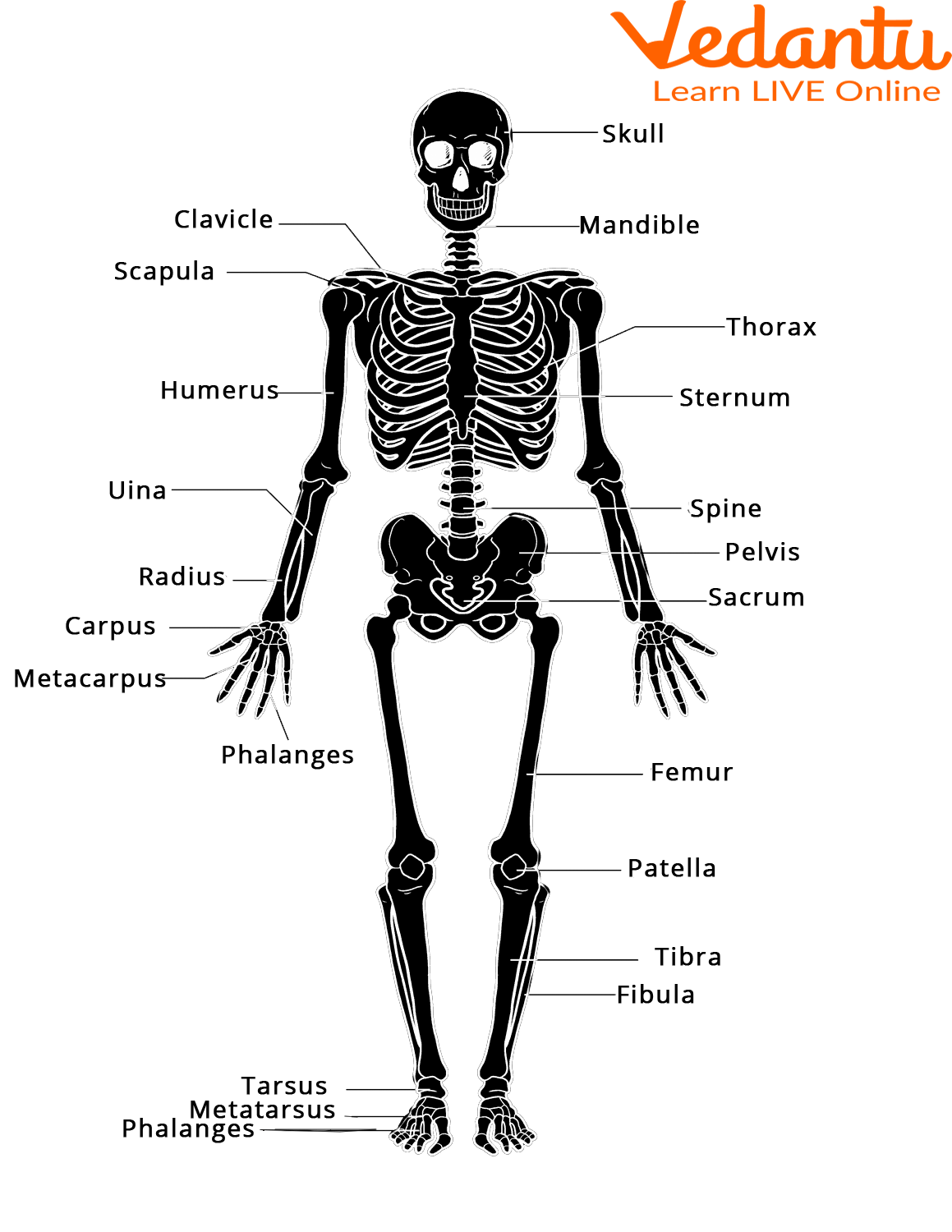
Human Skeletal System Learn Definition Functions And Facts An introduction to bones. we discuss their function, the different types of bones in the human body, and the cells that are involved. below is a 3d map of the skeletal system. click to explore. Main bones of the skeletal system. we’ll begin by looking at the skeletal system. as the name implies, the structural and functional unit is bone–a highly specialized and hard connective tissue. bones can be classified according to two major criteria, yielding different types of bones: compact and spongy bone (according to strength).
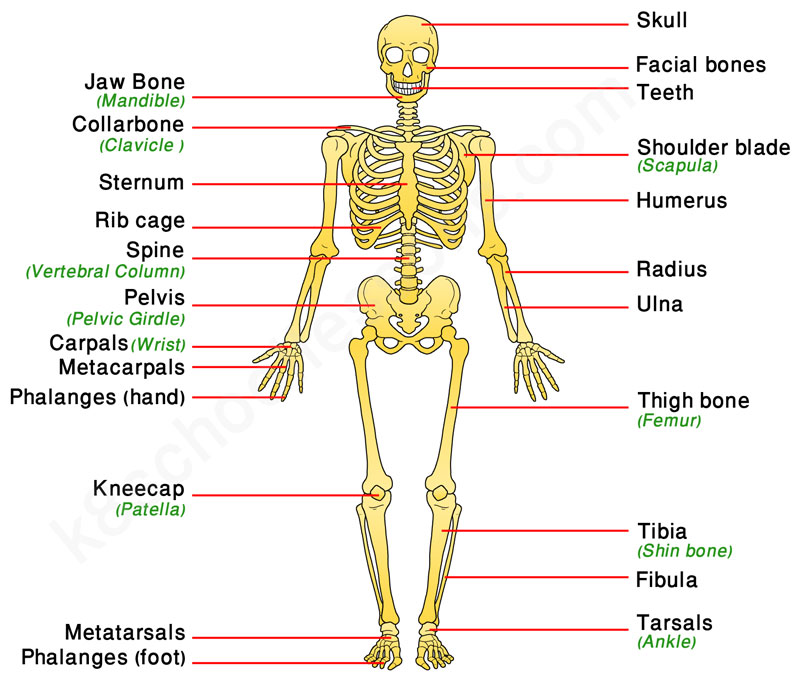
Human Skeletal System Human Body Facts Skeleton Bones Facts

Comments are closed.