The Difference Between Epileptic And Non Epileptic Seizures

What Is A Non Epileptic Seizure Special Needs Resource And Training Extremely low blood sugar. brain damage from stroke, brain surgery, or head injury. although some causes are the same between epileptic and non epileptic seizures, the difference your doctor will look for is whether the brain’s electrical activity is being disrupted. results from an eeg will look differently if epilepsy is not the cause. Seizures that are not due to epilepsy are sometimes called 'non epileptic seizures'. they can have a physical cause such as low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) or may be related to how the heart is working. or they may have a psychological cause. the most common type of non epileptic seizures (nes) is functional (sometimes called dissociative.

Psychogenic Non Epileptic Seizures Formulating A Differential The signs and symptoms of nes resemble those of epileptic seizures but vary between adults and children. adults. when an adult has a nonepileptic seizure, their symptoms may include:. Therapist. the unconscious processes that give rise to non epileptic seizures also may cause or contribute to other con ditions, such as depression and anxiety, which need to be identified and treated. non epileptic seizures differ from other psychogenic disor ders in one important aspect: non epileptic seizures can. Seizures come in many forms and are triggered by a number of events and conditions. one seizure alone doesn’t mean you have epilepsy, but if you have two or more seizures, you may be diagnosed. In adults, the most common imitators of epilepsy are syncope and psychogenic non epileptic seizures (pnes), followed by migraine, parasomnias, cerebrovascular disease including transitory ischaemic attack (tia), and movement disorders such as paroxysmal dystonia and non epileptic myoclonus (scheepers et al., 1998; benbadis, 2009; xu et al.
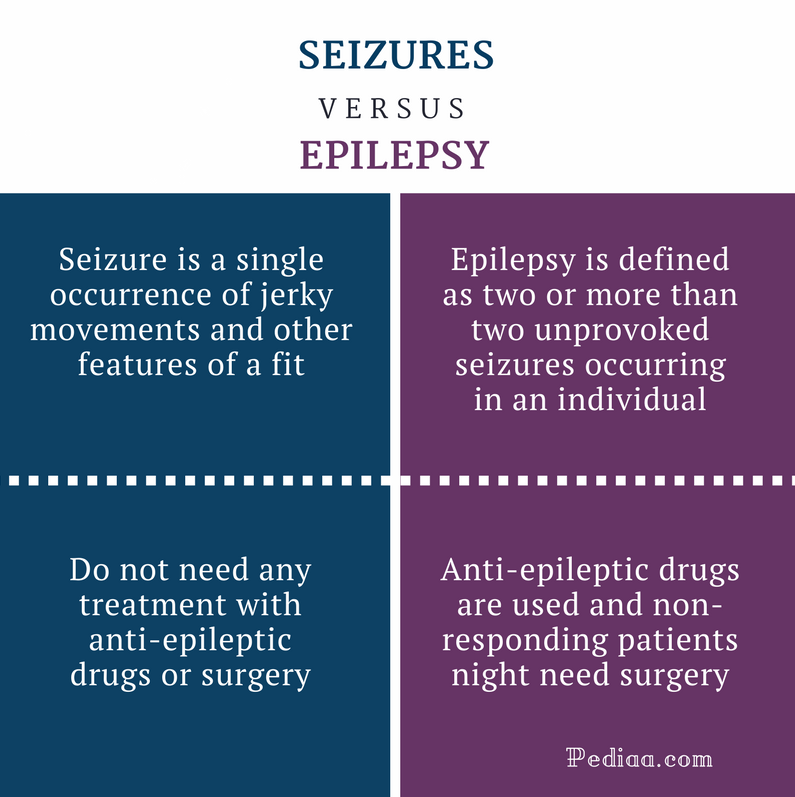
Difference Between Seizures And Epilepsy Clinical Features Types Seizures come in many forms and are triggered by a number of events and conditions. one seizure alone doesn’t mean you have epilepsy, but if you have two or more seizures, you may be diagnosed. In adults, the most common imitators of epilepsy are syncope and psychogenic non epileptic seizures (pnes), followed by migraine, parasomnias, cerebrovascular disease including transitory ischaemic attack (tia), and movement disorders such as paroxysmal dystonia and non epileptic myoclonus (scheepers et al., 1998; benbadis, 2009; xu et al. Non epileptic events may result in “blacking out” briefly. there may be hyperventilation, trembling, shuddering or confusion. visual disturbances, loss of speech, numbness or weakness may also occur. one or more limbs may undergo rhythmic shaking. significant shaking of all four limbs may resemble a “grand mal” seizure. A seizure happens when there is abnormal electrical activity in the brain, and it has numerous possible causes. in epilepsy, seizures happen without a clear cause. about 10% of people experience a.
Psychogenic Non Epileptic Seizures Carlat Publishing Non epileptic events may result in “blacking out” briefly. there may be hyperventilation, trembling, shuddering or confusion. visual disturbances, loss of speech, numbness or weakness may also occur. one or more limbs may undergo rhythmic shaking. significant shaking of all four limbs may resemble a “grand mal” seizure. A seizure happens when there is abnormal electrical activity in the brain, and it has numerous possible causes. in epilepsy, seizures happen without a clear cause. about 10% of people experience a.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/epilepsy-overview-4155857_final_edited-dcaf959b3f214bc3b6b6e48302a5430a.png)
Epilepsy Overview And More
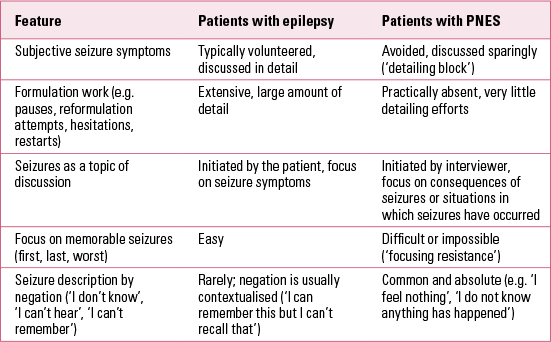
Psychogenic Non Epileptic Seizures Aetiology Diagnosis And Management

Comments are closed.