The Blood Brain Barrier Medical Short Illustration Brain Shorts

Blood Brain Barrier Medical Illustration Medivisuals The blood vessels that vascularize the central nervous system (cns) possess unique properties, termed the blood–brain barrier, which allow these vessels to t. Definition. blood brain barrier (bbb) is a selectively permeable membrane regulates the passage of a multitude of large and small molecules into the microenvironment of the neurons. it achieves this feat by with the aid of multiple cellular transport channels scattered along the membrane. these include:.
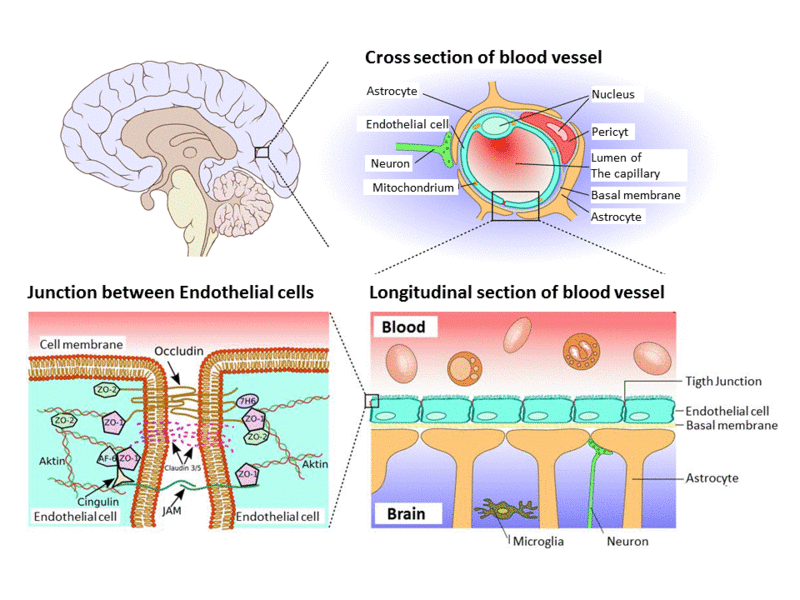
Blood Brain Barrier The blood brain barrier helps block harmful substances, such as toxins and bacteria from entering the brain. but, scientists knew that the brain also depends upon the delivery of hormones and key nutrients, including glucose and several amino acids, from other organs of the body. Blood brain barrier. your blood brain barrier (bbb) is a tightly locked layer of cells that defend your brain from harmful substances, germs and other things that could cause damage. it’s a key part of maintaining your brain health. it also holds good things inside your brain, maintaining the organ’s delicate chemical balance. The blood brain barrier (bbb) is a selective semi permeable membrane between the blood and the interstitium of the brain, allowing cerebral blood vessels to regulate molecule and ion movement between the blood and the brain.[1] the bbb is composed of endothelial cells (ecs), pericytes (pcs), capillary basement membrane, and astrocyte end feet, all of which aim to shield the brain from toxic. The blood–brain barrier (bbb) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system, thus protecting the brain from harmful or unwanted substances in the blood. [1] the blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial.
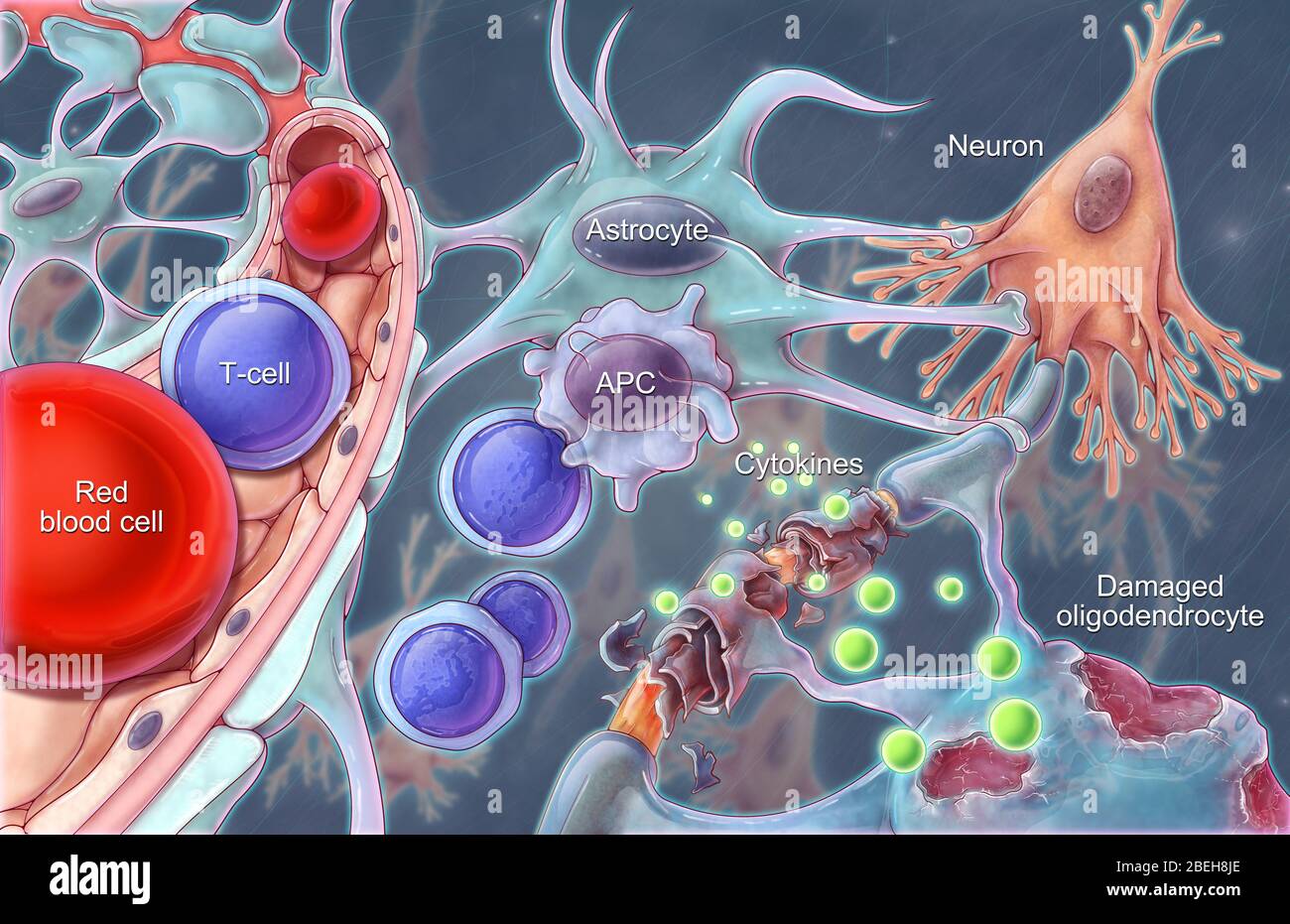
Ms Blood Brain Barrier Illustration Stock Photo Alamy The blood brain barrier (bbb) is a selective semi permeable membrane between the blood and the interstitium of the brain, allowing cerebral blood vessels to regulate molecule and ion movement between the blood and the brain.[1] the bbb is composed of endothelial cells (ecs), pericytes (pcs), capillary basement membrane, and astrocyte end feet, all of which aim to shield the brain from toxic. The blood–brain barrier (bbb) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system, thus protecting the brain from harmful or unwanted substances in the blood. [1] the blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial. Abstract. the blood brain barrier (bbb) is a semipermeable and extremely selective system in the central nervous system of most vertebrates, that separates blood from the brain's extracellular fluid. it plays a vital role in regulating the transport of necessary materials for brain function, furthermore, protecting it from foreign substances in. As the name suggests, this is a barrier between the brain’s blood vessels (capillaries) and the cells and other components that make up brain tissue. whereas the skull, meninges and cerebrospinal fluid protect against physical damage, the blood–brain barrier provides a defence against disease causing pathogens and toxins that may be present.

Blood Brain Barrier Medical Illustration Medical Illustration Abstract. the blood brain barrier (bbb) is a semipermeable and extremely selective system in the central nervous system of most vertebrates, that separates blood from the brain's extracellular fluid. it plays a vital role in regulating the transport of necessary materials for brain function, furthermore, protecting it from foreign substances in. As the name suggests, this is a barrier between the brain’s blood vessels (capillaries) and the cells and other components that make up brain tissue. whereas the skull, meninges and cerebrospinal fluid protect against physical damage, the blood–brain barrier provides a defence against disease causing pathogens and toxins that may be present.

Comments are closed.