The Basic Structure Of The Atom Chemistry And Our Universe How It All Works
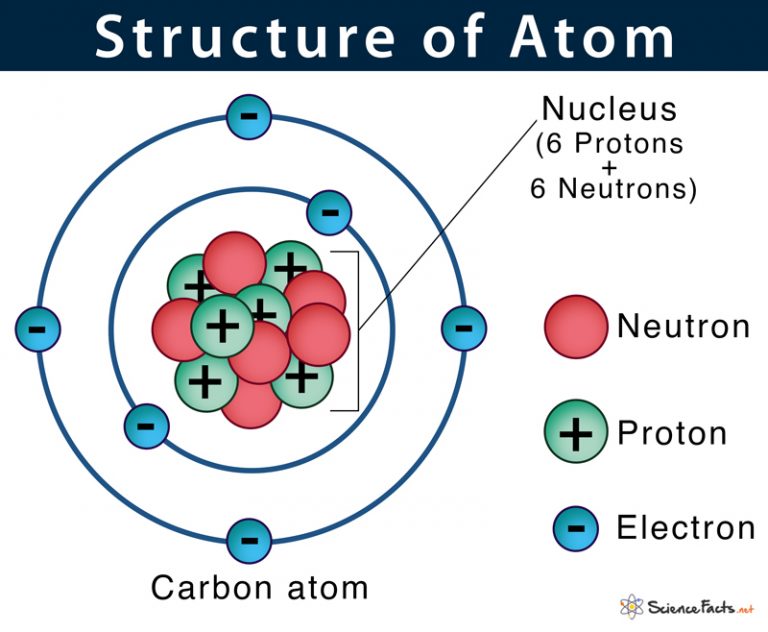
Atom Definition Structure Parts With Labeled Diagram Want to stream more content like this… and 1,000’s of courses, documentaries & more? 👉 👉 start your free trial of wondrium tinyurl yj45ynk8 👈. Understand how to estimate atomic mass and the concept of isotopes. investigate the formation of ions and their importance in chemical reactions. conclude with a comprehensive review of atomic structure, providing a solid foundation for further study in chemistry and its applications in understanding the universe.

Free Video The Basic Structure Of The Atom Chemistry And Our Since 1961, it has been defined with regard to the most abundant isotope of carbon, atoms of which are assigned masses of exactly 12 amu. (this isotope is known as “carbon 12” as will be discussed later in this module.) thus, one amu is exactly 1 12 1 12 of the mass of one carbon 12 atom: 1 amu = 1.6605 × × 10 −24 g. Each element has its own atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. 2.1: atomic theory and the structure of atoms is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. atoms are the ultimate building blocks of all matter. the modern atomic theory establishes the concepts of atoms and how. The term ‘atom’ was derived from the greek word ‘atomos’, meaning ‘indivisible’. the ancient greek and indian philosophers were the first to think atom as the basic unit of all matter in the universe. in the early 19 th century, scientists started understanding the atom’s structure with their inner parts in more detail. in 1926. Atom, the basic building block of all matter and chemistry. atoms can combine with other atoms to form molecules but cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary chemical processes. most of the atom is empty space. the rest consists of three basic types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
/GettyImages-141483984-56a133b65f9b58b7d0bcfdb1.jpg)
Basic Model Of The Atom Atomic Theory The term ‘atom’ was derived from the greek word ‘atomos’, meaning ‘indivisible’. the ancient greek and indian philosophers were the first to think atom as the basic unit of all matter in the universe. in the early 19 th century, scientists started understanding the atom’s structure with their inner parts in more detail. in 1926. Atom, the basic building block of all matter and chemistry. atoms can combine with other atoms to form molecules but cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary chemical processes. most of the atom is empty space. the rest consists of three basic types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Facts about the building blocks of the universe. atoms are made up of a nucleus, protons and electrons. when you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. here’s. The radius of an atom must be defined arbitrarily, such as the boundary in which the electron can be found with 95% probability. atomic radii are typically 30 300 pm. figure 2.1.1 2.1. 1: the structure of the nuclear atom with a central nucleus and surrounding electrons. the nucleus is itself composed of two kinds of particles.
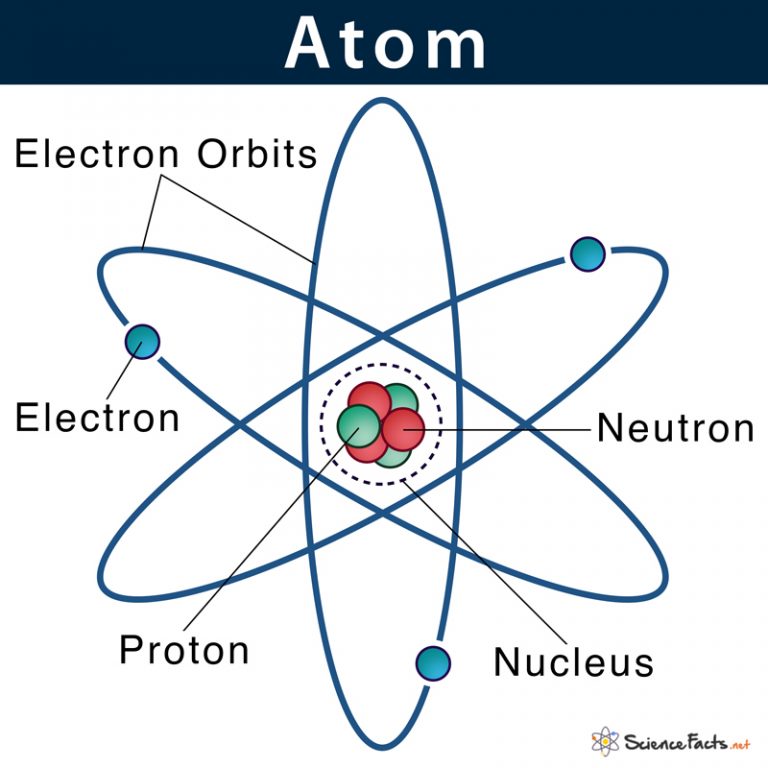
Atomic Nucleus Definition Structure Parts With Diagram Facts about the building blocks of the universe. atoms are made up of a nucleus, protons and electrons. when you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. here’s. The radius of an atom must be defined arbitrarily, such as the boundary in which the electron can be found with 95% probability. atomic radii are typically 30 300 pm. figure 2.1.1 2.1. 1: the structure of the nuclear atom with a central nucleus and surrounding electrons. the nucleus is itself composed of two kinds of particles.

The Structure Of The Atom Gcse Physics Combined Science Aqa

Comments are closed.