The Analysis Of Consumer Choice

The Analysis Of Consumer Choice The model of utility theory that economists have constructed to explain consumer choice assumes that consumers will try to maximize their utility. for example, when you decided to keep the ice cream bar and return the cookies, you, consciously or not, applied the marginal decision rule to the problem of maximizing your utility: you bought the. The theory of consumer choice assumes consumers wish to maximise their utility through the optimal combination of goods given their limited budget. to illustrate how consumers choose between different combinations of goods we can use equi marginal principle and indifference curves and budget lines. consumer equilibrium equimarginal.

The Analysis Of Consumer Choice Pdf Utility Marginal Utility Algebraically, we can write the budget constraint for two goods x and y as: equation 7.7. p x q x p y q y ≤ b. where px and py are the prices of goods x and y and qx and qy are the quantities of goods x and y chosen. the total income available to spend on the two goods is b, the consumer’s budget. In almost all cases, consumer choices are driven by prices. as price goes up, the quantity that consumers demand goes down. this correlation between the price of goods and the willingness to make purchases is represented clearly by the generation of a demand curve (with price as the y axis and quantity as the x axis). Equation 7.1. mux px> muy py m u x p x> m u y p y. the marginal benefit of shifting $1 from good y to the consumption of good x exceeds the marginal cost. in terms of utility, the gain from spending an additional $1 on good x exceeds the loss in utility from spending $1 less on good y. the consumer can increase utility by shifting spending from. Consumption choices. economic analysis of household behavior is based on the assumption that people seek the highest level of utility or satisfaction. individuals are the only judge of their own utility. in general, greater consumption of a good brings higher total utility. however, the additional utility received from each unit of greater.

The Analysis Of Consumer Choice Equation 7.1. mux px> muy py m u x p x> m u y p y. the marginal benefit of shifting $1 from good y to the consumption of good x exceeds the marginal cost. in terms of utility, the gain from spending an additional $1 on good x exceeds the loss in utility from spending $1 less on good y. the consumer can increase utility by shifting spending from. Consumption choices. economic analysis of household behavior is based on the assumption that people seek the highest level of utility or satisfaction. individuals are the only judge of their own utility. in general, greater consumption of a good brings higher total utility. however, the additional utility received from each unit of greater. Moreover, an operational data analytics (oda) framework is presented to estimate the general consumer choice model using data. this framework, generalizing the existing estimation methods for specific structural models, strikes a delicate balance between the (likely imprecise) structural knowledge and the data. The theory of consumer choice is the branch of microeconomics that relates preferences to consumption expenditures and to consumer demand curves.it analyzes how consumers maximize the desirability of their consumption (as measured by their preferences subject to limitations on their expenditures), by maximizing utility subject to a consumer budget constraint. [1].
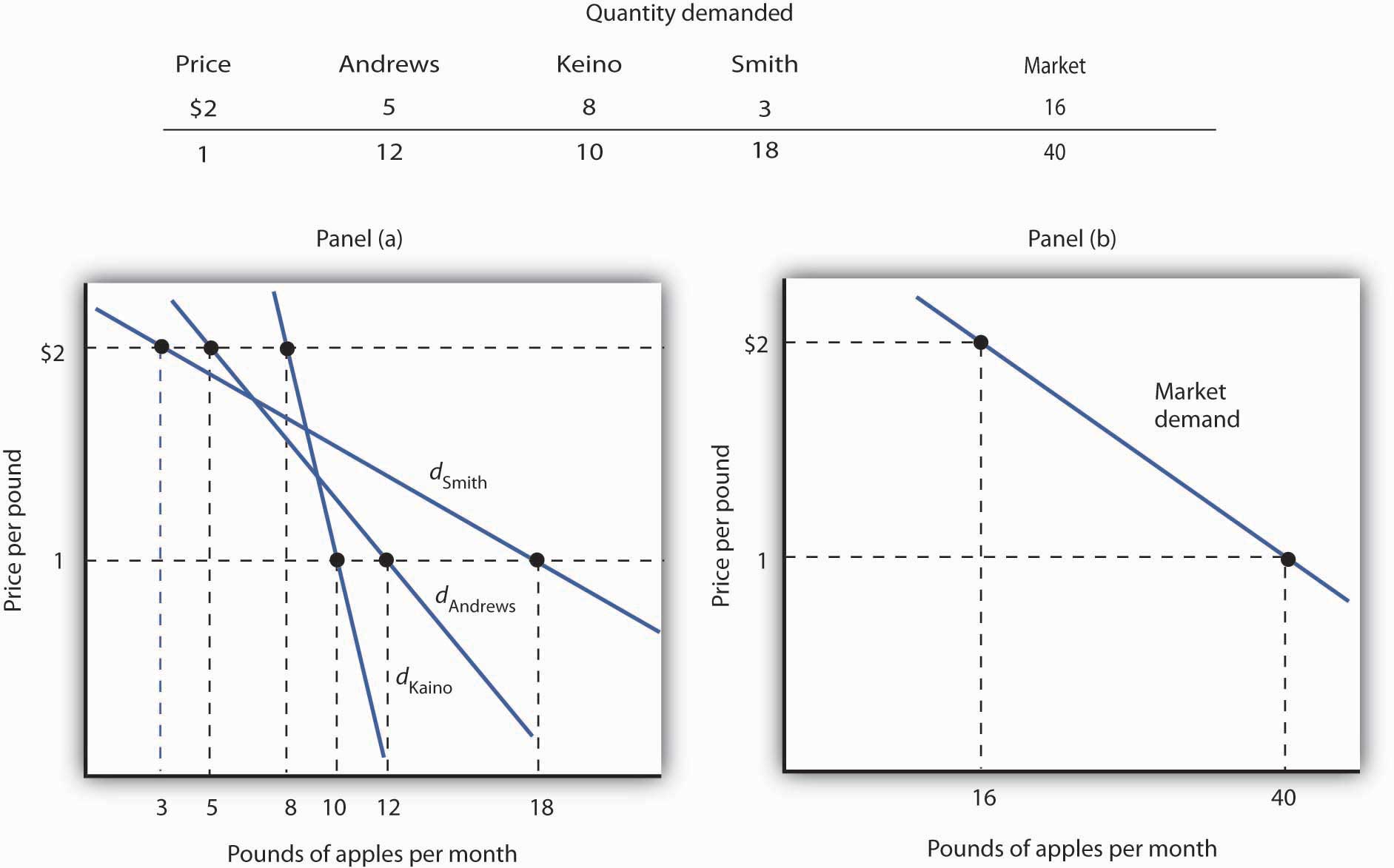
The Analysis Of Consumer Choice Moreover, an operational data analytics (oda) framework is presented to estimate the general consumer choice model using data. this framework, generalizing the existing estimation methods for specific structural models, strikes a delicate balance between the (likely imprecise) structural knowledge and the data. The theory of consumer choice is the branch of microeconomics that relates preferences to consumption expenditures and to consumer demand curves.it analyzes how consumers maximize the desirability of their consumption (as measured by their preferences subject to limitations on their expenditures), by maximizing utility subject to a consumer budget constraint. [1].

Ppt Chapter 6 Consumer Choice Demand Powerpoint Presentation Id

Comments are closed.