The 5 Demand Shift Factors Change In Demand Vs Change In Quantity
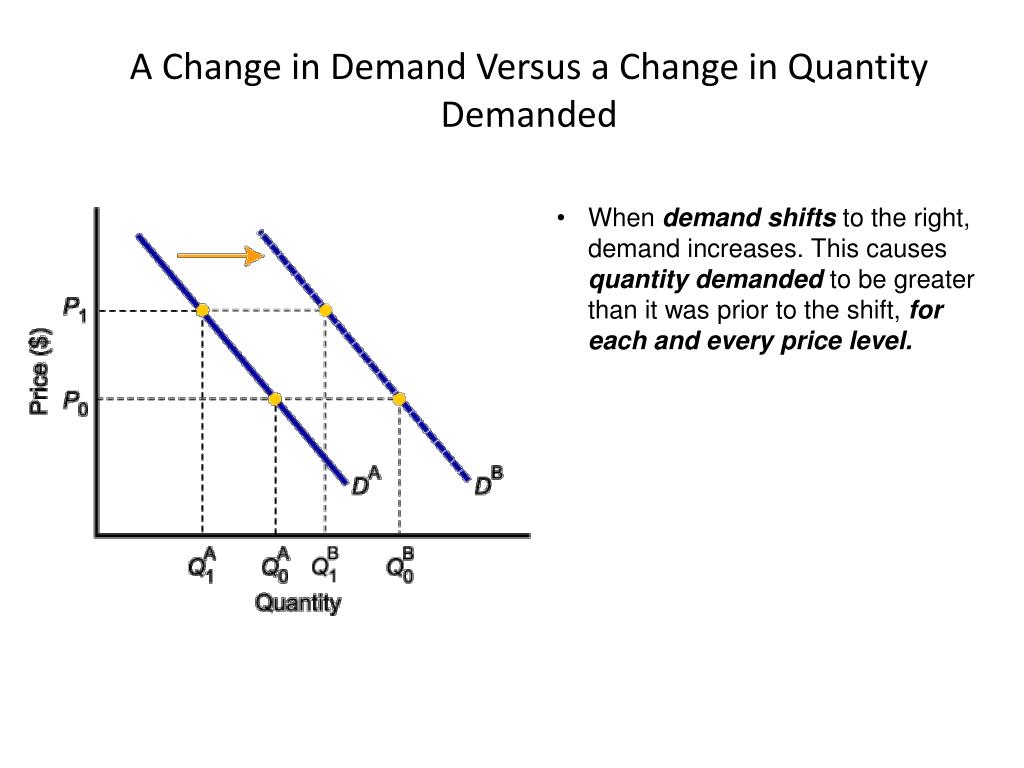
Ppt Change In Quantity Demanded Vs Change In Demand Powerpoint In economics there are 5 demand shift factors which move the demand curve to the right or left. in this video we explain what determines a shift in the deman. Course: ap®︎ college macroeconomics > unit 1. lesson 4: demand. law of demand. price of related products and demand. change in expected future prices and demand. changes in income, population, or preferences. normal and inferior goods. change in demand versus change in quantity demanded. lesson summary: demand and the determinants of demand.
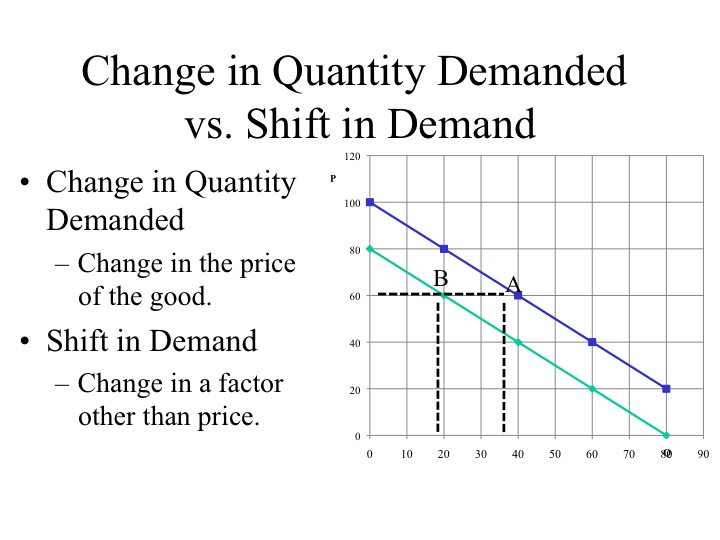
Econ 150 Microeconomics The terms, change in quantity demanded refers to expansion or contraction of demand, while change in demand means increase or decrease in demand. 1. expansion and contraction of demand: the variations in the quantities demanded of a product with change in its price, while other factors are at constant, are termed as expansion or contraction of. A change in the price of a good or service causes a change in the quantity demanded—a movement along the demand curve. a change in a demand shifter causes a change in demand, which is shown as a shift of the demand curve. demand shifters include preferences, the prices of related goods and services, income, demographic characteristics, and. Figure 1. change in demand. a change in demand means that the entire demand curve shifts either left or right. the initial demand curve d 0 shifts to become either d 1 or d 2. this could be caused by a shift in tastes, changes in population, changes in income, prices of substitute or complement goods, or changes future expectations. a change in. It can be a little confusing, so let's review. a change in quantity demanded refers to a movement along a fixed demand curve that's caused by a change in price. a change in demand refers to a shift in the demand curve that's caused by one of the shifters: income, preferences, changes in the price of related goods and so on.

Shifting Supply And Demand Blended Economics Figure 1. change in demand. a change in demand means that the entire demand curve shifts either left or right. the initial demand curve d 0 shifts to become either d 1 or d 2. this could be caused by a shift in tastes, changes in population, changes in income, prices of substitute or complement goods, or changes future expectations. a change in. It can be a little confusing, so let's review. a change in quantity demanded refers to a movement along a fixed demand curve that's caused by a change in price. a change in demand refers to a shift in the demand curve that's caused by one of the shifters: income, preferences, changes in the price of related goods and so on. Refer to fig 3.2, when the price of tea, a substitute for coffee rises, more coffee is demanded at each price, as people substitute away from tea and consume more coffee. the result is a shift in demand from the original curve d1 to d2. the quantity of coffee demanded at a price of $6 per pound rises from 25 million pounds per month (point a. A change in demand represents a shift in consumer desire to purchase a particular good or service, irrespective of a variation in its price. the change could be triggered by a shift in income.

Shift In Demand Vs Change In Quantity Demanded At Genoveva Davis Blog Refer to fig 3.2, when the price of tea, a substitute for coffee rises, more coffee is demanded at each price, as people substitute away from tea and consume more coffee. the result is a shift in demand from the original curve d1 to d2. the quantity of coffee demanded at a price of $6 per pound rises from 25 million pounds per month (point a. A change in demand represents a shift in consumer desire to purchase a particular good or service, irrespective of a variation in its price. the change could be triggered by a shift in income.

Comments are closed.