Tectonic Reconstruction And Evolution Of Se Asia A The Se Tibetan

Tectonic Reconstruction And Evolution Of Se Asia A The Se Tibetan However, no attempt has yet been made to summarize the long term sedimentary delivery and paleogeographic evolution of mainland se asia, in particular the se tibetan uplift and its surrounding areas. this study, on the other hand, is unique with regards of extensive compilation of both provenance data and offshore depositional records. The philippine sea plate is the largest of these, and provides an important boundary for reconstruction of se asia and northern australia from its motion history (hall et al., 1995a). however, many of the marginal basins of se asia lack magnetic anomalies, and many have not been sampled by the ocean drilling programme, so that their ages and.

Se Asian Plate Tectonic Reconstruction Parameters Implemented Into The The se tibetan plateau, tectonically situated in the eastern india eurasia oblique convergence zone, has experienced multiple stages of deformation since the cenozoic. three major tectonic boundaries—the ailaoshan red river, chongshan lincang inthanon, and gaoligong mogok shear zones—delineate the first order tectonic framework in this region. the most striking structural features in the. Tectonic reconstruction and evolution of se asia. (a) the se tibetan plateau may have experienced crustal shortening and thickening during the eocene early oligocene, forming extensive folds and. However, a critical element in understanding orogenic processes is the accurate dating of events. as one of the most important accommodation zones during the india asia collision, the tectonic deformation of the southeast (se) margin of the tibetan plateau provides meaningful constraints on the tectonic evolution of the tibetan plateau. The india–asia collision zone consists of the following major tectonic domains: (1) the himalayan orogen, (2) the tibetan plateau, (3) the southeast asia extrusion system, (4) the central asia deformation domain stretching from the tian shan in the south to the baikal rift zone in the north, (5) the north china deformation domain, and (6) the.
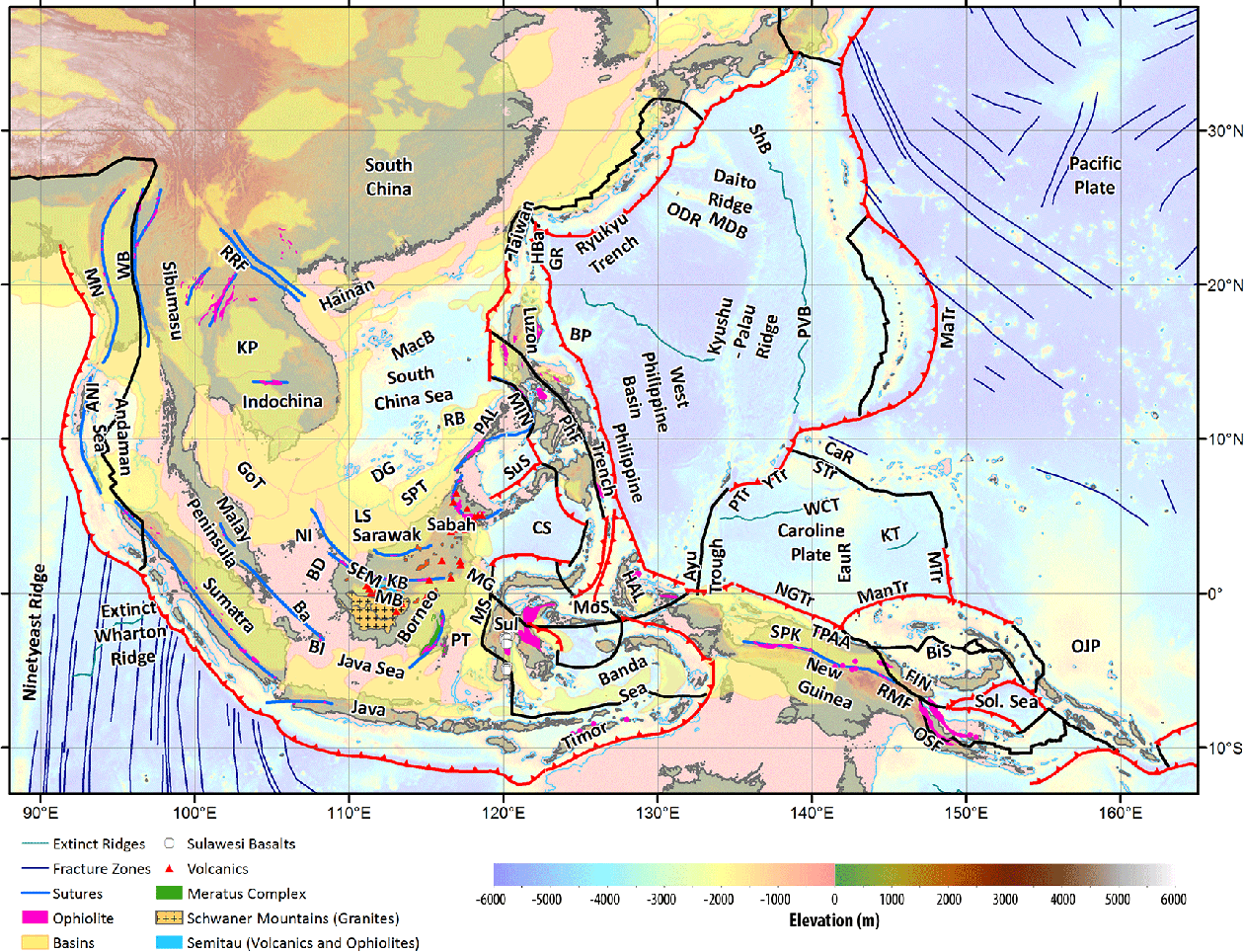
Figure 1 From The Cretaceous And Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution Of However, a critical element in understanding orogenic processes is the accurate dating of events. as one of the most important accommodation zones during the india asia collision, the tectonic deformation of the southeast (se) margin of the tibetan plateau provides meaningful constraints on the tectonic evolution of the tibetan plateau. The india–asia collision zone consists of the following major tectonic domains: (1) the himalayan orogen, (2) the tibetan plateau, (3) the southeast asia extrusion system, (4) the central asia deformation domain stretching from the tian shan in the south to the baikal rift zone in the north, (5) the north china deformation domain, and (6) the. An improved understanding of the elevation history of the tibetan plateau is crucial in discriminating among the various tectonic models for the evolution of the india asia continental collision. We use these paleomagnetic data to kinematically restore cenozoic tectonic motions of the core of se asia relative to indochina. because sundaland is a large elongated block, any rotation of this block has a direct effect on the orientation of the sunda trench that bounds the block in the southwest.

A Generalized Tectonic Map Of The Tibetan Plateau And Se Asia An improved understanding of the elevation history of the tibetan plateau is crucial in discriminating among the various tectonic models for the evolution of the india asia continental collision. We use these paleomagnetic data to kinematically restore cenozoic tectonic motions of the core of se asia relative to indochina. because sundaland is a large elongated block, any rotation of this block has a direct effect on the orientation of the sunda trench that bounds the block in the southwest.

Comments are closed.