Structure Of Dna Function Summary Diagram Model

Structure Of Dna Function Summary Diagram Model It is called double helix because, in the three dimensional model, dna molecule was seen to have a spiral or helical structure made up of two polynucleotide chains. this helical structure was made when the two polynucleotide chains are wound around each other. 3. the polynucleotide chains are coiled anti parallel. Dna structure and functions. dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, a macromolecule that carries genetic information in all living organisms, from the tiniest microorganisms to the most complex multicellular humans. dna is a fundamental molecule that holds life’s blueprint. within a eukaryotic cell (plant and animal), they are found inside the.

Dna Structure Visual Ly The structure and function of dna. biologists in the 1940s had difficulty in accepting dna as the genetic material because of the apparent simplicity of its chemistry. dna was known to be a long polymer composed of only four types of subunits, which resemble one another chemically. early in the 1950s, dna was first examined by x ray diffraction. Now let’s consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). the building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in. Dna molecules are polymers and are made up of many smaller molecules, called nucleotides. each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base. dna molecules consist of two dna strands, which are twisted around one another to form a spiral shape known as the double helix. the double helix structure of dna was. Dna definition. deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. dna is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. large compressed dna molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the.
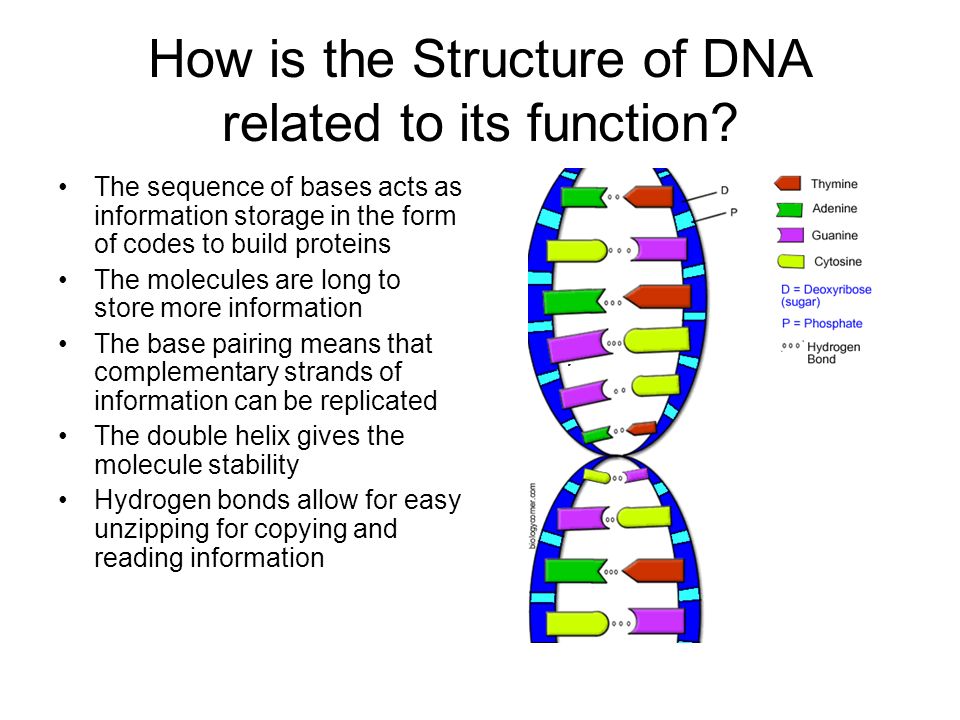
Dna Structure And Function Protein Synthesis Parker S Ap Bio 3rd Period Dna molecules are polymers and are made up of many smaller molecules, called nucleotides. each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base. dna molecules consist of two dna strands, which are twisted around one another to form a spiral shape known as the double helix. the double helix structure of dna was. Dna definition. deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. dna is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. large compressed dna molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the. In fact, watson and crick were worried that they would be "scooped" by pauling, who proposed a different model for the three dimensional structure of dna just months before they did. in the end. The pyrimidines, cytosine (c) and thymine (t), are smaller nitrogenous bases that have only a six carbon ring structure. figure 10.12 nitrogenous bases within dna are categorized into the two ringed purines adenine and guanine and the single ringed pyrimidines cytosine and thymine. thymine is unique to dna.
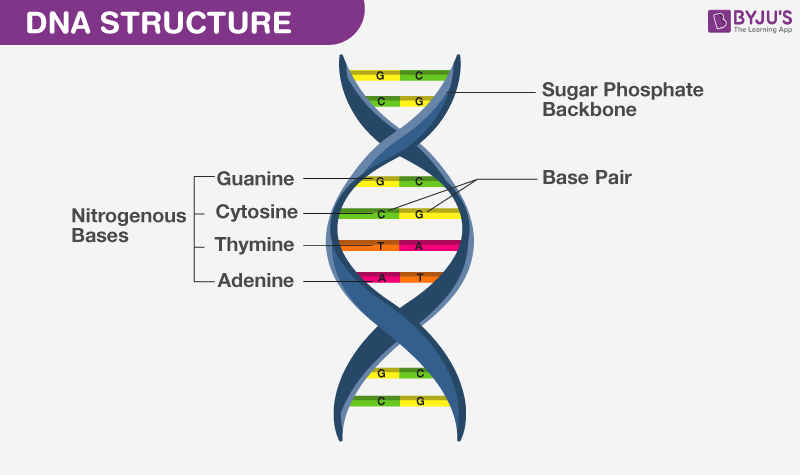
What Is Dna Meaning Dna Types Structure And Functions In fact, watson and crick were worried that they would be "scooped" by pauling, who proposed a different model for the three dimensional structure of dna just months before they did. in the end. The pyrimidines, cytosine (c) and thymine (t), are smaller nitrogenous bases that have only a six carbon ring structure. figure 10.12 nitrogenous bases within dna are categorized into the two ringed purines adenine and guanine and the single ringed pyrimidines cytosine and thymine. thymine is unique to dna.

Comments are closed.