Structure Of A Neuron Owlcation
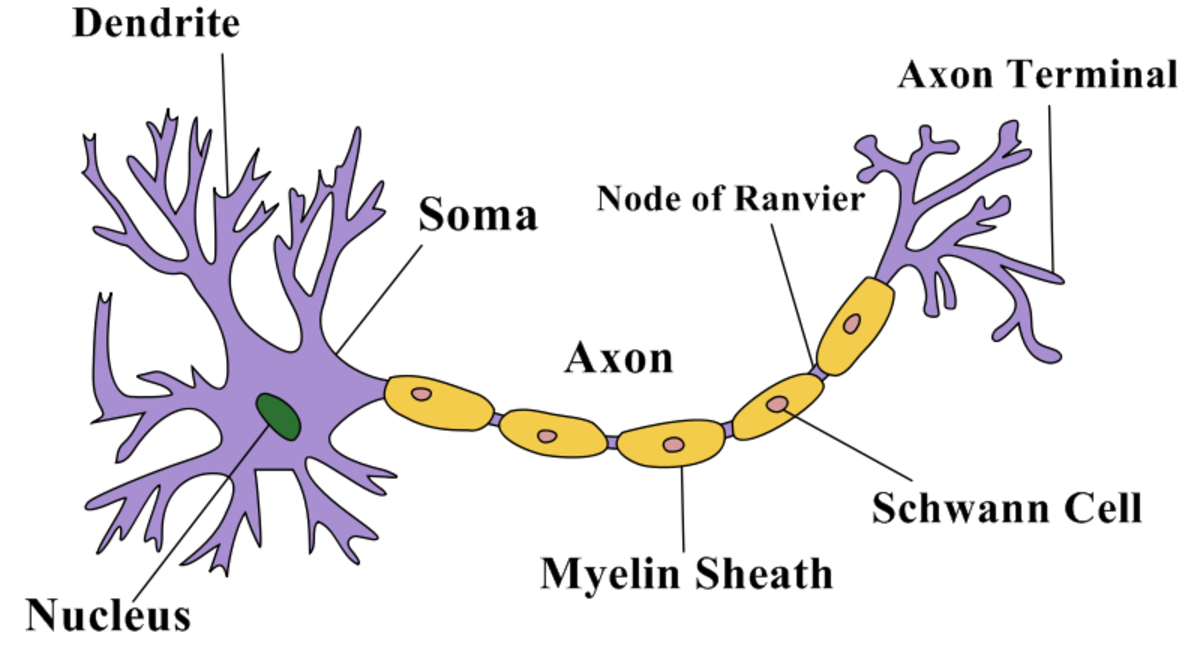
Structure Of A Neuron Owlcation The structure of a neuron. although neurons look complicated, their design is actually quite simple. the neuron is broken up into two major regions: a region for receiving and processing incoming information from other cells. a region for conducting and transmitting information to other cells. the type of information that is received, processed. Neurons and glia. the brain contains two types of cells, each being about the same in number. neurons are the centers of information reception, comprehension, and shipping in the brain, and glia are what maintain the surroundings of the neurons by acting as a scaffolding and a chemical regulator. in the human brain, roughly 86 billion neurons.
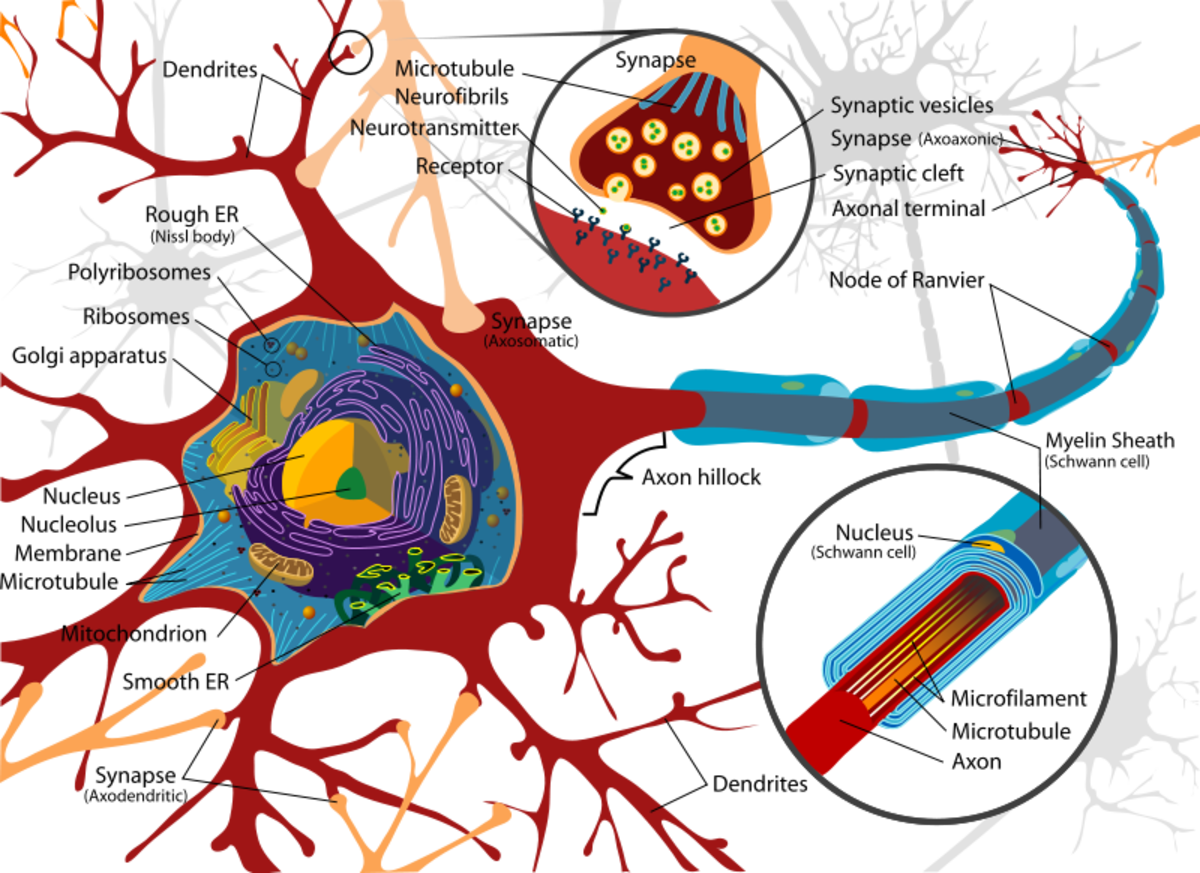
Structure Of A Neuron Owlcation The surface of a living brain is a pink grey color while the underneath is lighter. the surface of the brain is filled with "grey matter" that contains the cell bodies of the neurons in the brain. the cell body of a neuron contains its nucleus. the paler "white matter" is where the axons of the neurons are located. A neuron is a nerve cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system. neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites (which receive signals), and an axon (which sends signals). synaptic connections allow communication between neurons, facilitating the relay of information throughout the body. As such, neurons typically consist of four main functional parts which include the: receptive part (dendrites), which receive and conduct electrical signals toward the cell body. integrative part (usually equated with the cell body soma), containing the nucleus and most of the cell's organelles, acting as the trophic center of the entire neuron. General structure of the neuron another general structure of the neuron cell body (soma) a b figure 1 1a and b generic structure of neuron. this is an artist’sconception of the generic structure of a neuron. all neurons have a cell body known as the soma, which is the command center of the nerve and contains the nucleus of the cell.
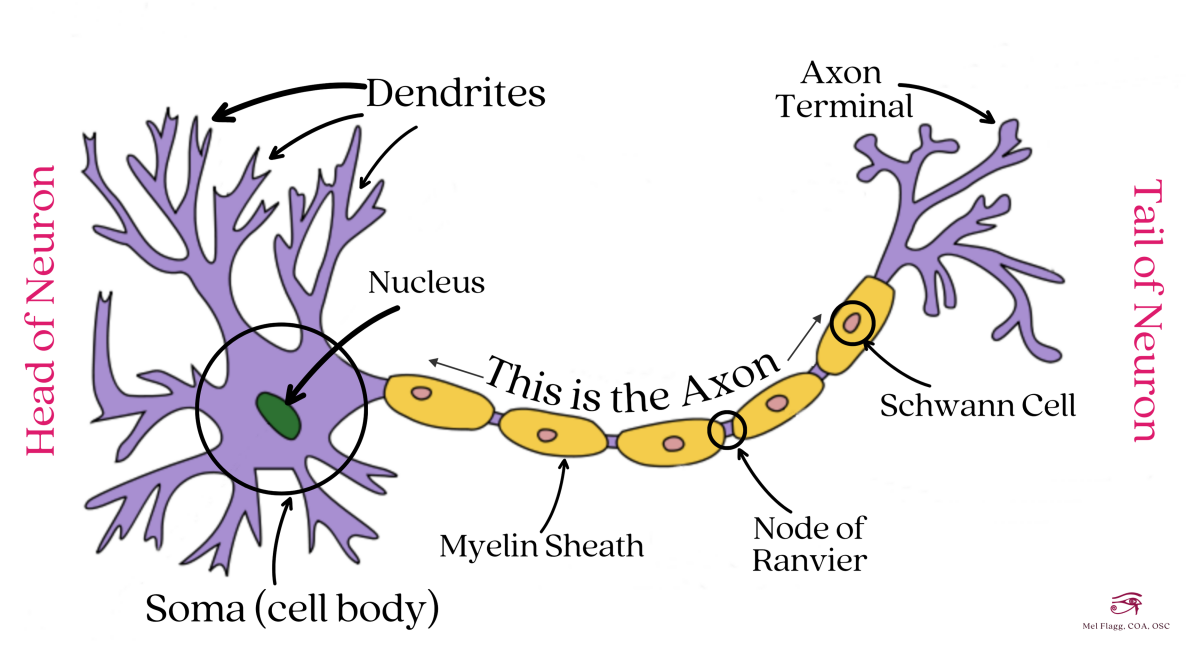
Structure Of A Neuron Owlcation As such, neurons typically consist of four main functional parts which include the: receptive part (dendrites), which receive and conduct electrical signals toward the cell body. integrative part (usually equated with the cell body soma), containing the nucleus and most of the cell's organelles, acting as the trophic center of the entire neuron. General structure of the neuron another general structure of the neuron cell body (soma) a b figure 1 1a and b generic structure of neuron. this is an artist’sconception of the generic structure of a neuron. all neurons have a cell body known as the soma, which is the command center of the nerve and contains the nucleus of the cell. Some neurons are responsible for taste while others sense pain. traditionally, scientists classify neurons based on function into three broad types: sensory. motor. interneurons. sensory, motor, and interneurons are the most common neuron types, of these, interneurons are the most abundant. Overview of neuron structure and function. the membrane potential. electrotonic and action potentials. saltatory conduction in neurons. neuronal synapses (chemical) the synapse. neurotransmitters and receptors. q & a: neuron depolarization, hyperpolarization, and action potentials. overview of the functions of the cerebral cortex.

Neuroscience Basics The Neuron Owlcation Some neurons are responsible for taste while others sense pain. traditionally, scientists classify neurons based on function into three broad types: sensory. motor. interneurons. sensory, motor, and interneurons are the most common neuron types, of these, interneurons are the most abundant. Overview of neuron structure and function. the membrane potential. electrotonic and action potentials. saltatory conduction in neurons. neuronal synapses (chemical) the synapse. neurotransmitters and receptors. q & a: neuron depolarization, hyperpolarization, and action potentials. overview of the functions of the cerebral cortex.

Comments are closed.