Stemi St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis Criteria Ecg
Stemi St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis Criteria Ecg Stemi (st elevation acute myocardial infarction): epidemiology, diagnosis (ecg), criteria & management. acute stemi (st elevation myocardial infarction) is the most severe manifestation of coronary artery disease. this chapter deals with the pathophysiology, definitions, criteria and management of patients with acute stemi. An acute st segment elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) arises from the occlusion of 1 or more coronary arteries, causing transmural myocardial ischemia and subsequent myocardial injury or necrosis. risk factors for stemi include hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and diabetes, which contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and.
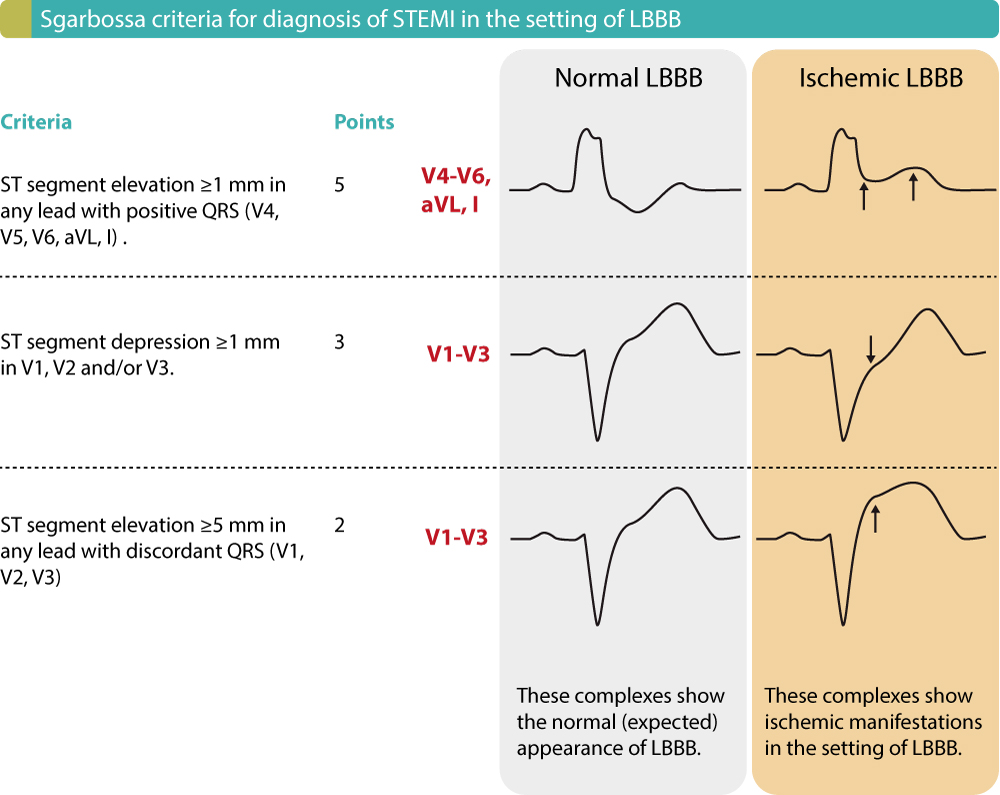
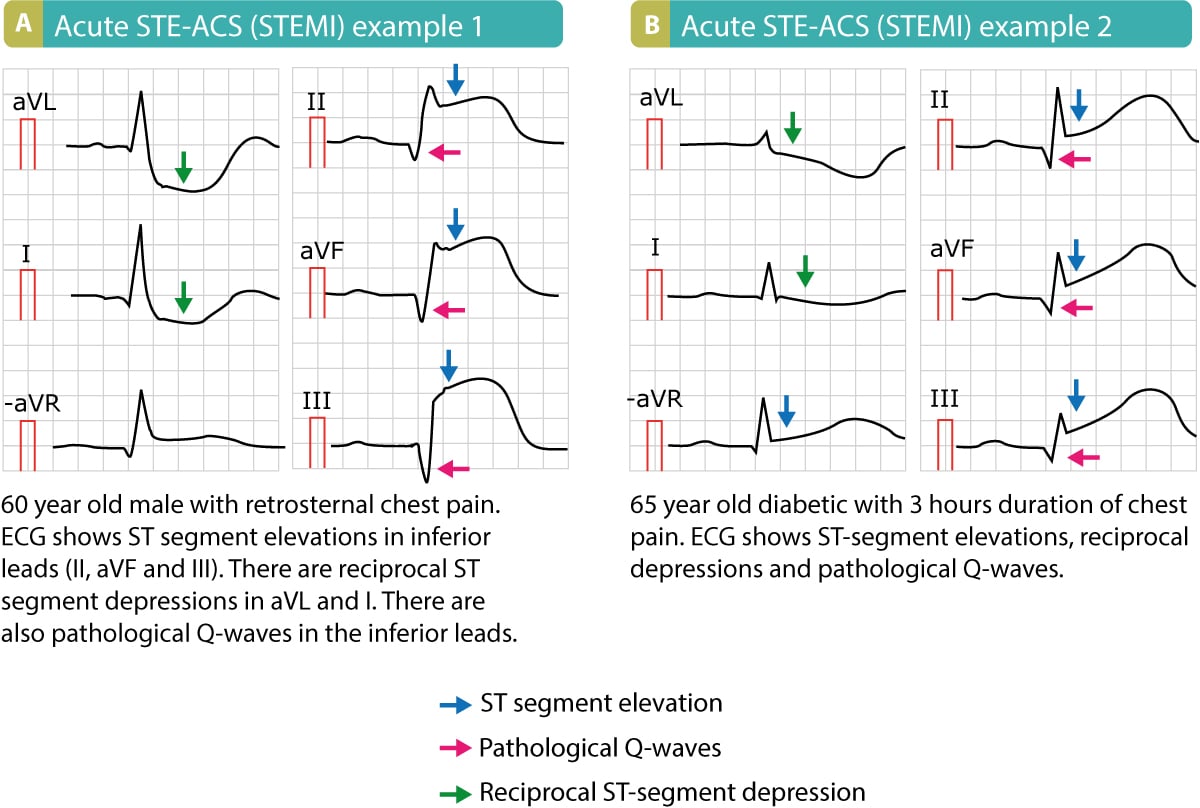
Stemi St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis Criteria Ecg Acute coronary syndromes. spontaneous myocardial infarction related to atherosclerotic plaque rupture, ulceration, erosion, or dissection with resulting intraluminal thrombus in one or more of the coronary arteries leading to decreased myocardial blood flow or distal platelet emboli with ensuing myocyte necrosis. Normal mb levels 3 to 4 hours after the last episode of symptoms rule out myocardial infarction. ecg criteria for ischemia & infarction ecg in myocardial ischemia. acute myocardial ischemia manifests on ecg as st deviation (st elevation or st depression) and t wave changes. st deviation and t wave changes are collectively referred to as st t. In stemi ste acs, on the other hand, reciprocal st segment depressions are typical and there may be t wave inversions in the same leads showing st segment elevation. t wave inversion may, however, occur in perimyocarditis, but only after normalization of the st segment elevations (i.e these two ecg changes do not occur simultaneously). Although considerable improvement has occurred in the process of care for patients with st elevation myocardial infarction (stemi), room for improvement exists. 1–3 the purpose of the present guideline is to focus on the numerous advances in the diagnosis and management of patients with stemi since 1999. this is reflected in the changed name.

Stemi St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis Criteria Ecg In stemi ste acs, on the other hand, reciprocal st segment depressions are typical and there may be t wave inversions in the same leads showing st segment elevation. t wave inversion may, however, occur in perimyocarditis, but only after normalization of the st segment elevations (i.e these two ecg changes do not occur simultaneously). Although considerable improvement has occurred in the process of care for patients with st elevation myocardial infarction (stemi), room for improvement exists. 1–3 the purpose of the present guideline is to focus on the numerous advances in the diagnosis and management of patients with stemi since 1999. this is reflected in the changed name. An acute st elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) is a clinical event characterised by transmural myocardial ischaemia resulting in myocardial injury or necrosis. it is one of three types of acute coronary syndrome. the other forms include unstable angina and non st elevation myocardial infarction (nstemi). the diagnosis of stemi requires the. Myocardial infarction is the medical term for a heart attack. an infarction is a blockage of blood flow to the myocardium, the heart muscle. that blockage causes the heart muscle to die. a stemi is a myocardial infarction that causes a distinct pattern on an electrocardiogram (abbreviated either as ecg or ekg).

Comments are closed.