Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy Of Structure
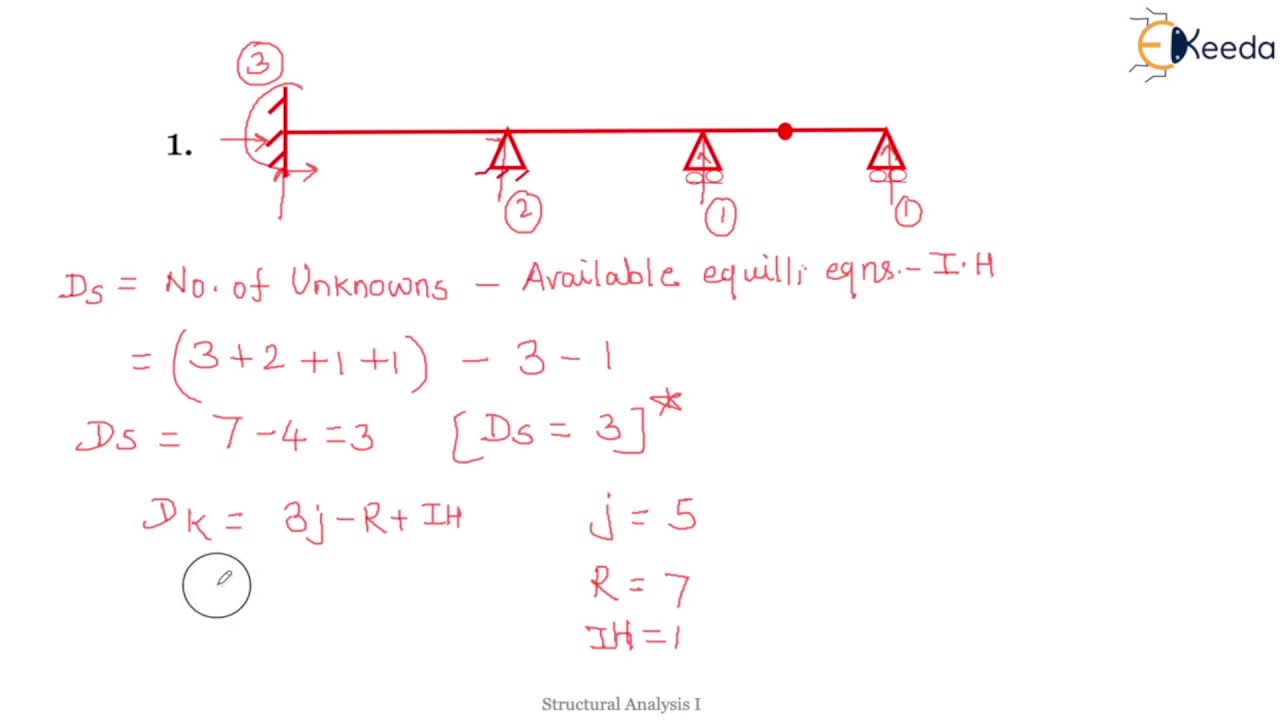
Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy For Beam Problem 3 And Problem 4 The total static indeterminacy is given by the sum of external static indeterminacy (dse) and internal static indeterminacy (dsi) what is kinematic indeterminacy? it is defined as the number of non zero joints displacement of the structure. For beams and framed structures, the formula below can be used to check the degree of static indeterminacy of the structure. d = s i 3m – 3p. where; d = degree of static indeterminacy. s = number of support reactions. i = number of internal forces in hinges (usually 2 per internal hinge) m = number of closed loops without hinges.

Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy Of Structure Ppt The number of independent deflections is called the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy or the number of active degrees of freedom. it encompasses all displacements and rotations of movable joints. the determination of the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy is briefly established in the following examples. q(x) a b c ωb ωc. An indeterminate structure is one whose unknown forces cannot be determined by the conditions of static equilibrium alone and will require, in addition, a consideration of the compatibility conditions of different parts of the structure for its complete analysis. furthermore, structures must be stable to be able to serve their desirable functions. The degree of static indeterminacy is equal to the number of redundant equations of equilibrium and depends on the number of members (m), joints (j), and external reaction components (r). examples are given to demonstrate calculating the degree of redundancy for different plane frame and grid structures. 1.1 static and kinematic indeterminacy. An indeterminate structure is one whose unknown forces cannot be determined by the conditions of static equilibrium alone and will require, in addition, a consideration of the compatibility conditions of different parts of the structure for its complete analysis. furthermore, structures must be stable to be able to serve their desirable functions.

Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy Of Structure Ppt The degree of static indeterminacy is equal to the number of redundant equations of equilibrium and depends on the number of members (m), joints (j), and external reaction components (r). examples are given to demonstrate calculating the degree of redundancy for different plane frame and grid structures. 1.1 static and kinematic indeterminacy. An indeterminate structure is one whose unknown forces cannot be determined by the conditions of static equilibrium alone and will require, in addition, a consideration of the compatibility conditions of different parts of the structure for its complete analysis. furthermore, structures must be stable to be able to serve their desirable functions. The calculation of static indeterminacy, denoted as ‘d s ‘, is essential for understanding how to analyze and design a structure effectively. it is determined by the formula: ds = r – e. where ‘r’ represents the number of unknown reactions and ‘e’ represents the number of equilibrium equations available. in three dimensional. Degree of static and kinematic indeterminacy video lecture from basic fundamental of structural analysis chapter of structural analysis 2 for engineering stu.

Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy Of Structure The calculation of static indeterminacy, denoted as ‘d s ‘, is essential for understanding how to analyze and design a structure effectively. it is determined by the formula: ds = r – e. where ‘r’ represents the number of unknown reactions and ‘e’ represents the number of equilibrium equations available. in three dimensional. Degree of static and kinematic indeterminacy video lecture from basic fundamental of structural analysis chapter of structural analysis 2 for engineering stu.

Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy Of Structure

Comments are closed.