Star And Sun Scale

Star And Sun Scale Magnitude (astronomy) in astronomy, magnitude is a measure of the brightness of an object, usually in a defined passband. an imprecise but systematic determination of the magnitude of objects was introduced in ancient times by hipparchus. magnitude values do not have a unit. the scale is logarithmic and defined such that a magnitude 1 star is. According to this ancient scale, the brightest stars in our sky are 1st magnitude. and the very dimmest stars visible to the eye alone are 6th magnitude. so, a 2nd magnitude star is modestly bright.

Star And Sun Scale A pure white star has a b v of about 0.2, our yellow sun is 0.63, orange red betelgeuse is 1.85, and the bluest star believed possible is –0.4, pale blue white. so successful was the ubv system that it was extended redward with r and i filters to define standard red and near infrared magnitudes. Absolute magnitude is defined as the apparent magnitude that a star or object would have if it were observed from a distance of 10 parsecs (33 light years; 3.1 × 10 14 kilometres; 1.9 × 10 14 miles). therefore, it is of greater use in stellar astrophysics since it refers to a property of a star regardless of how close it is to earth. The sun appears way brighter than rigel in our sky so its apparent magnitude is higher (magnitude −26.8 and 0.18, respectively). however, if we placed both the sun and rigel at 10 parsecs away from the earth, rigel would impressively outshine the sun. that’s because the distant star has a higher absolute magnitude: 6.69 vs 4.83 for the sun. 1 pixel = 1,000 km. this 2d visual model illustrates the scale of the sun and planets in our solar system, and their current distance from each other.
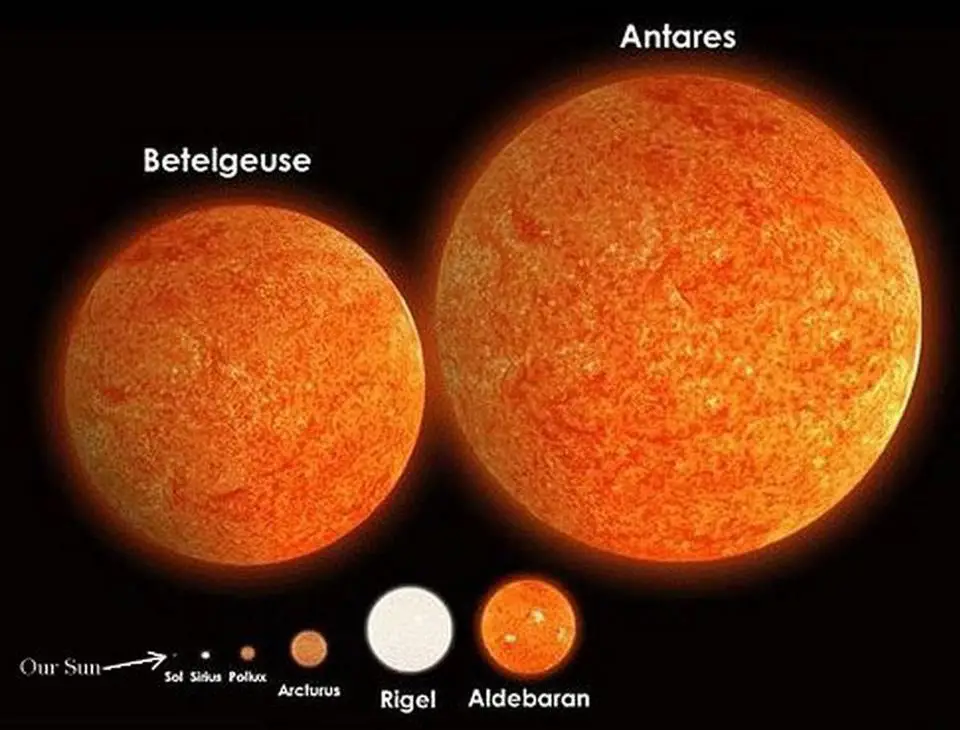
Star And Sun Scale The sun appears way brighter than rigel in our sky so its apparent magnitude is higher (magnitude −26.8 and 0.18, respectively). however, if we placed both the sun and rigel at 10 parsecs away from the earth, rigel would impressively outshine the sun. that’s because the distant star has a higher absolute magnitude: 6.69 vs 4.83 for the sun. 1 pixel = 1,000 km. this 2d visual model illustrates the scale of the sun and planets in our solar system, and their current distance from each other. Absolute magnitude. in astronomy, absolute magnitude (m) is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale; the more luminous (intrinsically bright) an object, the lower its magnitude number. an object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object. The sun is over 6 trillion times brighter than the faintest star visible to the naked eye. it's awkward to deal with numbers this large. as you will see below, the magnitude system is logarithmic, which turns the huge range in brightness ratios into a much smaller range in magnitude differences: the difference between the sun and the faintest.

Comments are closed.