Spectrum Management For 5g Applications

Low To High 5g Bands Explained Nybsys To use spectrum efficiently, some regulators are offering spectrum to non traditional players for private networks to support localized 5g applications. localized spectrum allows operators to tailor private networks according to their specific needs, especially for applications requiring a high degree of precision and low latency. However, after almost a decade of intense academic and industrial research on the 5g wireless networks and the subsequent commercial deployment, it has become clear that the 5g wireless networks will fall short in supporting the vision of the internet of everything (ioe), which will aim to provision the advanced bandwidth hungry applications such as augmented reality (ar), virtual reality (vr.
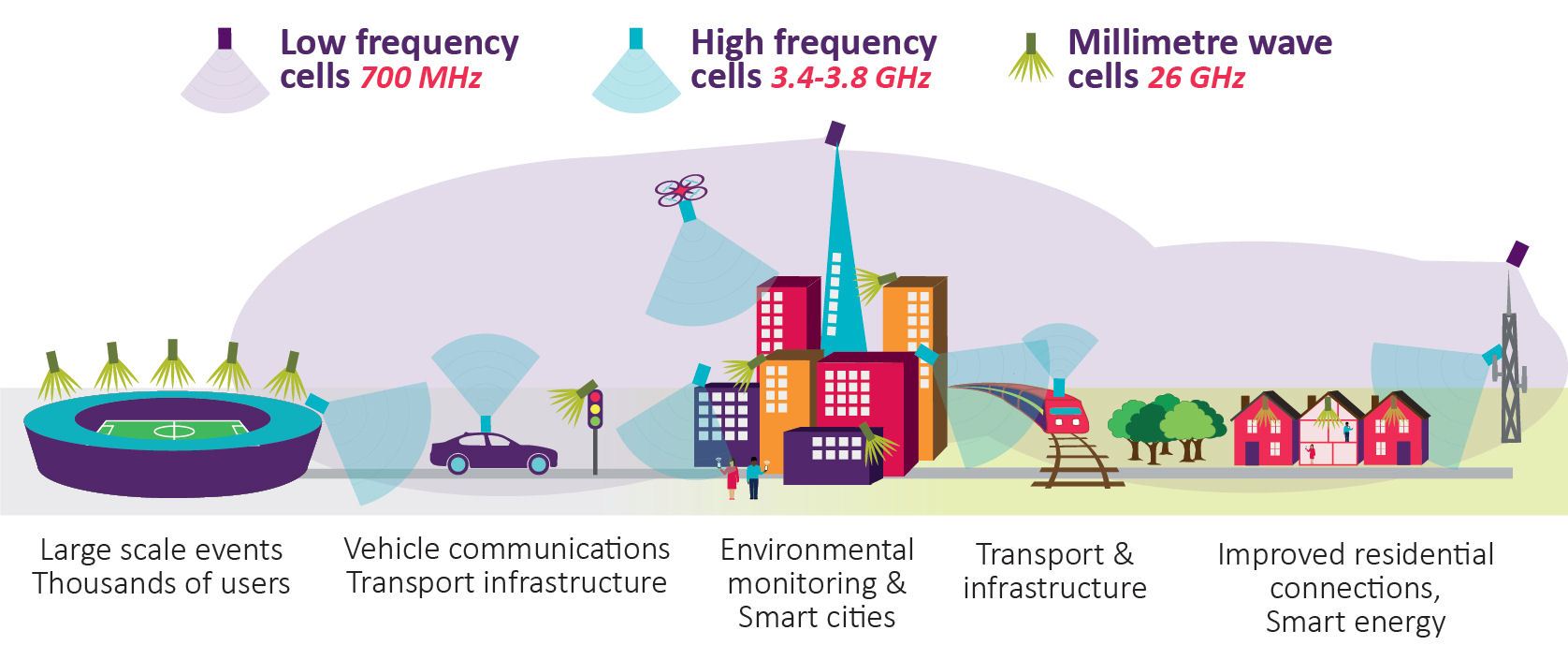
5g Frequency Bands Spectrum Allocations Cablefree Spectrum sharing and dynamic spectrum management techniques in 5g and beyond networks: a survey encourage urllc services in the application of 5g 6g broad use cases such as network slicing and. Enabling these emerging applications over the fifth generation (5g) of wireless cellular systems requires meeting numerous challenges pertaining to spectrum sharing and management. in fact, most 5g applications will be highly reliant on intelligent spectrum management techniques, which should adapt to dynamic network environments while also. Spectrum management could help in their efficient utilization. i. introduction future 5g networks hold great prospects for introducing new applications that provide users with a unique quality of experience (qoe). the interconnection between a high number of devices in the internet of things (iot) networks, signifies. 5g spectrum management implications – spectrum management 9 modern spectrum management • management reports and dashboards automatically produced • kpis, applications pending, licences issued, fees collected • monitoring data allows trend analysis to report on • frequency bands becoming congested • frequency bands under utilised and.

Spectrum Decision Framework To Support Cognitive Radio Based Iot In 5g Spectrum management could help in their efficient utilization. i. introduction future 5g networks hold great prospects for introducing new applications that provide users with a unique quality of experience (qoe). the interconnection between a high number of devices in the internet of things (iot) networks, signifies. 5g spectrum management implications – spectrum management 9 modern spectrum management • management reports and dashboards automatically produced • kpis, applications pending, licences issued, fees collected • monitoring data allows trend analysis to report on • frequency bands becoming congested • frequency bands under utilised and. The electromagnetic spectrum, harnessed for use as radio frequencies, is increasingly in high demand. traditionally used by maritime services, space agencies, and broadcasters, numerous businesses, organizations, and government entities are now vying for spectrum as they discover that this natural resource enables innovative applications, such as 5g communication networks and geospatial. This necessitates the use of an intelligent device that is aware of its environment and capable of dynamically adjusting to the current radio frequency (rf) environment by sharing spectral resources and using spectrum more effectively. figure 3 outlines various features supported by cr for intelligent spectrum management.
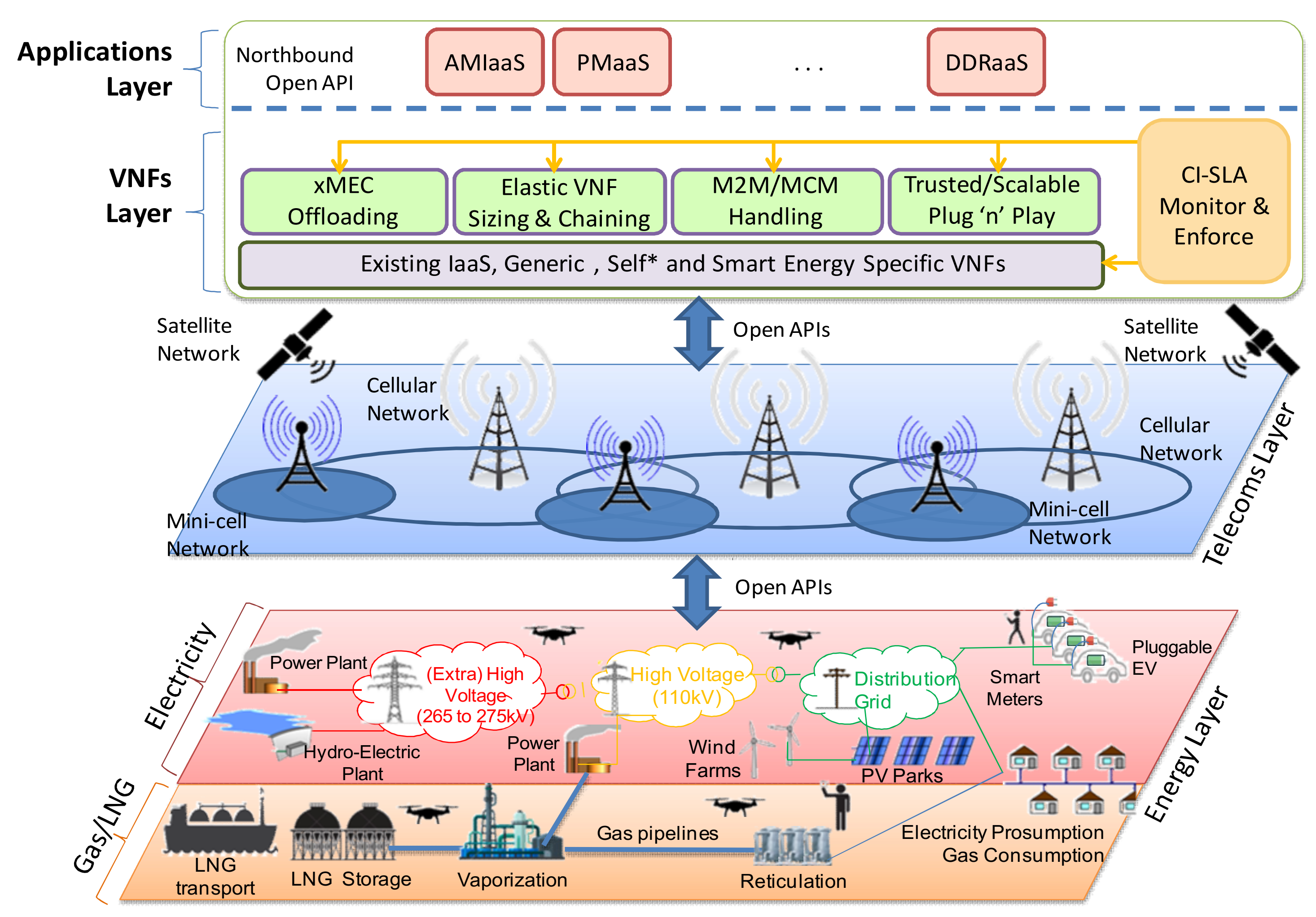
5g Digital Cellular Networks Entso E The electromagnetic spectrum, harnessed for use as radio frequencies, is increasingly in high demand. traditionally used by maritime services, space agencies, and broadcasters, numerous businesses, organizations, and government entities are now vying for spectrum as they discover that this natural resource enables innovative applications, such as 5g communication networks and geospatial. This necessitates the use of an intelligent device that is aware of its environment and capable of dynamically adjusting to the current radio frequency (rf) environment by sharing spectral resources and using spectrum more effectively. figure 3 outlines various features supported by cr for intelligent spectrum management.

Comments are closed.