Somatic Nervous System Chapter 14 Part 1

Solution Chapter 14 The Somatic Nervous System Studypool Educational lecture from hole's anatomy covering the first half of the somatic nervous system including the general senses, taste, smell, and hearing. vision. General sense. any sensory system that is distributed throughout the body and incorporated into organs of multiple other systems, such as the walls of the digestive organs or the skin. kinesthesia. sense of body movement based on sensation in skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, and the skin. proprioception.
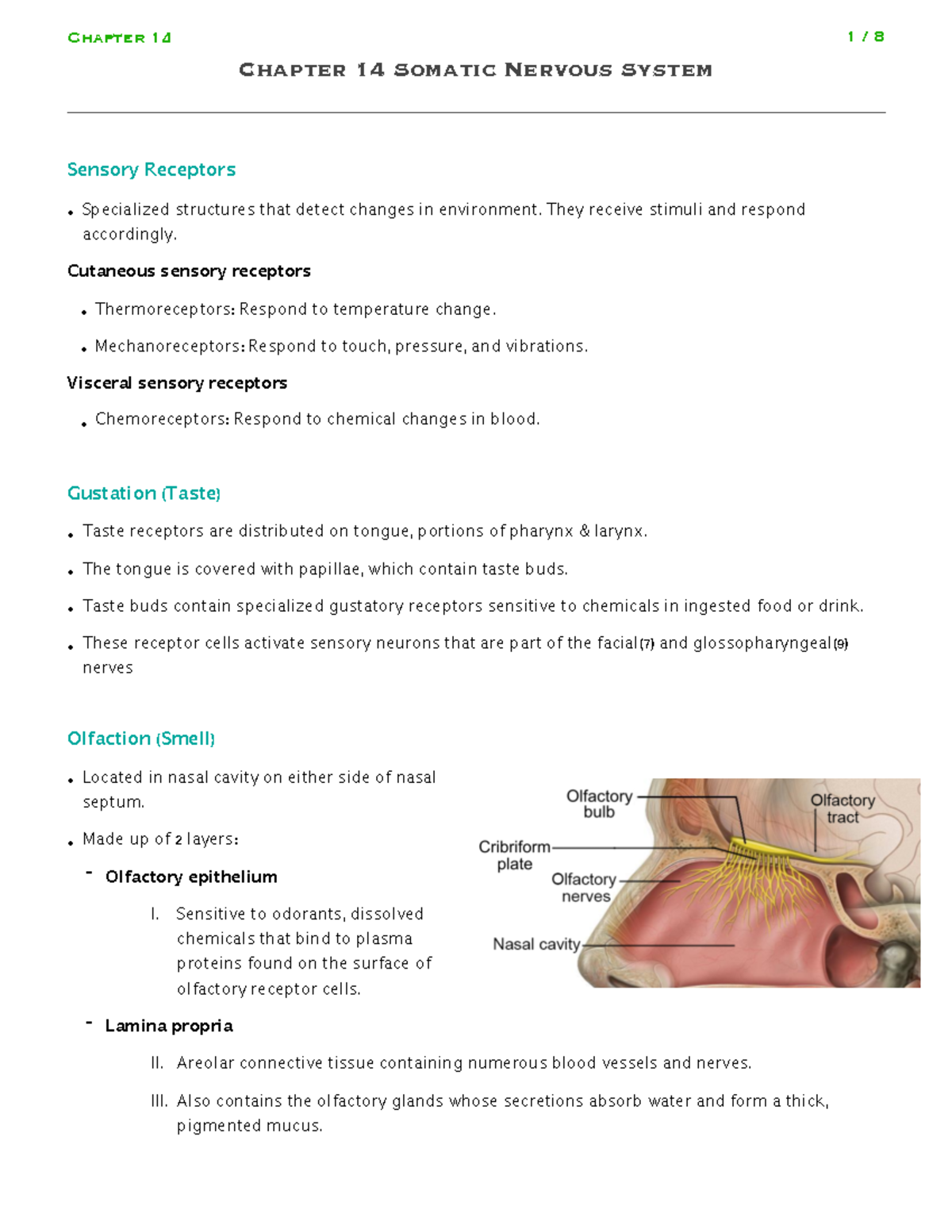
Chapter 14 Somatic Nervous System Chapter 14 Somatic Nervous System 1) vestibule = a central, egg shaped cavity that houses receptors for static equilibrium or linear movements such as acceleration, deceleration and head position relative to gravity. 2) semicircular canals = three canals that contain the receptors for dynamic equilibrium or the rotational movements of the head. What is the defining characteristic of the somatic nervous system? controls skeletal muscles. what is the initial processing of sensory perception in the cerebral cortex? progresses to associative processing. what is the location of sensory cortical areas? occipital, temporal, and parietal lobes. Somatic senses inform the nervous system about the external environment, but the response to that is through voluntary muscle movement. the term “voluntary” suggests that there is a conscious decision to make a movement. however, some aspects of the somatic system use voluntary muscles without conscious control. 14.5: key terms; 14.6. Chapter 14: the somatic nervous system. 14 sensory perception. sensory perception involves the various senses, including olfaction (smell), gustation (taste), somatosensation (skin and body sensations), audition (hearing), equilibrium (balance), and vision. the special senses, such as taste and vision, are associated with specific organs, while.

Biology 2020 Chapter 14 1 The Somatic Nervous System Olfaction Video 2 Somatic senses inform the nervous system about the external environment, but the response to that is through voluntary muscle movement. the term “voluntary” suggests that there is a conscious decision to make a movement. however, some aspects of the somatic system use voluntary muscles without conscious control. 14.5: key terms; 14.6. Chapter 14: the somatic nervous system. 14 sensory perception. sensory perception involves the various senses, including olfaction (smell), gustation (taste), somatosensation (skin and body sensations), audition (hearing), equilibrium (balance), and vision. the special senses, such as taste and vision, are associated with specific organs, while. Specific sense within a broader major sense such as sweet as a part of the sense of taste, or color as a part of vision superior colliculus structure in the midbrain that combines visual, auditory, and somatosensory input to coordinate spatial and topographic representations of the three sensory systems. 14.3 motor responses. video tutorials. crash course: anatomy and physiology . taste and smell. hearing and balance. vision. part 1 intro to the nervous system. part 2 action potential. part 3 synapses.

Chapter 14 Somatic Nervous System Pdf Chapter 14 Somatic Nervous Specific sense within a broader major sense such as sweet as a part of the sense of taste, or color as a part of vision superior colliculus structure in the midbrain that combines visual, auditory, and somatosensory input to coordinate spatial and topographic representations of the three sensory systems. 14.3 motor responses. video tutorials. crash course: anatomy and physiology . taste and smell. hearing and balance. vision. part 1 intro to the nervous system. part 2 action potential. part 3 synapses.

Pdf Chapter 14 The Somatic Nervous System Dokumen Tips

Biology 2020 Chapter 14 1 The Somatic Nervous System Special Senses

Comments are closed.