Solved See Figure 1 Assume The Following Circuit Component Chegg
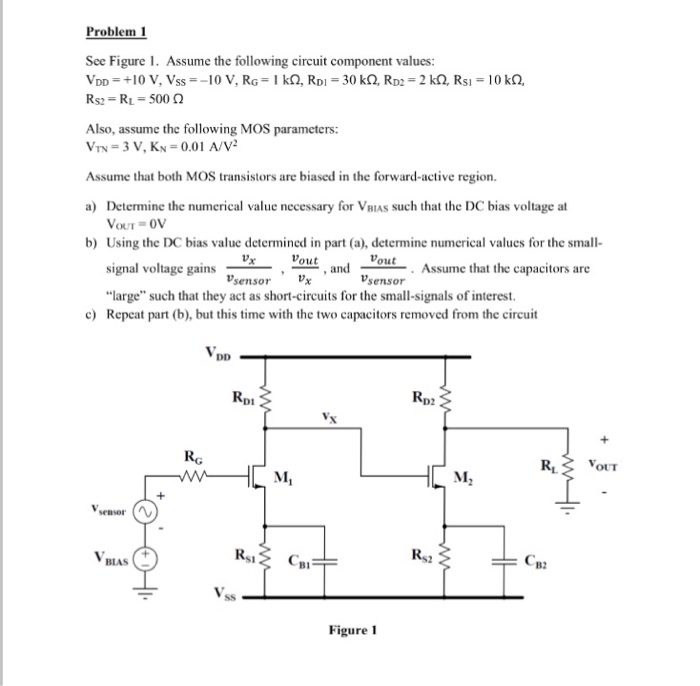
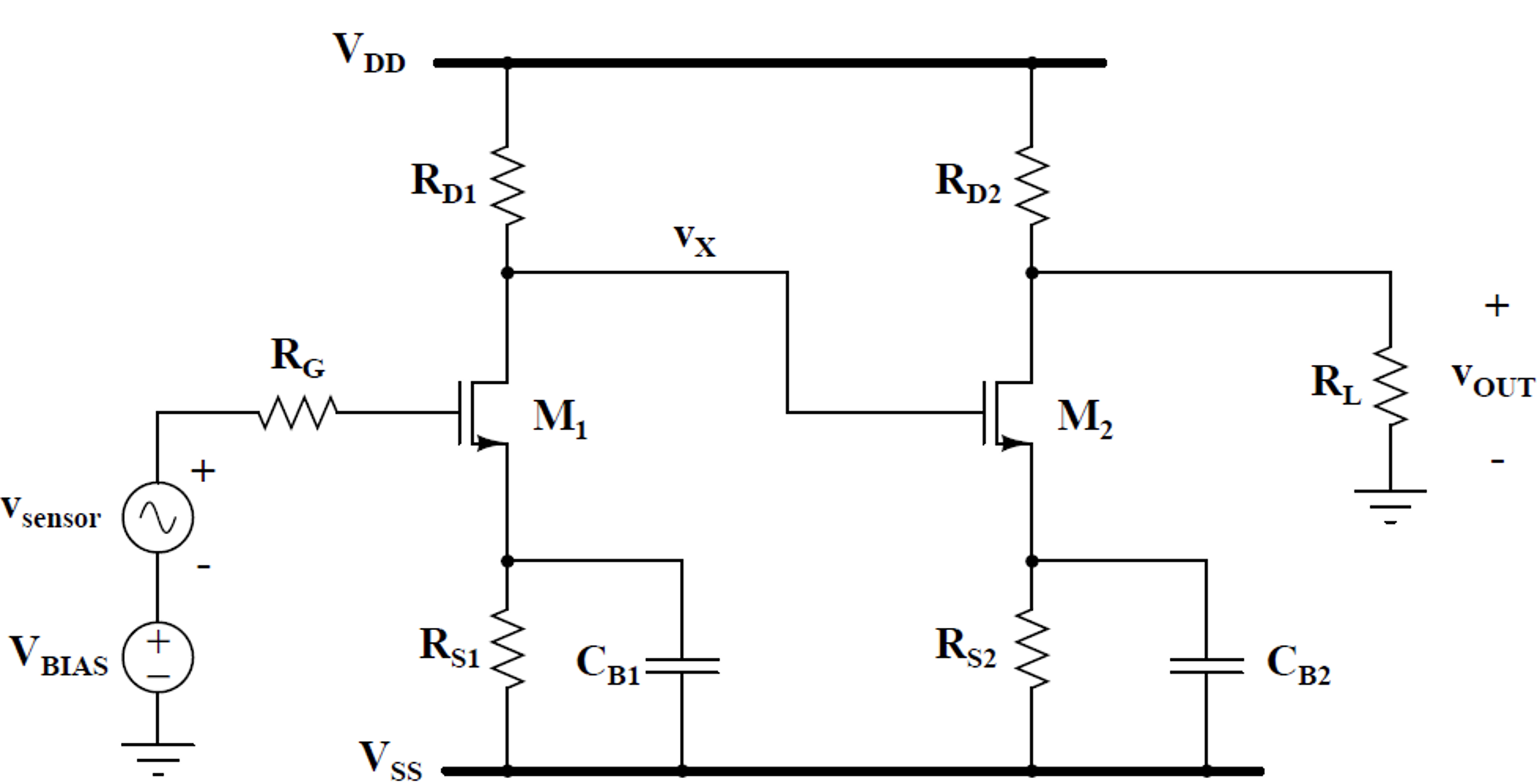
Solved See Figure 1 Assume The Following Circuit Component Chegg Also, assume the following mos parameters: vtn =3v,kn =0.01a v2 assume that both mos transistors are biased in the forward active see figure 1. assume the following circuit component values:. Engineering; electrical engineering; electrical engineering questions and answers; see figure 1. assume the following circuit component values: v dd = 10 v, v ss = 10 v, r g = 1 k ohm, r d1 = 30 ka r d2 = 2 k ohm, r s1 = 10 k ohm, r s2 = r l = 500 ohm also, assume the following mos parameters: v tn = 3 v, k n = 0.01 a v^2 assume that both mos transistors are biased in the forward active region.
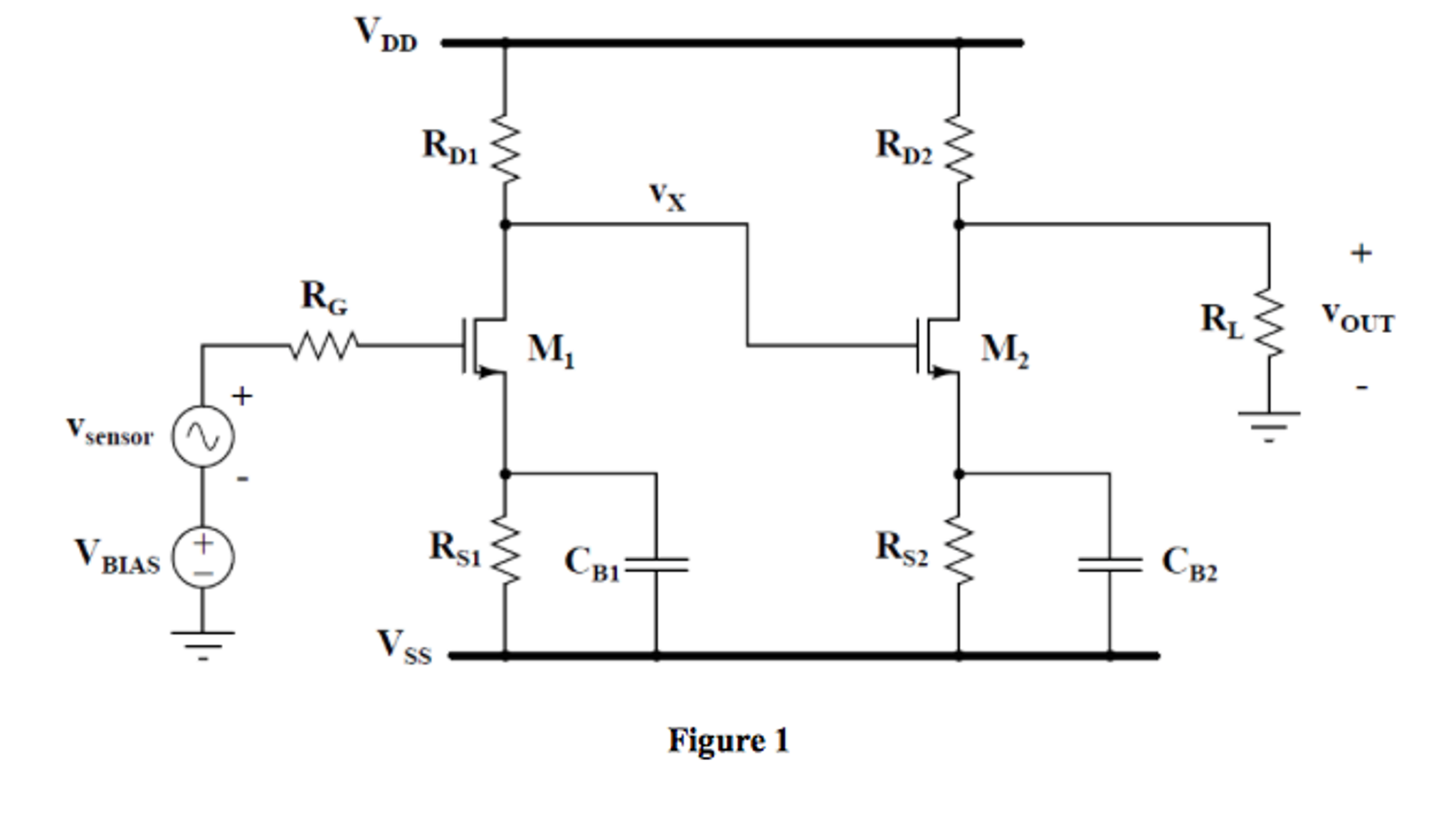
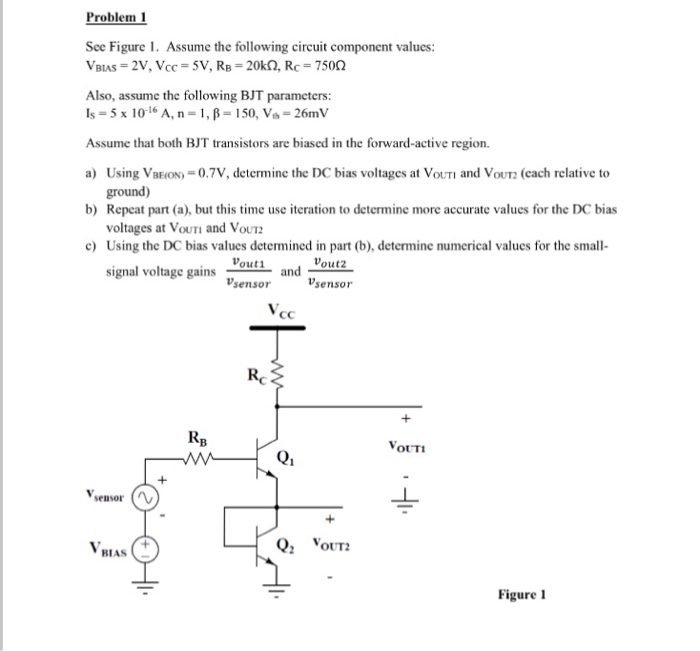
Solved See Figure 1 Assume The Following Circuit Component Chegg Question: see figure 1. assume the following circuit component values: v bias = 2v, v cc = 5v, r b = 20k ohm, r c = 750 ohm also, assume the following bjt parameters: i s = 5 times 10^ 16 a, n = 1, beta = 150, v th = 26mv assume that both bjt transistors are biased in the forward active region. Circuit problem solving procedure: 1) calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit. first combine all the series resistors and then calculate the parallel ones. use the following equations: series: req = n ∑ i ri. parallel: 1 req = n ∑ i 1 ri. 2) use your result of equivalent resistance to find the total current coming out of the battery:. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like any circuit in which the current is split or follows two (or more) alternative paths is called a(n) ? circuit., any circuit in which the same current flows through all components is a(n) ? circuit., a circuit in which some of the components are series connected, while other components are parallel connected, is called a(n) ? or. No, it is a normal reading for this circuit. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like refer to figure 8 2. replace the values shown with the following. solve for all the unknown values. i (t)= 0.6 a r1 = 470 Ω r2 = 360 Ω r3 = 510 Ω r4 = 430 Ω, refer to figure 8 5. replace the values shown with the following.
Solved See Figure 1 Assume The Following Circuit Component Chegg Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like any circuit in which the current is split or follows two (or more) alternative paths is called a(n) ? circuit., any circuit in which the same current flows through all components is a(n) ? circuit., a circuit in which some of the components are series connected, while other components are parallel connected, is called a(n) ? or. No, it is a normal reading for this circuit. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like refer to figure 8 2. replace the values shown with the following. solve for all the unknown values. i (t)= 0.6 a r1 = 470 Ω r2 = 360 Ω r3 = 510 Ω r4 = 430 Ω, refer to figure 8 5. replace the values shown with the following. Lesson 2: compound circuits. series resistors. parallel resistors. finding equivalent resistance. simplifying resistor networks. simplifying resistor networks. simplifying resistor networks. solved example: finding current and voltage in a circuit. finding currents and voltages (pure circuits). The designed circuit with component values and current and voltage values is shown in figure 5.8.2. figure 5.11.1. refer to fig. 5.11.1. we assume that the.
Solved 1 See Figure 1 Assume The Following Circuit Chegg Lesson 2: compound circuits. series resistors. parallel resistors. finding equivalent resistance. simplifying resistor networks. simplifying resistor networks. simplifying resistor networks. solved example: finding current and voltage in a circuit. finding currents and voltages (pure circuits). The designed circuit with component values and current and voltage values is shown in figure 5.8.2. figure 5.11.1. refer to fig. 5.11.1. we assume that the.
Solved See Figure 1 Assume The Following Circuit Component Chegg
Solved For The Circuit Shown Figure 1 Assume The Chegg

Comments are closed.