Solved Determine The Degree Of Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy O
Solved 23 Determine The Degree Of Static Indeterminacy And Chegg Now to calculate the total degree of static indeterminacy internal and external static indeterminacy has added. at last value of kinematic indeterminacy has calculated. one support is hinge has one, and there is one hinge which has three kinematic indeterminacy. Download solution pdf. concept: degree of static determinacy is given by –. d s = 3m – 3j r e. degree of kinematic indeterminacy is given by –. d k = 3j – r e. here, m – number of members. j – number of joints.
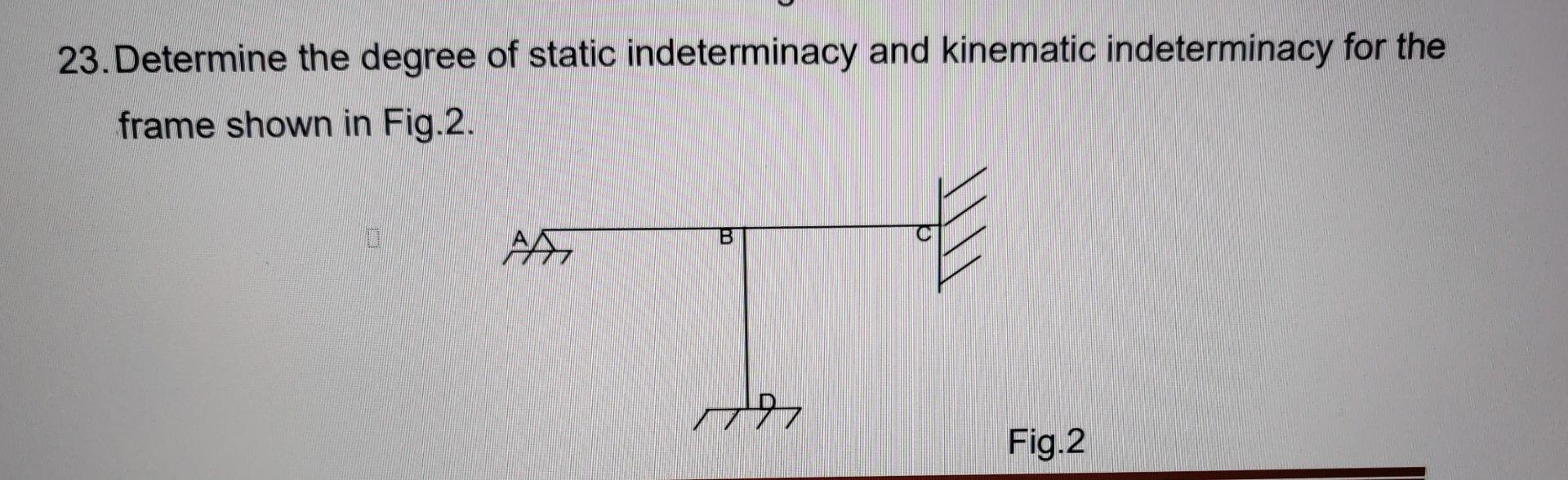
Solved Find The Degree Of Static Indeterminacy And Kinematic Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 23. determine the degree of static indeterminacy and kinematic indeterminacy for the frame shown in fig.2. 7797 fig.2. Classify the beams shown in figure 3.1 through figure 3.5 as stable, determinate, or indeterminate, and state the degree of indeterminacy where necessary. \(fig. 3.1\). beam. solution. first, draw the free body diagram of each beam. to determine the classification, apply equation 3.3 or equation 3.4. The number of independent deflections is called the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy or the number of active degrees of freedom. it encompasses all displacements and rotations of movable joints. the determination of the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy is briefly established in the following examples. q(x) a b c ωb ωc. Classify the beams shown in figure 3.1 through figure 3.5 as stable, determinate, or indeterminate, and state the degree of indeterminacy where necessary. fig. 3.1. beam. solution. first, draw the free body diagram of each beam. to determine the classification, apply equation 3.3 or equation 3.4. using equation 3.3, r = 7, m = 2, c = 0, j = 3.

Solved Determine The Degree Of Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy O The number of independent deflections is called the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy or the number of active degrees of freedom. it encompasses all displacements and rotations of movable joints. the determination of the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy is briefly established in the following examples. q(x) a b c ωb ωc. Classify the beams shown in figure 3.1 through figure 3.5 as stable, determinate, or indeterminate, and state the degree of indeterminacy where necessary. fig. 3.1. beam. solution. first, draw the free body diagram of each beam. to determine the classification, apply equation 3.3 or equation 3.4. using equation 3.3, r = 7, m = 2, c = 0, j = 3. The analyses of indeterminate beams and frames follow the general procedure described previously. first, the primary structures and the redundant unknowns are selected, then the compatibility equations are formulated, depending on the number of the unknowns, and solved. there are several methods of computation of flexibility coefficients when. Degree of internal static indeterminacy extra members than required internal redundancy equilibrium of each joint can be specified by two scalar force equations 2j equations for a truss with “j” number of joints known quantities for a truss with “m” number of two force members, and maximum 3.

Comments are closed.