Solved Calculate Mean Median Mode From The Following Grouped Data

Solution Mean Median And Mode For Grouped Data Studypool Summary. for grouped data, we cannot find the exact mean, median and mode, we can only give estimates. to estimate the mean use the midpoints of the class intervals: estimated mean = sum of (midpoint × frequency) sum of frequency. to estimate the median use: estimated median = l (n 2) − b g × w. where:. To find mean using direct method, we can use the following steps: step 1: for each class, find the class mark xi, as. x=1 2 (lower limit upper limit) step 2: calculate fi.xi for each i. step 3: use the formula mean = ∑ (fi.xi) ∑fi. example: find the mean of the following data. class interval.
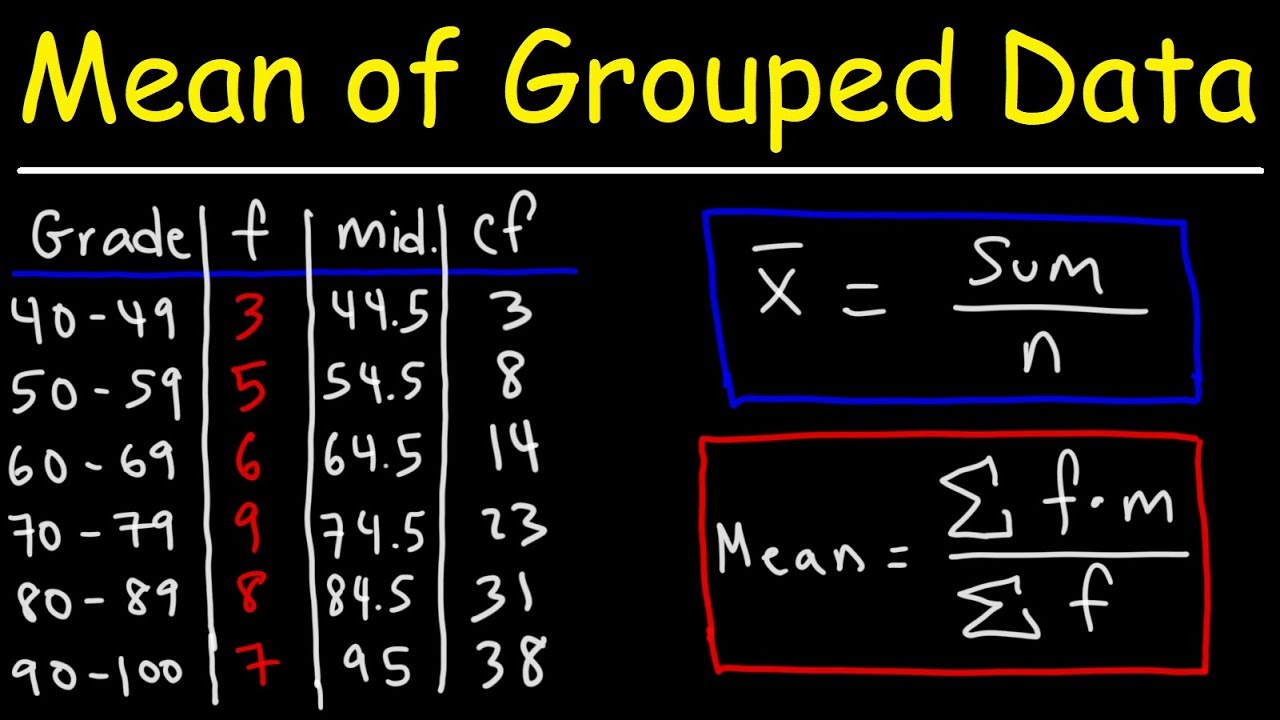
Calculation Of Mean Median And Mode Of Grouped Data Classnotes Ng This statistics tutorial explains how to calculate the mean of grouped data. it also explains how to identify the interval that contains the median and mode. Arrange data points from smallest to largest and locate the central number. this is the median. if there are 2 numbers in the middle, the median is the average of those 2 numbers. the mode is the number in a data set that occurs most frequently. count how many times each number occurs in the data set. the mode is the number with the highest tally. For example, suppose we have the following grouped data: while it’s not possible to calculate the exact mode since we don’t know the raw data values, it is possible to estimate the mode using the following formula: mode of grouped data = l w [ (fm – f1) ( (fm f1) (fm – f2) )] where: l: lower limit of modal class. w: width of modal. The formula to find the median of grouped data is: median = l [ ( (n 2) – cf) f] × h. where l = lower limit of median class, n = number of observations, h = class size, f = frequency of median class, cf = cumulative frequency of class preceding the median class. q5.

Solution Calculating Mean Mode And Median From Grouped Data Studypool For example, suppose we have the following grouped data: while it’s not possible to calculate the exact mode since we don’t know the raw data values, it is possible to estimate the mode using the following formula: mode of grouped data = l w [ (fm – f1) ( (fm f1) (fm – f2) )] where: l: lower limit of modal class. w: width of modal. The formula to find the median of grouped data is: median = l [ ( (n 2) – cf) f] × h. where l = lower limit of median class, n = number of observations, h = class size, f = frequency of median class, cf = cumulative frequency of class preceding the median class. q5. Mean, median, and mode are measures of the central tendency. these values are used to define the various parameters of the given data set. the measure of central tendency (mean, median, and mode) gives useful insights about the data studied, these are used to study any type of data such as the average salary of employees in an organization, the median age of any class, the number of people who. Here’s the best way to solve it. to find the mean of the given grouped data, calculate the mid values ( x) for each class interval and then compute the product of these mid values with their respective frequencies ( f ⋅ x ). 1. calculate mean, median, mode from the following grouped data: 1 x frequency 0 10 11 2015 21 30 31 40 41 50 3.

Comments are closed.