Social Change Introduction Meaning Definitions Characteristics

What Is Social Change Definitions Characteristics Aspects And Social change: definition, characteristics, causes, types, and examples. humans are social beings. we exist in a social world and observe norms, rules and traditions that are all social constructs. therefore social change is a concept that is threaded to the very root of society. similar to the earth completing a strenuous rotation around the. Social change, in sociology, the alteration of mechanisms within the social structure, characterized by changes in cultural symbols, rules of behaviour, social organizations, or value systems. throughout the historical development of their discipline, sociologists have borrowed models of social change from other academic fields.
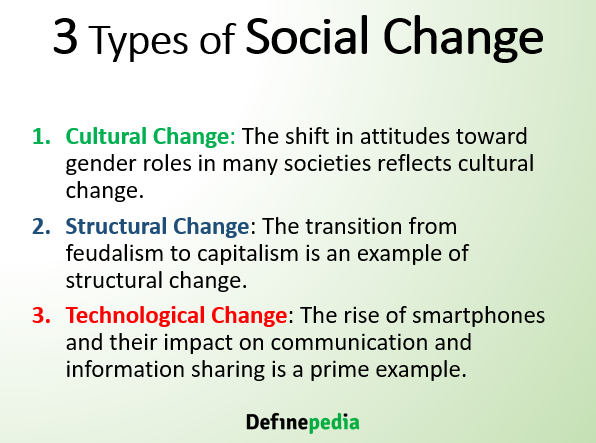
Social Change Meaning Definition Types Characteristics Factors Of This section delves into the nature of social change within the sociology of development, emphasizing its universality across all aspects of life and its definition as changes in social relationships, organization, and structure. key scholars like maciver, page, and lundberg provide definitions, highlighting change in social relationships and structures. it outlines identifiable. This section defines social change as significant alterations in the social structure and functions of a society, encompassing changes in social relationships, norms, values, and cultural patterns. social transformation is presented as a radical, more abrupt form of social change, often through revolution, indicating a deep, far reaching change that significantly alters people's way of life. Similarly, fluctuations in human population size also drive societal changes. biological processes such as procreation, fertility, and mortality contribute to the pace of social change. factors like population size, density, migration, and immigration introduce further alterations to society’s fabric. 5. Introduction. social change is the significant alteration of social structure and cultural patterns through time. social structure refers to persistent networks of social relationships where interaction between people or groups has become routine and repetitive. culture refers to shared ways of living and thinking that include symbols and.

Chapter 21 Social Change Similarly, fluctuations in human population size also drive societal changes. biological processes such as procreation, fertility, and mortality contribute to the pace of social change. factors like population size, density, migration, and immigration introduce further alterations to society’s fabric. 5. Introduction. social change is the significant alteration of social structure and cultural patterns through time. social structure refers to persistent networks of social relationships where interaction between people or groups has become routine and repetitive. culture refers to shared ways of living and thinking that include symbols and. Sociological perspectives on social change fall into the functionalist and conflict approaches. as usual, both views together offer a more complete understanding of social change than either view by itself (vago, 2004). table 20.1 “theory snapshot” summarizes their major assumptions. table 20.1 theory snapshot. Essentially, any disruptive shift in the status quo, be it intentional or random, human caused or natural, can lead to social change. causes of social change. throughout this text, we have discussed various causes and effects of social change. below is a recap of some major drivers, including technology, social institutions, population, and the.

What Is Social Change Definitions Characteristics Aspects And Sociological perspectives on social change fall into the functionalist and conflict approaches. as usual, both views together offer a more complete understanding of social change than either view by itself (vago, 2004). table 20.1 “theory snapshot” summarizes their major assumptions. table 20.1 theory snapshot. Essentially, any disruptive shift in the status quo, be it intentional or random, human caused or natural, can lead to social change. causes of social change. throughout this text, we have discussed various causes and effects of social change. below is a recap of some major drivers, including technology, social institutions, population, and the.

Social Change In Sociology Definition 30 Examples 2024

Comments are closed.